Phases and Properties of Matter - Physical Chemistry
Card 0 of 20
What is the boiling point of a 100mL solution of water after the addition of 29g of sodium chloride?

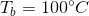
What is the boiling point of a 100mL solution of water after the addition of 29g of sodium chloride?
We can use the boiling point elevation equation in order to find the new boiling point for the solution.

The change in temperature will be equal to the boiling point elevation constant multiplied by the molality of the solution multiplied by the van't Hoff factor. The van't Hoff factor is a variable that incorporates how many ions the added solute will dissolve into when in solution. Sodium chloride will dissolve into two ions, so the van't Hoff factor is 2.


This means that the boiling point of the water has been elevated by 5.2 degrees, meaning that the boiling point of the solution is 105.2 degrees celsius.
We can use the boiling point elevation equation in order to find the new boiling point for the solution.
The change in temperature will be equal to the boiling point elevation constant multiplied by the molality of the solution multiplied by the van't Hoff factor. The van't Hoff factor is a variable that incorporates how many ions the added solute will dissolve into when in solution. Sodium chloride will dissolve into two ions, so the van't Hoff factor is 2.
This means that the boiling point of the water has been elevated by 5.2 degrees, meaning that the boiling point of the solution is 105.2 degrees celsius.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
When placing common household liquids in a single tube, the liquids will not mix, but instead form distinct layers. Imagine a beaker with corn syrup on the bottom, followed by milk, water, and vegetable oil on top. All liquids have equal volumes.
Based on this information, which of the following statements is true?
When placing common household liquids in a single tube, the liquids will not mix, but instead form distinct layers. Imagine a beaker with corn syrup on the bottom, followed by milk, water, and vegetable oil on top. All liquids have equal volumes.
Based on this information, which of the following statements is true?
Since we were told that all the liquids have equal volumes, the masses of the liquids for those volumes will determine which liquid is the most dense. The most dense liquid will sink to the bottom, and the least dense liquid will rise to the top. We know that the milk was underneath the water in the beaker, so we can conclude that milk has a greater density than water.
Since we were told that all the liquids have equal volumes, the masses of the liquids for those volumes will determine which liquid is the most dense. The most dense liquid will sink to the bottom, and the least dense liquid will rise to the top. We know that the milk was underneath the water in the beaker, so we can conclude that milk has a greater density than water.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Why is liquid water more dense than ice?
Why is liquid water more dense than ice?
While water exhibits hydrogen bonding and has metastable phases, these don't have anything to do with the density of water. The slope of the solid/liquid line is in fact negative. This tells something about the relative densities of the phases. For a phase diagram, moving along a line of constant temperature (vertically on a phase diagram tells us something about the densities. Moving up along the line indicates an increase in density (this makes sense, since gasses are the least dense, and occupy the bottom portion of a phase diagram). If you move along a constant temperature line, you will see that water has a higher density than ice, since the ordering goes vapor, ice, then water. This is a result of the packing in solid ice.
While water exhibits hydrogen bonding and has metastable phases, these don't have anything to do with the density of water. The slope of the solid/liquid line is in fact negative. This tells something about the relative densities of the phases. For a phase diagram, moving along a line of constant temperature (vertically on a phase diagram tells us something about the densities. Moving up along the line indicates an increase in density (this makes sense, since gasses are the least dense, and occupy the bottom portion of a phase diagram). If you move along a constant temperature line, you will see that water has a higher density than ice, since the ordering goes vapor, ice, then water. This is a result of the packing in solid ice.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
When 20 grams of a solute is added to a liter of water, the freezing point becomes  What is the molar mass of the solute?
What is the molar mass of the solute?
Assume that the solute does not make ions in solution.

When 20 grams of a solute is added to a liter of water, the freezing point becomes 
Assume that the solute does not make ions in solution.
We can use the freezing point depression equation in order to determine the molar mass of the unknown solute.

