Transcription - MCAT Biology
Card 0 of 16
Human chromosomes are divided into two arms, a long q arm and a short p arm. A karyotype is the organization of a human cell’s total genetic complement. A typical karyotype is generated by ordering chromosome 1 to chromosome 23 in order of decreasing size.
When viewing a karyotype, it can often become apparent that changes in chromosome number, arrangement, or structure are present. Among the most common genetic changes are Robertsonian translocations, involving transposition of chromosomal material between long arms of certain chromosomes to form one derivative chromosome. Chromosomes 14 and 21, for example, often undergo a Robertsonian translocation, as below.

A karyotype of this individual for chromosomes 14 and 21 would thus appear as follows:

Though an individual with aberrations such as a Robertsonian translocation may be phenotypically normal, they can generate gametes through meiosis that have atypical organizations of chromosomes, resulting in recurrent fetal abnormalities or miscarriages.
In chromosome 21, parts of the DNA are converted to protein, while other parts are interspersed, but do not correlate to the final protein sequence. The portions of the DNA that code for final amino acid sequence are called __________.
Human chromosomes are divided into two arms, a long q arm and a short p arm. A karyotype is the organization of a human cell’s total genetic complement. A typical karyotype is generated by ordering chromosome 1 to chromosome 23 in order of decreasing size.
When viewing a karyotype, it can often become apparent that changes in chromosome number, arrangement, or structure are present. Among the most common genetic changes are Robertsonian translocations, involving transposition of chromosomal material between long arms of certain chromosomes to form one derivative chromosome. Chromosomes 14 and 21, for example, often undergo a Robertsonian translocation, as below.

A karyotype of this individual for chromosomes 14 and 21 would thus appear as follows:

Though an individual with aberrations such as a Robertsonian translocation may be phenotypically normal, they can generate gametes through meiosis that have atypical organizations of chromosomes, resulting in recurrent fetal abnormalities or miscarriages.
In chromosome 21, parts of the DNA are converted to protein, while other parts are interspersed, but do not correlate to the final protein sequence. The portions of the DNA that code for final amino acid sequence are called __________.
In the splicing model of DNA expression, certain regions of DNA are converted to proteins while intervening portions are cut out. The portions of "junk DNA" are known as introns, while exons are the sequences actually converted to protein. Okazaki fragments may appear tempting, but actually refers to fragments of DNA synthesized during replication of the lagging strand.
In the splicing model of DNA expression, certain regions of DNA are converted to proteins while intervening portions are cut out. The portions of "junk DNA" are known as introns, while exons are the sequences actually converted to protein. Okazaki fragments may appear tempting, but actually refers to fragments of DNA synthesized during replication of the lagging strand.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What enzyme is required for transcription of mRNA in eukaryotes?
What enzyme is required for transcription of mRNA in eukaryotes?
RNA polymerase II is required for transcription of mRNA, snRNA, and miRNA. Alternatively, RNA polymerase I transcribes some rRNA and RNA polymerase III transcribes tRNA, some rRNA, and other small RNAs. DNA polymerase is required for DNA replication but does not play a role in transcription.
RNA polymerase II is required for transcription of mRNA, snRNA, and miRNA. Alternatively, RNA polymerase I transcribes some rRNA and RNA polymerase III transcribes tRNA, some rRNA, and other small RNAs. DNA polymerase is required for DNA replication but does not play a role in transcription.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
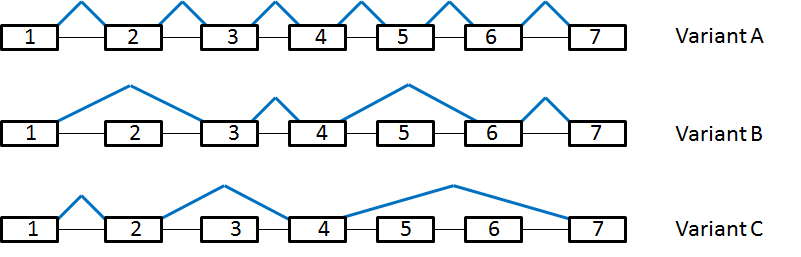
Three isoforms of a particular protein (variants A, B, and C) are expressed. In the following diagram, exons are indicating by boxes, introns by the black lines, and splice junctions by blue lines. Assume each exon is greater than 500 bp in length (figure not drawn to scale).
In the absence of available antibodies for Western blotting, how would one experimentally determine if variant C was expressed in HeLa cells?
Three isoforms of a particular protein (variants A, B, and C) are expressed. In the following diagram, exons are indicating by boxes, introns by the black lines, and splice junctions by blue lines. Assume each exon is greater than 500 bp in length (figure not drawn to scale).
