Hydrocarbon Products - Organic Chemistry
Card 0 of 15
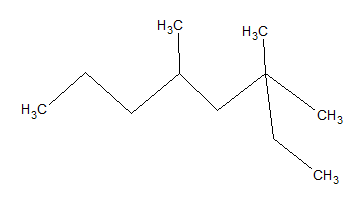
What is the IUPAC name of the given molecule?

What is the IUPAC name of the given molecule?
The longest carbon chain that can be formed is eight carbons. The base molecule is octane.
Using IUPAC rules, substituents should have the lowest possible numbers; thus, we start counting carbons from the right side rather than the left. If you count from the correct side, there are two methyl groups on carbon 3 and one on carbon 5. Thus, the name of the moleculue is 3,3,5-trimethyloctane.
The longest carbon chain that can be formed is eight carbons. The base molecule is octane.
Using IUPAC rules, substituents should have the lowest possible numbers; thus, we start counting carbons from the right side rather than the left. If you count from the correct side, there are two methyl groups on carbon 3 and one on carbon 5. Thus, the name of the moleculue is 3,3,5-trimethyloctane.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

How could you brominate the compound?

How could you brominate the compound?
The given molecule is an alkane. The only way to brominate an alkane is with bromine gas and UV light. The energy from the light serves to creat two radical bromines. These radicals are capable of bonding with alkanes. If the given compound were an alkene, either hydrobromic acid or bromine and peroxides would work.
The given molecule is an alkane. The only way to brominate an alkane is with bromine gas and UV light. The energy from the light serves to creat two radical bromines. These radicals are capable of bonding with alkanes. If the given compound were an alkene, either hydrobromic acid or bromine and peroxides would work.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Predict the absolute configuration about the double bond formed in the given E1 reaction.

Predict the absolute configuration about the double bond formed in the given E1 reaction.

Unlike E2 reactions, in which hydrogen abstraction occurs simultaneously with the dissociation of the leaving group (limiting the configuration of the reaction's product), E1 reactions occur in two distinct steps. The slow rate-determining step that must first occur is the dissociation of the leaving group. Leaving behind a carbocation intermediate, it is often necessary to consider possible carbocation rearrangements that would stabilize the positive charge.
In this case, no such rearrangement is favorable as their are no locations of greater stability available.
However, what must be considered is that the intermediate is free to orient itself in its most stable conformation prior to the formation of the double bond in the second step. As a result, the E product (the larger substituents are on oriented opposite one another with respect to the double bond) is yielded primarily.
Unlike E2 reactions, in which hydrogen abstraction occurs simultaneously with the dissociation of the leaving group (limiting the configuration of the reaction's product), E1 reactions occur in two distinct steps. The slow rate-determining step that must first occur is the dissociation of the leaving group. Leaving behind a carbocation intermediate, it is often necessary to consider possible carbocation rearrangements that would stabilize the positive charge.
In this case, no such rearrangement is favorable as their are no locations of greater stability available.
However, what must be considered is that the intermediate is free to orient itself in its most stable conformation prior to the formation of the double bond in the second step. As a result, the E product (the larger substituents are on oriented opposite one another with respect to the double bond) is yielded primarily.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

Which reagents are required to carry out the given reaction?
Which reagents are required to carry out the given reaction?
To carry out this reaction, we need to create a radical as an intermediate, which is an unpaired electron. We do so by introducing  , UV light, and heat to the 1-methyl cyclohexane. The light and the heat react with the
, UV light, and heat to the 1-methyl cyclohexane. The light and the heat react with the  to break the bond and create two radical bromine atoms. One of the radical bromine atoms removes a hydrogen from the carbon on the 1-methyl cyclohexane that is most substituted, and a radical carbon is formed. Finally, the second radical bromine reacts with the radical carbon to form the final product.
to break the bond and create two radical bromine atoms. One of the radical bromine atoms removes a hydrogen from the carbon on the 1-methyl cyclohexane that is most substituted, and a radical carbon is formed. Finally, the second radical bromine reacts with the radical carbon to form the final product.
To carry out this reaction, we need to create a radical as an intermediate, which is an unpaired electron. We do so by introducing 

Compare your answer with the correct one above

What is the IUPAC name of the given diene?

What is the IUPAC name of the given diene?
You must begin counting the carbons so that the first functional substituent has the lowest possible number. In this case, C1 is connected to C2 by the double bond, meaning we start counting from the left.
The longest carbon chain is seven carbons so the parent molecule is heptane. With this numbering, there are methyl groups on carbons 3 and 6 and a chlorine on carbon 5.
Substituents are named in alphabetical order and two double bonds result in a diene. Thus, the correct answer is 5-chloro-3,6-dimethyl-1,5-heptadiene.
You must begin counting the carbons so that the first functional substituent has the lowest possible number. In this case, C1 is connected to C2 by the double bond, meaning we start counting from the left.
The longest carbon chain is seven carbons so the parent molecule is heptane. With this numbering, there are methyl groups on carbons 3 and 6 and a chlorine on carbon 5.
Substituents are named in alphabetical order and two double bonds result in a diene. Thus, the correct answer is 5-chloro-3,6-dimethyl-1,5-heptadiene.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

What is the value of  from Huckel's rule for the given aromatic compound?
from Huckel's rule for the given aromatic compound?

