Lymphatic System - MCAT Biology
Card 0 of 20
Lymph in the thoracic duct __________.
I. contains fluid and cells collected from the left hand
II. contains chylomicrons collected from the intestine
III. contains fluid and cells collected from the left leg
IV. contains fluid and cells from the head and neck
V. all of these are true
Lymph in the thoracic duct __________.
I. contains fluid and cells collected from the left hand
II. contains chylomicrons collected from the intestine
III. contains fluid and cells collected from the left leg
IV. contains fluid and cells from the head and neck
V. all of these are true
You either know the anatomy of lymphatic flow, or you don't and you need to review it. All statements are true. The thoracic duct is the major collecting point for lymph from both lower limbs, the intestine, and certainly the left arm and left side of the head and neck. It empties into the junction of the left subclavian vein and the left jugular vein, most commonly. The question did not ask you to argue about whether or not lymph from the right arm and right side of the head and neck rejoined the venous circulation through the thoracic duct or a smaller accessory thoracic duct on the right side, because this is somewhat variable.
You either know the anatomy of lymphatic flow, or you don't and you need to review it. All statements are true. The thoracic duct is the major collecting point for lymph from both lower limbs, the intestine, and certainly the left arm and left side of the head and neck. It empties into the junction of the left subclavian vein and the left jugular vein, most commonly. The question did not ask you to argue about whether or not lymph from the right arm and right side of the head and neck rejoined the venous circulation through the thoracic duct or a smaller accessory thoracic duct on the right side, because this is somewhat variable.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The lymph collected from the majority of the body drains into the vena cava via what vessel?
The lymph collected from the majority of the body drains into the vena cava via what vessel?
It is important to know that the lymphatic system is an open system, meaning that it drains the interstitial fluid from the body and delivers it to the circulatory system in two different ways. The majority of the lymph drains from the body through the thoracic duct into the vena cava. The thoracic duct is also what drains fats collected in the liver and turned into chylomicrons.
Lymph from the head and right arm drains via the right lymphatic duct back to the vena cava, but this does not constitute the majority of lymph flow.
It is important to know that the lymphatic system is an open system, meaning that it drains the interstitial fluid from the body and delivers it to the circulatory system in two different ways. The majority of the lymph drains from the body through the thoracic duct into the vena cava. The thoracic duct is also what drains fats collected in the liver and turned into chylomicrons.
Lymph from the head and right arm drains via the right lymphatic duct back to the vena cava, but this does not constitute the majority of lymph flow.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The lymph from the head, neck, and right arm drains into the vena cava via what duct?
The lymph from the head, neck, and right arm drains into the vena cava via what duct?
It is important to know that lymph from the head, neck, and right arm drains via the right lymphatic duct into the vena cava, to be added to the venous circulation. The other important lymphatic duct is the thoracic duct, which drains lymph from the remainder of the body.
It is important to know that lymph from the head, neck, and right arm drains via the right lymphatic duct into the vena cava, to be added to the venous circulation. The other important lymphatic duct is the thoracic duct, which drains lymph from the remainder of the body.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is not a component of the lymphatic fluid?
Which of the following is not a component of the lymphatic fluid?
The lymph is collected in the periphery from the fluid that is not reabsorbed by oncotic pressure in the capillary beds. Proteins (including the main blood component albumin), chylomicrons (collected from enterocytes in the liver), and water are all parts of lymph. These components can exit the capillary walls in areas of significant hydrostatic pressure, and enter the lymph to avoid being trapped in the interstitium.
Red blood cells are too large to pass through capillary walls, and thus would not be released into the interstitium or absorbed into the lymphatic system.
The lymph is collected in the periphery from the fluid that is not reabsorbed by oncotic pressure in the capillary beds. Proteins (including the main blood component albumin), chylomicrons (collected from enterocytes in the liver), and water are all parts of lymph. These components can exit the capillary walls in areas of significant hydrostatic pressure, and enter the lymph to avoid being trapped in the interstitium.
Red blood cells are too large to pass through capillary walls, and thus would not be released into the interstitium or absorbed into the lymphatic system.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What would you NOT expect to find in lymph fluid?