In the absence of available antibodies for Western blotting, how would one experimentally determine if variant C was expressed in HeLa cells?
Although each splice variant contains exons 4 and 7, PCR products between these exons in variants A and B would be too large to be detected using real time PCR; therefore, amplifying that region would conclusively identify the presence of variant C in HeLa cells. If variant C is not expressed in HeLa cells, one would expect a negative (or unamplified) result using real time PCR.
Variant A expression: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
Variant B expression: 1, 3, 4, 6, 7
Variant C expression: 1, 2, 4, 7
By amplifying exons 5 and 6, and looking for a negative result, we can identify the presence of variant C.
Although each splice variant contains exons 4 and 7, PCR products between these exons in variants A and B would be too large to be detected using real time PCR; therefore, amplifying that region would conclusively identify the presence of variant C in HeLa cells. If variant C is not expressed in HeLa cells, one would expect a negative (or unamplified) result using real time PCR.
Variant A expression: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7
Variant B expression: 1, 3, 4, 6, 7
Variant C expression: 1, 2, 4, 7
By amplifying exons 5 and 6, and looking for a negative result, we can identify the presence of variant C.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding transcription in eukaryotic cells?
Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding transcription in eukaryotic cells?
Remember that DNA is found in the nucleus of cells. As a result, it would not make sense that transcription would take place in the cytoplasm.
RNA polymerase replaces thymine with uracil, and a specific DNA sequence (the promoter) shows RNA polymerase where to begin transcription on the template strand. RNA polymerase will only transcribe one DNA strand (the template strand) because the complementary strand would result in a different mRNA product.
Remember that DNA is found in the nucleus of cells. As a result, it would not make sense that transcription would take place in the cytoplasm.
RNA polymerase replaces thymine with uracil, and a specific DNA sequence (the promoter) shows RNA polymerase where to begin transcription on the template strand. RNA polymerase will only transcribe one DNA strand (the template strand) because the complementary strand would result in a different mRNA product.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following statements is true concerning DNA replication and transcription?
Which of the following statements is true concerning DNA replication and transcription?
In both replication and transcription, DNA is the template used to create the desired product. RNA polymerase uses a promoter, and DNA polymerase uses an RNA primer, in order to determine where to begin. DNA polymerase moves much more quickly than RNA polymerase, and RNA polymerase only uses one of the two strands in order to make the desired product.
In both replication and transcription, DNA is the template used to create the desired product. RNA polymerase uses a promoter, and DNA polymerase uses an RNA primer, in order to determine where to begin. DNA polymerase moves much more quickly than RNA polymerase, and RNA polymerase only uses one of the two strands in order to make the desired product.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
An operon is a section of DNA that is composed of a promoter, an operator, and all of the structural genes that will be transcribed in one mRNA. The lac operon is perhaps the most famous example of how prokaryotic organisms will simultaneously transcribe all of the structural genes necessary to accomplish a certain function in the cell. In the absence of glucose, the lac operon will be transcribed so that lactose can be metabolized in the cell for energy.
Which of the following conditions would result in an increase in transcription of the structural genes found on the lac operon?
An operon is a section of DNA that is composed of a promoter, an operator, and all of the structural genes that will be transcribed in one mRNA. The lac operon is perhaps the most famous example of how prokaryotic organisms will simultaneously transcribe all of the structural genes necessary to accomplish a certain function in the cell. In the absence of glucose, the lac operon will be transcribed so that lactose can be metabolized in the cell for energy.
Which of the following conditions would result in an increase in transcription of the structural genes found on the lac operon?
When glucose levels are low, there is an increase in cyclic AMP. The cAMP wil then activate CAP, which will attach upstream to the promoter of the lac operon and promote transcription.
When glucose levels are low, there is an increase in cyclic AMP. The cAMP wil then activate CAP, which will attach upstream to the promoter of the lac operon and promote transcription.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
In 2013, scientists linked a cellular response called the unfolded protein response (UPR) to a series of neurodegenerative diseases, including such major health issues as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Disease. According to their work, the unfolded protein response is a reduction in translation as a result of a series of enzymes that modify a translation initiation factor, eIF2, as below:

In the above sequence, the unfolded protein sensor binds to unfolded protein, such as the pathogenic amyloid-beta found in the brains of Alzheimer’s Disease patients. This sensor then phosphorylates PERK, or protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase. This leads to downstream effects on eIF2, inhibition of which represses translation. It is thought that symptoms of neurodegenerative disease may be a result of this reduced translation.
In contrast to translation, transcription __________.