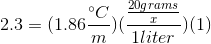

We can use the freezing point depression equation in order to determine the molar mass of the unknown solute.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A sample of argon gas at a pressure of 0.959atm and a temperature of  , occupies a volume of 563mL. If the gas is compressed at constant temperature until its pressure is 1.40atm, what will be the final volume of the sample of gas?
, occupies a volume of 563mL. If the gas is compressed at constant temperature until its pressure is 1.40atm, what will be the final volume of the sample of gas?
A sample of argon gas at a pressure of 0.959atm and a temperature of 
The argon gas, as the problem states, is under constant temperature with varying volume and pressure, so we need to use Boyle's Law:

We are given the initial pressure, the initial volume, and the final pressure, and need to solve for the final volume. Therefore, we can rearrange Boyle's law to be as follows:

Plug in known values and solve.


The argon gas, as the problem states, is under constant temperature with varying volume and pressure, so we need to use Boyle's Law:
We are given the initial pressure, the initial volume, and the final pressure, and need to solve for the final volume. Therefore, we can rearrange Boyle's law to be as follows:
Plug in known values and solve.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A sample of methane gas at a pressure of 0.723atm and a temperature of  , occupies a volume of 16.0L. If the gas is allowed to expand at constant temperature to a volume of 24.2L, what will the pressure of the gas sample be?
, occupies a volume of 16.0L. If the gas is allowed to expand at constant temperature to a volume of 24.2L, what will the pressure of the gas sample be?
A sample of methane gas at a pressure of 0.723atm and a temperature of 
The methane gas, as the problem states, is under constant temperature with varying volume and pressure, so we need to use Boyle's Law:

We are given the initial pressure, the initial volume, and the final volume and need to solve for the final pressure. Therefore, we can rearrange Boyle's law to be as follows:

Plug in known values and solve.


The methane gas, as the problem states, is under constant temperature with varying volume and pressure, so we need to use Boyle's Law:
We are given the initial pressure, the initial volume, and the final volume and need to solve for the final pressure. Therefore, we can rearrange Boyle's law to be as follows:
Plug in known values and solve.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A researcher places a closed piston container at room temperature. He places a Bunsen burner at the bottom of the container and observes that the piston moves up. What can best explain this phenomenon?
A researcher places a closed piston container at room temperature. He places a Bunsen burner at the bottom of the container and observes that the piston moves up. What can best explain this phenomenon?
There are three main gas laws. Avogadro’s law states that the moles of a gas is directly proportional to the volume (under constant pressure and temperature). Boyle’s law states that the pressure of the gas is inversely proportional to the volume (under constant moles and temperature). This means that the pressure decreases proportionally when the volume increases. Charles’ law states that the temperature is directly proportional to the volume (under constant moles and pressure). The question states that the piston moves up. This means that the volume of the gas is expanding inside and pushing the piston up to make room for the expanding gas. The gas expansion occurs due to increased temperature (Charles’ law).
There are three main gas laws. Avogadro’s law states that the moles of a gas is directly proportional to the volume (under constant pressure and temperature). Boyle’s law states that the pressure of the gas is inversely proportional to the volume (under constant moles and temperature). This means that the pressure decreases proportionally when the volume increases. Charles’ law states that the temperature is directly proportional to the volume (under constant moles and pressure). The question states that the piston moves up. This means that the volume of the gas is expanding inside and pushing the piston up to make room for the expanding gas. The gas expansion occurs due to increased temperature (Charles’ law).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
An unknown gas is being analyzed in lab. You place  of this gas in a container at
of this gas in a container at  . You observe that the pressure and volume of the gas is
. You observe that the pressure and volume of the gas is  and
and  , respectively. What is the identity of the gas? Assume the gas behaves ideally.
, respectively. What is the identity of the gas? Assume the gas behaves ideally.
An unknown gas is being analyzed in lab. You place 



To solve this question we need to use the ideal gas law equation:

Above,  is pressure in
is pressure in  ,
,  is volume in liters,
is volume in liters,  is moles,
is moles,  is
is  , and
, and  is temperature in Kelvins. The question gives us pressure, volume, and temperature; therefore, we can solve for
is temperature in Kelvins. The question gives us pressure, volume, and temperature; therefore, we can solve for  . First, we need to convert temperature from Celsius to Kelvins.
. First, we need to convert temperature from Celsius to Kelvins.