What would you NOT expect to find in lymph fluid?
Lymph is a fluid that travels through its own kind of circulatory system. The lymphatic system as a whole helps maintain distribution of fluids and maintain blood composition. Plasma from blood leaks out of capillaries and gets collected and redistributed by the lymph system. It also transports other molecules, like proteins, triglycerides, and white blood cells. You would not expect to find a red blood cells in this fluid, as they do not leak out of veins and capillaries.
Lymph is a fluid that travels through its own kind of circulatory system. The lymphatic system as a whole helps maintain distribution of fluids and maintain blood composition. Plasma from blood leaks out of capillaries and gets collected and redistributed by the lymph system. It also transports other molecules, like proteins, triglycerides, and white blood cells. You would not expect to find a red blood cells in this fluid, as they do not leak out of veins and capillaries.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
During the course of a day, approximately three liters of plasma are filtered out of the capillaries, but are not reabsorbed into the vessels. This means that the volume of fluid stays in the interstitial space around the capillaries.
What does the body do with this large volume of fluid?
During the course of a day, approximately three liters of plasma are filtered out of the capillaries, but are not reabsorbed into the vessels. This means that the volume of fluid stays in the interstitial space around the capillaries.
What does the body do with this large volume of fluid?
Lymphatic fluid is formed by absorbing the excess plasma that has been filtered from the capillaries. This occurs because more plasma is filtered out of the capillaries than can be reabsorbed back into the capillaries. This leads to a net filtration of plasma into the interstitium. The role of the lymphatic system is to absorb this filtered plasma and return it to circulation via a duct into the right atrium. A failure to collect the extracellular fluids can lead to swelling of the extremities, known as edema.
When the lymphatic vessels collect fluid they also carry it through the lymph nodes, which house large populations of lymphocytes. These lymphocytes screen the blood for foreign antigens and can launch an immune response if pathogens are found.
Lymphatic fluid is formed by absorbing the excess plasma that has been filtered from the capillaries. This occurs because more plasma is filtered out of the capillaries than can be reabsorbed back into the capillaries. This leads to a net filtration of plasma into the interstitium. The role of the lymphatic system is to absorb this filtered plasma and return it to circulation via a duct into the right atrium. A failure to collect the extracellular fluids can lead to swelling of the extremities, known as edema.
When the lymphatic vessels collect fluid they also carry it through the lymph nodes, which house large populations of lymphocytes. These lymphocytes screen the blood for foreign antigens and can launch an immune response if pathogens are found.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following systems is NOT directly aided by the lymphatic system?
Which of the following systems is NOT directly aided by the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system has a variety of functions in the body. It collects excess interstitial fluid and returns it to the blood (cardiovascular system), it has lymph nodes that screen the lymphatic fluid for pathogens (immune system), and it reroutes fat digestates to the neck veins (digestive system). The lymphatic system does not aid the endocrine system, as hormones travel in the bloodstream.
The lymphatic system has a variety of functions in the body. It collects excess interstitial fluid and returns it to the blood (cardiovascular system), it has lymph nodes that screen the lymphatic fluid for pathogens (immune system), and it reroutes fat digestates to the neck veins (digestive system). The lymphatic system does not aid the endocrine system, as hormones travel in the bloodstream.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is NOT a part of the lymphatic system?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the lymphatic system?
All of the following are parts of the lymphatic system, except the liver. The liver is considered to be primarily a part of the digestive system.
All of the following are parts of the lymphatic system, except the liver. The liver is considered to be primarily a part of the digestive system.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is a primary lymphoid structure?
I. Thymus
II. Spleen
III. Lymph node
Which of the following is a primary lymphoid structure?
I. Thymus
II. Spleen
III. Lymph node
Primary lymphoid tissues refer to the tissues where lymphoid cells are generated, while secondary lymphoid tissues are the functional organs of the lymphatic system.
Lymphocytes are generated and developed in the bone marrow and thymus only. The spleen and lymph nodes are examples of secondary lymphatic organs.