In 2013, scientists linked a cellular response called the unfolded protein response (UPR) to a series of neurodegenerative diseases, including such major health issues as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Disease. According to their work, the unfolded protein response is a reduction in translation as a result of a series of enzymes that modify a translation initiation factor, eIF2, as below:

In the above sequence, the unfolded protein sensor binds to unfolded protein, such as the pathogenic amyloid-beta found in the brains of Alzheimer’s Disease patients. This sensor then phosphorylates PERK, or protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase. This leads to downstream effects on eIF2, inhibition of which represses translation. It is thought that symptoms of neurodegenerative disease may be a result of this reduced translation.
In contrast to translation, transcription __________.
Transcription takes place in the nucleus, where DNA access is ensured. DNA is then turned into an mRNA transcript, which can exit the nucleus and move to the cytosol for translation.
Transcription takes place in the nucleus, where DNA access is ensured. DNA is then turned into an mRNA transcript, which can exit the nucleus and move to the cytosol for translation.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which class of upstream DNA element is responsible for increasing transcription of target genes?
Which class of upstream DNA element is responsible for increasing transcription of target genes?
An enhancer is a cis-acting element that is responsible for activating or increasing expression of a target gene. An insulator is a boundary element between inactive and active domains of DNA. Both activators and repressors are trans-acting (protein) factors that modulate gene expression.
An enhancer is a cis-acting element that is responsible for activating or increasing expression of a target gene. An insulator is a boundary element between inactive and active domains of DNA. Both activators and repressors are trans-acting (protein) factors that modulate gene expression.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Prokaryotic mRNA usually includes several genes on the same transcript. An operon is a genetic unit which typically consists of a promoter, an operator, and all of the functional genes that will be coded for by a single mRNA. In biology, the lac operon is the most commonly used example. The lac operon is transcribed when a prokaryote has a glucose deficiency, and requires lactose in order to create glucose.
The lac operon is modulated by specific proteins which can regulate the amount of transcription. A lac repressor will attach to the operator and reduce transcription if it is not necessary at a given time. The lac repressor will be removed in the presence of lactose by becoming attached to a lactose molecule. Meanwhile, catabolite activator protein (CAP) will attach upstream to the promoter and signal RNA polymerase to begin transcription if transcription is needed.
How would you describe the levels of lac operon transcription when a prokaryote has high glucose and lactose levels available?
Prokaryotic mRNA usually includes several genes on the same transcript. An operon is a genetic unit which typically consists of a promoter, an operator, and all of the functional genes that will be coded for by a single mRNA. In biology, the lac operon is the most commonly used example. The lac operon is transcribed when a prokaryote has a glucose deficiency, and requires lactose in order to create glucose.
The lac operon is modulated by specific proteins which can regulate the amount of transcription. A lac repressor will attach to the operator and reduce transcription if it is not necessary at a given time. The lac repressor will be removed in the presence of lactose by becoming attached to a lactose molecule. Meanwhile, catabolite activator protein (CAP) will attach upstream to the promoter and signal RNA polymerase to begin transcription if transcription is needed.
How would you describe the levels of lac operon transcription when a prokaryote has high glucose and lactose levels available?
While it is true that the lac operon is used when lactose is present, the prokaryote in this scenario also has high levels of glucose present. As a result, the lac operon is not necessary in the given environment, so it will be transcribed at a very low rate. It is energetically favorable to use the glucose already present, rather than to convert lactose to glucose; this causes the lac operon to be activated only when glucose levels are low and lactose is available.
While it is true that the lac operon is used when lactose is present, the prokaryote in this scenario also has high levels of glucose present. As a result, the lac operon is not necessary in the given environment, so it will be transcribed at a very low rate. It is energetically favorable to use the glucose already present, rather than to convert lactose to glucose; this causes the lac operon to be activated only when glucose levels are low and lactose is available.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Prokaryotic mRNA usually includes several genes on the same transcript. An operon is a genetic unit which typically consists of a promoter, an operator, and all of the functional genes that will be coded for by a single mRNA. In biology, the lac operon is the most commonly used example. The lac operon is transcribed when a prokaryote has a glucose deficiency, and requires lactose in order to create glucose.
The lac operon is modulated by specific proteins which can regulate the amount of transcription. A lac repressor will attach to the operator and reduce transcription if it is not necessary at a given time. The lac repressor will be removed in the presence of lactose by becoming attached to a lactose molecule. Meanwhile, catabolite activator protein (CAP) will attach upstream to the promoter and signal RNA polymerase to begin transcription if transcription is needed.
In a low glucose, high lactose environment, which of the following statements is false?