Rearrange the ideal gas law and solve for  :
:



The question states that you place one gram of gas in the container. Since we know the moles, we can solve for the molecular weight of the gas and figure out its identity from the molecular weight.

The molecular weight of oxygen gas,  is
is  ; therefore, the unknown gas must be oxygen.
; therefore, the unknown gas must be oxygen.
To solve this question we need to use the ideal gas law equation:
Above, 







Rearrange the ideal gas law and solve for 
The question states that you place one gram of gas in the container. Since we know the moles, we can solve for the molecular weight of the gas and figure out its identity from the molecular weight.
The molecular weight of oxygen gas, 

Compare your answer with the correct one above
At constant temperature and moles, which of the following is true regarding pressure and volume of a gas?
At constant temperature and moles, which of the following is true regarding pressure and volume of a gas?
First, we need to figure out which gas law is applicable here. The question states that temperature and moles are constant. This means that we are dealing with Boyle’s law, which states that pressure is inversely proportional to volume. Inversely proportional means that the pressure decreases as volume increases and vice versa. Note that the relationship is still linear (change in one variable causes a proportional change in the other variable), but the two variables have a negative correlation. Positive correlation means increasing or decreasing a variable would also increase or decrease the other variable, respectively.
First, we need to figure out which gas law is applicable here. The question states that temperature and moles are constant. This means that we are dealing with Boyle’s law, which states that pressure is inversely proportional to volume. Inversely proportional means that the pressure decreases as volume increases and vice versa. Note that the relationship is still linear (change in one variable causes a proportional change in the other variable), but the two variables have a negative correlation. Positive correlation means increasing or decreasing a variable would also increase or decrease the other variable, respectively.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
According to __________ law, increasing temperature will __________ volume at constant pressure and constant moles.
According to __________ law, increasing temperature will __________ volume at constant pressure and constant moles.
Recall that Charles’ law defines the relationship between temperature and volume at constant pressure and constant moles. The law states that the two variables are directly proportional to each other. This means that increasing or decreasing temperature will have the same effect on volume. This makes sense because increasing the temperature increases the kinetic energy of the particles. This makes it easier for particles to move away from each other and expand, which results in an increase in volume.
Recall that Charles’ law defines the relationship between temperature and volume at constant pressure and constant moles. The law states that the two variables are directly proportional to each other. This means that increasing or decreasing temperature will have the same effect on volume. This makes sense because increasing the temperature increases the kinetic energy of the particles. This makes it easier for particles to move away from each other and expand, which results in an increase in volume.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following forces is considered the weakest?
Which of the following forces is considered the weakest?
The intermolecular forces from strongest to weakest are ionic, hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole, then London dispersion forces. All compounds experience some form of London dispersion force, but the force only becomes relevant if no other forces are contributing to the attraction of molecules or atoms.
The intermolecular forces from strongest to weakest are ionic, hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole, then London dispersion forces. All compounds experience some form of London dispersion force, but the force only becomes relevant if no other forces are contributing to the attraction of molecules or atoms.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which intermolecular force will be the most powerful in a sample of ethanol 