What is the value of 
Huckel's rule states that an aromatic compound must have  delocalized electrons. The electrons in each double bond are delocalized for this molecule. There are nine double bonds, and thus eighteen delocalized electrons.
delocalized electrons. The electrons in each double bond are delocalized for this molecule. There are nine double bonds, and thus eighteen delocalized electrons.
If 4n+2=18, then n=4.
Huckel's rule states that an aromatic compound must have 
If 4n+2=18, then n=4.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following reagents would convert butanone into 2-butene?
Which of the following reagents would convert butanone into 2-butene?
Two sets of reagents are required to convert butanone into 2-butene. First, we use  to reduce the butanone into a 2-butanol. Second, we use heat and acid to dehydrate the butanol and yield the final desired product.
to reduce the butanone into a 2-butanol. Second, we use heat and acid to dehydrate the butanol and yield the final desired product.
1.  ; 2. Heat/
; 2. Heat/ may seem like an acceptable answer choice. However, note that the Grignard reagent converts the butanone into a tertiary alcohol, rather than a secondary alcohol as needed.
may seem like an acceptable answer choice. However, note that the Grignard reagent converts the butanone into a tertiary alcohol, rather than a secondary alcohol as needed.
Two sets of reagents are required to convert butanone into 2-butene. First, we use 
1. 

Compare your answer with the correct one above
2-butone is reacted with  to form a product. That product was then heated in acid
to form a product. That product was then heated in acid  to form a final product. What is the final product?
to form a final product. What is the final product?
2-butone is reacted with 

2-butone is a carbonyl compound that can readily be reduced by  into a secondary alcohol, 2-butanol. When 2-butanol is heated in acid, we get dehydration, which leads to 2-butene.
into a secondary alcohol, 2-butanol. When 2-butanol is heated in acid, we get dehydration, which leads to 2-butene.
2-butone is a carbonyl compound that can readily be reduced by 
Compare your answer with the correct one above

What is the reactant of the given reaction?

What is the reactant of the given reaction?
This is an addition reaction with 3 products. The unknown reactant reacts with  and gives those three products. Addition reactions begin with double bonded compounds and so these electrons are used to react with some reagent
and gives those three products. Addition reactions begin with double bonded compounds and so these electrons are used to react with some reagent  . One needs to work backwards to figure out how something was formed and in this case, there are mechanistic pathways, and one of the pathways involves a hydride shift. These 3 products often exist in different concentrations after the reaction.
. One needs to work backwards to figure out how something was formed and in this case, there are mechanistic pathways, and one of the pathways involves a hydride shift. These 3 products often exist in different concentrations after the reaction.
This is an addition reaction with 3 products. The unknown reactant reacts with 

Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following reagents can be used to create a E alkene from an alkyne?
Which of the following reagents can be used to create a E alkene from an alkyne?
Metallic sodium in liquid ammonia creates solvated electrons which can convert an alkyne to an E alkene. The same will not happen when sodium is combined with water, where sodium reacts violently to create sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. Lindlar's catalyst is a poisoned catalyst used to form alkenes from alkynes, bud results in a Z conformation. Without the poisoned catalyst, an alkane will be formed.
Metallic sodium in liquid ammonia creates solvated electrons which can convert an alkyne to an E alkene. The same will not happen when sodium is combined with water, where sodium reacts violently to create sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. Lindlar's catalyst is a poisoned catalyst used to form alkenes from alkynes, bud results in a Z conformation. Without the poisoned catalyst, an alkane will be formed.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

What is the major product for the reaction given?

What is the major product for the reaction given?
Below is the mechanism for the reaction given to form the alkene:

Below is the mechanism for the reaction given to form the alkene:

Compare your answer with the correct one above

What is the major product for the reaction given?

What is the major product for the reaction given?
The reason this is the major product is because on tertiary alcohols are best dehydrated based on the E1 mechanism below:

The reason this is the major product is because on tertiary alcohols are best dehydrated based on the E1 mechanism below:

Compare your answer with the correct one above

What is the major product for the reaction given?

What is the major product for the reaction given?
The reason this is the major product is because tertiary alcohols are best dehydrated based on the E1 mechanism below:

The reason this is the major product is because tertiary alcohols are best dehydrated based on the E1 mechanism below:

Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the best reagent for abstracting a hydrogen from ethyne?
What is the best reagent for abstracting a hydrogen from ethyne?
The triple bond in ethyne makes the hydrogens slightly more acidic than those found in ethane. A very strong base, such as the conjugate base of ammonia, would be able to abstract that hydrogen. The abstraction turns the base into ammonia. It also creates a carbanion that can be used for chain extension and alkyne synthesis.
The triple bond in ethyne makes the hydrogens slightly more acidic than those found in ethane. A very strong base, such as the conjugate base of ammonia, would be able to abstract that hydrogen. The abstraction turns the base into ammonia. It also creates a carbanion that can be used for chain extension and alkyne synthesis.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

What is the product of the compound when it reacts with two equivalents of base?

What is the product of the compound when it reacts with two equivalents of base?
For each equivalent of base, a pi bond is formed between the carbons initially bound to the bromine atoms. For each bond formed, a bromine leaving group leaves the hydrocarbon. One equivalent of base abstracts a hydrogen. The electrons from the bond to the hydrogen create a pi bond. This occurs twice, and a triple bond is formed. The result is a 5-carbon chain with a triple bond between the second and third carbons. This molecule is 2-pentyne.
For each equivalent of base, a pi bond is formed between the carbons initially bound to the bromine atoms. For each bond formed, a bromine leaving group leaves the hydrocarbon. One equivalent of base abstracts a hydrogen. The electrons from the bond to the hydrogen create a pi bond. This occurs twice, and a triple bond is formed. The result is a 5-carbon chain with a triple bond between the second and third carbons. This molecule is 2-pentyne.
Compare your answer with the correct one above