Prokaryotic mRNA usually includes several genes on the same transcript. An operon is a genetic unit which typically consists of a promoter, an operator, and all of the functional genes that will be coded for by a single mRNA. In biology, the lac operon is the most commonly used example. The lac operon is transcribed when a prokaryote has a glucose deficiency, and requires lactose in order to create glucose.
The lac operon is modulated by specific proteins which can regulate the amount of transcription. A lac repressor will attach to the operator and reduce transcription if it is not necessary at a given time. The lac repressor will be removed in the presence of lactose by becoming attached to a lactose molecule. Meanwhile, catabolite activator protein (CAP) will attach upstream to the promoter and signal RNA polymerase to begin transcription if transcription is needed.
In a low glucose, high lactose environment, which of the following statements is false?
In a low glucose, high lactose environment, there is only lactose to metabolize. Lactose will attach to the lac repressor and remove it from the operator. Glucose does NOT attach to any of the lac operon regulators. It is glucose's absence, rather than its presence, which promotes the transcription of the lac operon.
In a low glucose, high lactose environment, there is only lactose to metabolize. Lactose will attach to the lac repressor and remove it from the operator. Glucose does NOT attach to any of the lac operon regulators. It is glucose's absence, rather than its presence, which promotes the transcription of the lac operon.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Prokaryotic mRNA usually includes several genes on the same transcript. An operon is a genetic unit which typically consists of a promoter, an operator, and all of the functional genes that will be coded for by a single mRNA. In biology, the lac operon is the most commonly used example. The lac operon is transcribed when a prokaryote has a glucose deficiency, and requires lactose in order to create glucose.
The lac operon is modulated by specific proteins which can regulate the amount of transcription. A lac repressor will attach to the operator and reduce transcription if it is not necessary at a given time. The lac repressor will be removed in the presence of lactose by becoming attached to a lactose molecule. Meanwhile, catabolite activator protein (CAP) will attach upstream to the promoter and signal RNA polymerase to begin transcription if transcription is needed.
Imagine that there is a mutation on the lac repressor which makes it unable for lactose to attach. What would you expect to happen?
Prokaryotic mRNA usually includes several genes on the same transcript. An operon is a genetic unit which typically consists of a promoter, an operator, and all of the functional genes that will be coded for by a single mRNA. In biology, the lac operon is the most commonly used example. The lac operon is transcribed when a prokaryote has a glucose deficiency, and requires lactose in order to create glucose.
The lac operon is modulated by specific proteins which can regulate the amount of transcription. A lac repressor will attach to the operator and reduce transcription if it is not necessary at a given time. The lac repressor will be removed in the presence of lactose by becoming attached to a lactose molecule. Meanwhile, catabolite activator protein (CAP) will attach upstream to the promoter and signal RNA polymerase to begin transcription if transcription is needed.
Imagine that there is a mutation on the lac repressor which makes it unable for lactose to attach. What would you expect to happen?
The lac repressor is attached to the operator in the absence of lactose; it will only be removed from the operator if lactose attaches to it. Since there is a mutation that forbids this attachment, the lac repressor will always be on the operator. This will result in very low lac operon transcription, even in the presence of lactose.
Catabolite activator protein (CAP) will still bind upstream of the promoter, but RNA polymerase will be unable to access the operon due to the repressor's presence.
The lac repressor is attached to the operator in the absence of lactose; it will only be removed from the operator if lactose attaches to it. Since there is a mutation that forbids this attachment, the lac repressor will always be on the operator. This will result in very low lac operon transcription, even in the presence of lactose.
Catabolite activator protein (CAP) will still bind upstream of the promoter, but RNA polymerase will be unable to access the operon due to the repressor's presence.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Although there are about 30,000 genes in the human body, approximately 120,000 proteins can be created in the body. This is caused by __________.
Although there are about 30,000 genes in the human body, approximately 120,000 proteins can be created in the body. This is caused by __________.
The primary transcript (immediately following transcription) is composed of multiple segments of RNA called introns and exons. While introns are always cleaved from the primary transcript, the exons may or may not stay on the primary transcript, which will eventually be translated. Since different numbers and orders of exons can arise from the same transcript, there are multiple proteins that can possibly be made from one primary transcript.
Intron and exon splicing, the addition of the 5' cap, and the addition of the poly A tail are all crucial post-transcriptional modifications in eukaryotes, but only the alternative splicing patterns result in variable transcripts. Eukaryotes do not follow the polycistronic model, in which one mRNA will code for multiple genes or proteins. The degeneracy of the genetic code refers to the multiple codons that will produce the same amino acids; this feature increases the variability of the DNA sequence, but does not affect the number of possible transcripts, genes, or proteins formed.