Which intermolecular force will be the most powerful in a sample of ethanol
Ethanol will not form ions in solution, so we are left with the other three options as plausible answers. Of the three, the strongest force is hydrogen bonding, which only occurs if a hydrogen is directly attached to a nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine in the molecule. Ethanol has a hydrogen attached to an oxygen, and is thus capable of hydrogen bonding.
Ethanol will not form ions in solution, so we are left with the other three options as plausible answers. Of the three, the strongest force is hydrogen bonding, which only occurs if a hydrogen is directly attached to a nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine in the molecule. Ethanol has a hydrogen attached to an oxygen, and is thus capable of hydrogen bonding.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is not an intensive property?
Which of the following is not an intensive property?
Intensive properties are not dependent on the amount of substance. Melting point, pressure, temperature, and density are some examples of intensive properties. Therefore, volume of a substance is not an example of an intensive property, rather, it is an extensive property which depends on the amount of substance. Some other examples of extensive properties include weight, energy, and electric charge.
Intensive properties are not dependent on the amount of substance. Melting point, pressure, temperature, and density are some examples of intensive properties. Therefore, volume of a substance is not an example of an intensive property, rather, it is an extensive property which depends on the amount of substance. Some other examples of extensive properties include weight, energy, and electric charge.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the follow are false?
I. Three phases can coexist at the triple point.
II. It is not possible for ice to transition directly to water vapor without become a liquid first.
III. The slope of the ice/water phase curve is positive
IV. Distinct phases are not achievable above the critical point
Which of the follow are false?
I. Three phases can coexist at the triple point.
II. It is not possible for ice to transition directly to water vapor without become a liquid first.
III. The slope of the ice/water phase curve is positive
IV. Distinct phases are not achievable above the critical point
Condition I is true. The only place three phases can coexist is at the triple point.
Condition II is false. Water in fact can undergo deposition and move from the solid phase to the gas phase directly. This occurs at pressures below 0.006atm.
Condition III is false. A peculiar fact of the water phase diagram is the slope of the solid/liquid line. For most phase diagrams, the slope is sharply positive, but that of water is negative.
Condition IV is true. No distinct phases exist above the critical point.
Condition I is true. The only place three phases can coexist is at the triple point.
Condition II is false. Water in fact can undergo deposition and move from the solid phase to the gas phase directly. This occurs at pressures below 0.006atm.
Condition III is false. A peculiar fact of the water phase diagram is the slope of the solid/liquid line. For most phase diagrams, the slope is sharply positive, but that of water is negative.
Condition IV is true. No distinct phases exist above the critical point.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
An unknown molecule (molecule A), in its solid phase, is found to have a density of  . Eight grams of this molecule is added to a cubic container with length of
. Eight grams of this molecule is added to a cubic container with length of  . The container is then heated until all of the solid has melted. What can you conclude from the given information?
. The container is then heated until all of the solid has melted. What can you conclude from the given information?
An unknown molecule (molecule A), in its solid phase, is found to have a density of 


The dimensions of the cubic container are  by
by 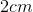 by
by  (cube has same length, height, and width); therefore, the volume of the cubic container is
(cube has same length, height, and width); therefore, the volume of the cubic container is

Recall that  is the same as
is the same as  ; therefore, the container can contain
; therefore, the container can contain  of volume. This means that all of the solid will fit into the container. Upon melting, the solid will expand and the volume will increase (as it becomes liquid). This means that the volume of the container will not be sufficient for the liquid and, consequently, lead to an overflow of the liquid.
of volume. This means that all of the solid will fit into the container. Upon melting, the solid will expand and the volume will increase (as it becomes liquid). This means that the volume of the container will not be sufficient for the liquid and, consequently, lead to an overflow of the liquid.
The dimensions of the cubic container are 
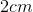