Primary lymphoid tissues refer to the tissues where lymphoid cells are generated, while secondary lymphoid tissues are the functional organs of the lymphatic system.
Lymphocytes are generated and developed in the bone marrow and thymus only. The spleen and lymph nodes are examples of secondary lymphatic organs.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following are you most likely to find in the medulla of a lymph node?
Which of the following are you most likely to find in the medulla of a lymph node?
In the lymph node, the B-cells are located in the cortex and the T-cells are located in the medulla. The stromal cells are structural cells that are not particular to an area of the lymph node. Dendritic cells will move through the lymph node to present antigens to the adaptive immune system cells.
In the lymph node, the B-cells are located in the cortex and the T-cells are located in the medulla. The stromal cells are structural cells that are not particular to an area of the lymph node. Dendritic cells will move through the lymph node to present antigens to the adaptive immune system cells.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Hypersensitivity reactions occur when body tissues are affected by an abnormal immune reaction. The result is damage to normal tissues and clinical illness. A peanut allergy is an example of a hypersensitivity reaction, but there are three additional broad classes.
One class involves the abnormal production or deposition of antibodies. Antibodies are B-cell derived molecules that normally adhere to pathogens, rendering them unable to continue an infection. When antibodies are produced against normal tissues, however, disease can result. Figure 1 depicts a schematic structure of an antibody.
Antibodies can be divided into two peptide chains: heavy and light. Heavy chains form the backbone of the antibody, and are attached to light chains via covalent bonding. Each heavy and light chain is then further divided into constant and variable regions. Variable regions exhibit molecular variety, generating a unique chemical identity for each antibody. These unique patterns help guarantee that the body can produce antibodies to recognize many possible molecular patterns on invading pathogens.
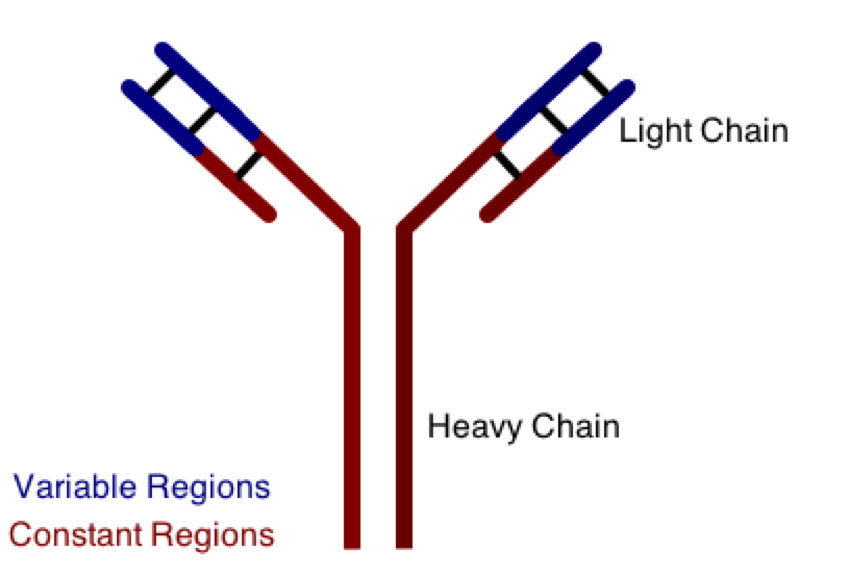
Antibodies and antigens interact in secondary lymphoid tissue, such as the spleen. In addition to its role in promoting this interaction, what is the primary function of the spleen?
Hypersensitivity reactions occur when body tissues are affected by an abnormal immune reaction. The result is damage to normal tissues and clinical illness. A peanut allergy is an example of a hypersensitivity reaction, but there are three additional broad classes.
One class involves the abnormal production or deposition of antibodies. Antibodies are B-cell derived molecules that normally adhere to pathogens, rendering them unable to continue an infection. When antibodies are produced against normal tissues, however, disease can result. Figure 1 depicts a schematic structure of an antibody.