The primary transcript (immediately following transcription) is composed of multiple segments of RNA called introns and exons. While introns are always cleaved from the primary transcript, the exons may or may not stay on the primary transcript, which will eventually be translated. Since different numbers and orders of exons can arise from the same transcript, there are multiple proteins that can possibly be made from one primary transcript.
Intron and exon splicing, the addition of the 5' cap, and the addition of the poly A tail are all crucial post-transcriptional modifications in eukaryotes, but only the alternative splicing patterns result in variable transcripts. Eukaryotes do not follow the polycistronic model, in which one mRNA will code for multiple genes or proteins. The degeneracy of the genetic code refers to the multiple codons that will produce the same amino acids; this feature increases the variability of the DNA sequence, but does not affect the number of possible transcripts, genes, or proteins formed.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the purpose of the poly A tail attached to the primary transcript prior to translation?
What is the purpose of the poly A tail attached to the primary transcript prior to translation?
The poly A tail is an example of post-transcriptional processing. The poly A tail is attached to the end of the transcript, and protects it from being degraded by exonucleases. Exonucleases are essential in order to recycle the nucleobases used in mRNA, but can be harmful to RNA that has not yet been translated unless the poly A tail is present.
The poly A tail is an example of post-transcriptional processing. The poly A tail is attached to the end of the transcript, and protects it from being degraded by exonucleases. Exonucleases are essential in order to recycle the nucleobases used in mRNA, but can be harmful to RNA that has not yet been translated unless the poly A tail is present.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is not true about RNA?
Which of the following is not true about RNA?
There are a few different types of RNA, each serving different purposes. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is transcribed to a protein product, but transfer RNA (tRNA) acts as a carrier for amino acids while ribosomal RNA (rRNA) forms some structures of the ribosome. Micro RNA (miRNA) can be used to regulate transcription.
RNA can be single or double stranded, leading to both ssRNA and dsRNA viruses. The ribose sugar in RNA forms a five-carbon ring, much like deoxyribose in DNA. RNA contains both adenine and uracil, though thymine is not found in RNA.
There are a few different types of RNA, each serving different purposes. Messenger RNA (mRNA) is transcribed to a protein product, but transfer RNA (tRNA) acts as a carrier for amino acids while ribosomal RNA (rRNA) forms some structures of the ribosome. Micro RNA (miRNA) can be used to regulate transcription.
RNA can be single or double stranded, leading to both ssRNA and dsRNA viruses. The ribose sugar in RNA forms a five-carbon ring, much like deoxyribose in DNA. RNA contains both adenine and uracil, though thymine is not found in RNA.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following experimental methods cannot be used to measure the relative abundance of a particular mRNA?
Which of the following experimental methods cannot be used to measure the relative abundance of a particular mRNA?
Western blots are used to measure the relative abundance of proteins. While there is a correlation between the amount of mRNA and protein, using a western blot to measure mRNA would be inconclusive due to the variability of protein half life.
Northern blots are used to run mRNA samples on gels, DNA microarrys give the expression levels of certain genes, and rtPCR is used to detect RNA expression levels. Any of these methods could provide the relative abundance of a particular mRNA.
Western blots are used to measure the relative abundance of proteins. While there is a correlation between the amount of mRNA and protein, using a western blot to measure mRNA would be inconclusive due to the variability of protein half life.
Northern blots are used to run mRNA samples on gels, DNA microarrys give the expression levels of certain genes, and rtPCR is used to detect RNA expression levels. Any of these methods could provide the relative abundance of a particular mRNA.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is a common modification that occurs on histone tails to modulate gene expression?
What is a common modification that occurs on histone tails to modulate gene expression?
Both acetylation and methylation of histone tails modulate expression of target genes. Acetylation is always associated with active transcription while, in most cases, methylation is associated with repression of target genes. Acetylation generally loosens the DNA-histone association, allowing for transcription. In contrast, methylation generally tightens this association, blocking transcription proteins from binding to the DNA.
Hydroxylation is used to modify proteins and activate steroid hormones. Ubiquitination and sumoylation are post-translation protein modifications.
Both acetylation and methylation of histone tails modulate expression of target genes. Acetylation is always associated with active transcription while, in most cases, methylation is associated with repression of target genes. Acetylation generally loosens the DNA-histone association, allowing for transcription. In contrast, methylation generally tightens this association, blocking transcription proteins from binding to the DNA.
Hydroxylation is used to modify proteins and activate steroid hormones. Ubiquitination and sumoylation are post-translation protein modifications.
Compare your answer with the correct one above