Recall that 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is true regarding the liquid phase?
I. Liquids have lower entropy than gases
II. Compared to solids, more energy is required to separate liquid molecules
III. Liquids have higher intermolecular forces than gases
Which of the following is true regarding the liquid phase?
I. Liquids have lower entropy than gases
II. Compared to solids, more energy is required to separate liquid molecules
III. Liquids have higher intermolecular forces than gases
Liquid is an intermediate phase, between solid and gas. Solids are characterized by tightly packed molecules in an organized manner whereas gases are characterized by greatly spread out molecules that are highly disordered; liquids lie somewhere in the middle. This means that they are more disordered than solids (more entropy) and less disordered than gases (less entropy).
The boiling point of a substance is always higher than the melting point; therefore, you always need higher energy to break the interactions between liquid molecules.
The key difference between a liquid and a gas is the distance between the molecules. Liquid molecules are closer together whereas gas molecules are spread apart. Intermolecular forces are the forces between adjacent molecules. Since they are highly spread apart, the gas molecules have lower intermolecular forces.
Liquid is an intermediate phase, between solid and gas. Solids are characterized by tightly packed molecules in an organized manner whereas gases are characterized by greatly spread out molecules that are highly disordered; liquids lie somewhere in the middle. This means that they are more disordered than solids (more entropy) and less disordered than gases (less entropy).
The boiling point of a substance is always higher than the melting point; therefore, you always need higher energy to break the interactions between liquid molecules.
The key difference between a liquid and a gas is the distance between the molecules. Liquid molecules are closer together whereas gas molecules are spread apart. Intermolecular forces are the forces between adjacent molecules. Since they are highly spread apart, the gas molecules have lower intermolecular forces.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following are responsible for the high boiling point of water, compared to molecules of similar size?
Which of the following are responsible for the high boiling point of water, compared to molecules of similar size?
Hydrogen bonding occurs between water molecules. While intermolecular forces between molecules exist for most molecules, these forces are much weaker than the bond formed between a hydrogen from one molecule and an oxygen, fluorine, and/or nitrogen atom of another molecule. Since the molecules are held more tightly together, more energy is required to break those bonds. This results in a higher temperature required to boil water (boiling breaks bonds between molecules, and this causes the molecules to escape into the gas phase).
Hydrogen bonding occurs between water molecules. While intermolecular forces between molecules exist for most molecules, these forces are much weaker than the bond formed between a hydrogen from one molecule and an oxygen, fluorine, and/or nitrogen atom of another molecule. Since the molecules are held more tightly together, more energy is required to break those bonds. This results in a higher temperature required to boil water (boiling breaks bonds between molecules, and this causes the molecules to escape into the gas phase).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is true regarding solids?
Which of the following is true regarding solids?
There are three main phases: solids, liquids, and gases. Solids molecules are closely packed in an organized, lattice structure, liquid molecules are more spread apart and more disorganized, and gas molecules are spread even farther apart from each other and are extremely disorganized. Each type of solid is made up of unique type of atoms. For example, magnesium metal is made up of magnesium atoms whereas copper metal is made up of copper atoms. Since they are made up of unique atoms, different types of solids have different interactions between atoms. Some have strong interactions whereas others have very weak interactions; therefore, the energy required to break these interaction and separate the atoms/molecules (melt) is different for each solid.
Recall that entropy is the level of disorder in a system. As mentioned, solids are highly organized structures; therefore, they will have the lowest entropy.
There are three main phases: solids, liquids, and gases. Solids molecules are closely packed in an organized, lattice structure, liquid molecules are more spread apart and more disorganized, and gas molecules are spread even farther apart from each other and are extremely disorganized. Each type of solid is made up of unique type of atoms. For example, magnesium metal is made up of magnesium atoms whereas copper metal is made up of copper atoms. Since they are made up of unique atoms, different types of solids have different interactions between atoms. Some have strong interactions whereas others have very weak interactions; therefore, the energy required to break these interaction and separate the atoms/molecules (melt) is different for each solid.
Recall that entropy is the level of disorder in a system. As mentioned, solids are highly organized structures; therefore, they will have the lowest entropy.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
You freeze a sample of nitrogen. Compared to the reactant, the end product has __________ density and __________ mass.
You freeze a sample of nitrogen. Compared to the reactant, the end product has __________ density and __________ mass.
Freezing the is process of converting a liquid to a solid. This question is asking about the freezing process of liquid nitrogen to solid nitrogen; therefore, the end product of the reaction is solid nitrogen. Recall that solids are more tightly packed. This means that the volume taken up by the molecules in solid is lower than in liquid; therefore, solids generally have a lower volume. Mass, on the other hand, depends on the number of molecules present. Phase changes do not alter the amount of molecules present. For example, the end product in this question (solid nitrogen) will have the same amount of molecules as its liquid counterpart; therefore, the mass doesn’t change when the phase changes.
Density is defined as follows.