Antibodies can be divided into two peptide chains: heavy and light. Heavy chains form the backbone of the antibody, and are attached to light chains via covalent bonding. Each heavy and light chain is then further divided into constant and variable regions. Variable regions exhibit molecular variety, generating a unique chemical identity for each antibody. These unique patterns help guarantee that the body can produce antibodies to recognize many possible molecular patterns on invading pathogens.

Antibodies and antigens interact in secondary lymphoid tissue, such as the spleen. In addition to its role in promoting this interaction, what is the primary function of the spleen?
The spleen has two main functions. The first main function is immunological, while its second function is to filter unhealthy (senescent) red blood cells.
Most digestive enzymes are secreted by the pancreas into the small intestine. Systemic hormones come from a variety of glands throughout the body; the spleen does not have an endocrine function. White blood cells are synthesized in bone marrow and mature in the marrow and thymus. Serum proteins are synthesized in the liver.
The spleen has two main functions. The first main function is immunological, while its second function is to filter unhealthy (senescent) red blood cells.
Most digestive enzymes are secreted by the pancreas into the small intestine. Systemic hormones come from a variety of glands throughout the body; the spleen does not have an endocrine function. White blood cells are synthesized in bone marrow and mature in the marrow and thymus. Serum proteins are synthesized in the liver.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Destruction of the lymph nodes would most likely affect the immune system in which way?
Destruction of the lymph nodes would most likely affect the immune system in which way?
The secondary response of the immune system is significantly shorter in duration due to the storage of memory cells after the initial infection has been combated. During the primary infection, a B-cell will bind with an antigen. Once this occurs, the B-cells will begin to divide rapidly into plasma cells and memory cells. Plasma cells release high quantities of antibodies, which are integral in combating the infection. Memory cells are stored in lymph nodes so that if the same antigen is ever encountered again, it can be quickly dealt with by a fast-responding production of the correct form of plasma cell. If lymph nodes were destroyed, memory cells would not be able to mount this quick secondary response.
The secondary response of the immune system is significantly shorter in duration due to the storage of memory cells after the initial infection has been combated. During the primary infection, a B-cell will bind with an antigen. Once this occurs, the B-cells will begin to divide rapidly into plasma cells and memory cells. Plasma cells release high quantities of antibodies, which are integral in combating the infection. Memory cells are stored in lymph nodes so that if the same antigen is ever encountered again, it can be quickly dealt with by a fast-responding production of the correct form of plasma cell. If lymph nodes were destroyed, memory cells would not be able to mount this quick secondary response.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of these is a lymphoid organ that is active in young children, but decreases in size and importance in adulthood?
Which of these is a lymphoid organ that is active in young children, but decreases in size and importance in adulthood?
The thymus is a lymphoid organ located in the mediastinal space. The thymus is the site of T-lymphocyte differentiation. The mature T-cells leave the thymus and migrate to the spleen, lymph nodes, and other lymphoid tissues where they control cell-mediated immune responses. The thymus grows from birth to puberty, at which point it begins to shrink. The reason for this involution may be that the organ has produced enough T-cells and is no longer necessary.
The spleen is another lymphocyte-producing organ. The spleen filters blood, exposing it to lymphocytes that destroy foreign particles. The size of the spleen remains constant, except in cases of infections such as mononucleosis. The tonsils are a patch of lymphoid tissue that contain lymphocytes located in the pharynx. The tonsils and adenoids form a ring of immunologically active tissue. These tissues remain at a constant size except when infected by bacteria. Lymph nodes receive lymph from a single organ or region of the body. An increase in size, known as lymphadenopathy, could result from combating infection or cancer.
The thymus is a lymphoid organ located in the mediastinal space. The thymus is the site of T-lymphocyte differentiation. The mature T-cells leave the thymus and migrate to the spleen, lymph nodes, and other lymphoid tissues where they control cell-mediated immune responses. The thymus grows from birth to puberty, at which point it begins to shrink. The reason for this involution may be that the organ has produced enough T-cells and is no longer necessary.
