Gases
Practice Questions
Physical Chemistry › Gases
A sample of argon gas at a pressure of 0.959atm and a temperature of 
An unknown gas is being analyzed in lab. You place 



At constant temperature and moles, which of the following is true regarding pressure and volume of a gas?
A sample of argon gas at a pressure of 0.959atm and a temperature of 
An unknown gas is being analyzed in lab. You place 



At constant temperature and moles, which of the following is true regarding pressure and volume of a gas?
Given the ideal gas law:
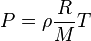
Where 




Based on the Ideal gas law, which of the following are true?
I. Pressure and volume are inversely proportional
II. Pressure and density are inversely proportional
III. Pressure and temperature are directly proportional
IV. Density and temperature are inversely proportional
V. R and M are inversely proportional
A researcher places a closed piston container at room temperature. He places a Bunsen burner at the bottom of the container and observes that the piston moves up. What can best explain this phenomenon?
A researcher places a closed piston container at room temperature. He places a Bunsen burner at the bottom of the container and observes that the piston moves up. What can best explain this phenomenon?
Given the van der Waals Equation:
Which statement accurately identifies and explains the corrections that van der Waals made to the ideal gas law, where the first correction is the 