Since its volume decreases and the mass stays the same, a solid will have a lower density than liquid. Note that water is an exception to this general rule, as solid ice has a lower density (higher volume) than the same mass of liquid water. This is due to the arrangement of its hydrogen bonds throughout its crystalline structure.
Freezing the is process of converting a liquid to a solid. This question is asking about the freezing process of liquid nitrogen to solid nitrogen; therefore, the end product of the reaction is solid nitrogen. Recall that solids are more tightly packed. This means that the volume taken up by the molecules in solid is lower than in liquid; therefore, solids generally have a lower volume. Mass, on the other hand, depends on the number of molecules present. Phase changes do not alter the amount of molecules present. For example, the end product in this question (solid nitrogen) will have the same amount of molecules as its liquid counterpart; therefore, the mass doesn’t change when the phase changes.
Density is defined as follows.
Since its volume decreases and the mass stays the same, a solid will have a lower density than liquid. Note that water is an exception to this general rule, as solid ice has a lower density (higher volume) than the same mass of liquid water. This is due to the arrangement of its hydrogen bonds throughout its crystalline structure.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Given the ideal gas law:
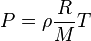
Where  is density,
is density,  is pressure,
is pressure,  is the gas constant,
is the gas constant,  is molar mass, and
is molar mass, and  is temperature.
is temperature.
Based on the Ideal gas law, which of the following are true?
I. Pressure and volume are inversely proportional
II. Pressure and density are inversely proportional
III. Pressure and temperature are directly proportional
IV. Density and temperature are inversely proportional
V. R and M are inversely proportional
Given the ideal gas law:
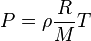
Where 




Based on the Ideal gas law, which of the following are true?
I. Pressure and volume are inversely proportional
II. Pressure and density are inversely proportional
III. Pressure and temperature are directly proportional
IV. Density and temperature are inversely proportional
V. R and M are inversely proportional
Condition I is true. Pressure and volume are inversely proportional. The ideal gas law with volume can be rederived to show this:
We introduce an expression for moles:
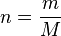

Where  is moles,
is moles,  is mass, and
is mass, and  is molar mass in
is molar mass in 
Rearranging (1) to solve for  and plugging into the following:
and plugging into the following:
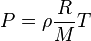
We get:
 (2)
(2)
Finally, we use the following for density, where  is volume, and plug into (2)
is volume, and plug into (2)


The masses cancel out and we have the ideal gas law expressed with volume and moles.
Condition II is false. It is clear from the equation that pressure and density are directly proportional.
Condition III is true because it is clear from the equation that temperature and pressure are directly proportional.
Condition IV is true because density and temperature are on the same side of the equation in the numerator, so the must be inversely proportional.
Condition V is false because the ideal gas constant and molar mass can be rearranged to be on opposite sides of the equation and in the numerator.
Condition I is true. Pressure and volume are inversely proportional. The ideal gas law with volume can be rederived to show this:
We introduce an expression for moles:
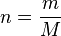
Where 


Rearranging (1) to solve for 
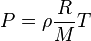
We get:

Finally, we use the following for density, where 
The masses cancel out and we have the ideal gas law expressed with volume and moles.
Condition II is false. It is clear from the equation that pressure and density are directly proportional.
Condition III is true because it is clear from the equation that temperature and pressure are directly proportional.
Condition IV is true because density and temperature are on the same side of the equation in the numerator, so the must be inversely proportional.
Condition V is false because the ideal gas constant and molar mass can be rearranged to be on opposite sides of the equation and in the numerator.
Compare your answer with the correct one above