The spleen is another lymphocyte-producing organ. The spleen filters blood, exposing it to lymphocytes that destroy foreign particles. The size of the spleen remains constant, except in cases of infections such as mononucleosis. The tonsils are a patch of lymphoid tissue that contain lymphocytes located in the pharynx. The tonsils and adenoids form a ring of immunologically active tissue. These tissues remain at a constant size except when infected by bacteria. Lymph nodes receive lymph from a single organ or region of the body. An increase in size, known as lymphadenopathy, could result from combating infection or cancer.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which lymphoid organ is the site of erythrocyte, leukocyte, and lymphocyte production?
Which lymphoid organ is the site of erythrocyte, leukocyte, and lymphocyte production?
The spleen forms erythrocytes (red blood cells), and leukocytes (white blood cells, including lymphocytes) during the embryonic stage. After birth, only lymphocytes are produced.
The tonsils and adenoids are patches of lymphoid tissue located in the pharynx that filter pathogens that enter the body through the mouth and nose. Lymph nodes produce lymphocytes in response to infections by pathogens. The thymus is an organ that produces lymphocytes in infants and young children.
The spleen forms erythrocytes (red blood cells), and leukocytes (white blood cells, including lymphocytes) during the embryonic stage. After birth, only lymphocytes are produced.
The tonsils and adenoids are patches of lymphoid tissue located in the pharynx that filter pathogens that enter the body through the mouth and nose. Lymph nodes produce lymphocytes in response to infections by pathogens. The thymus is an organ that produces lymphocytes in infants and young children.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The surface of which lymphoid organ is covered with stratified squamous epithelium and located at the entrance to the oropharynx?
The surface of which lymphoid organ is covered with stratified squamous epithelium and located at the entrance to the oropharynx?
The surface of each tonsil is covered with stratified squamous epithelium, which forms deep crypts that detect and respond to pathogens entering the body. The tonsils are located on either side of the throat at the back of the tongue.
Adenoids are lymphoid tissue located in the nasopharynx, in the midline at the back of the throat. The spleen is in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen. The spleen has a smooth surface, as it is covered by an outer capsule of connective tissue. The thymus is in the mediastinum between the lungs. The thymus is composed of two lobes containing multiple lobules divided into an outer cortex and an inner medulla. The thymus is the site of T-cell differentiation. Lymph nodes filter lymph and remove foreign particles. Lymph nodes are located throughout the body, and are concentrated in the neck, axilla, and groin.
The surface of each tonsil is covered with stratified squamous epithelium, which forms deep crypts that detect and respond to pathogens entering the body. The tonsils are located on either side of the throat at the back of the tongue.
Adenoids are lymphoid tissue located in the nasopharynx, in the midline at the back of the throat. The spleen is in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen. The spleen has a smooth surface, as it is covered by an outer capsule of connective tissue. The thymus is in the mediastinum between the lungs. The thymus is composed of two lobes containing multiple lobules divided into an outer cortex and an inner medulla. The thymus is the site of T-cell differentiation. Lymph nodes filter lymph and remove foreign particles. Lymph nodes are located throughout the body, and are concentrated in the neck, axilla, and groin.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What lymphoid organ is one of the primary sites of cancer metastasis?
What lymphoid organ is one of the primary sites of cancer metastasis?
Lymph nodes function to drain lymph. As lymph carries interstitial fluid, it also carries pathogens and cancer cells. Malignant cells may spread through the lymphatic circulation.
Tonsils and adenoids are collections of lymphoid tissue in the pharynx that filter microbes that enter through the mouth and nose. They enlarge during infectious processes. The spleen filters blood, exposing it to macrophages and lymphocytes that destroy foreign particles and aged blood cells. The thymus is the primary site for T-cell differentiation. The mature T-cells leave the thymus and travel to the spleen, lymph nodes, and other lymphoid tissue where they control cell-mediated immune responses.
Lymph nodes function to drain lymph. As lymph carries interstitial fluid, it also carries pathogens and cancer cells. Malignant cells may spread through the lymphatic circulation.
Tonsils and adenoids are collections of lymphoid tissue in the pharynx that filter microbes that enter through the mouth and nose. They enlarge during infectious processes. The spleen filters blood, exposing it to macrophages and lymphocytes that destroy foreign particles and aged blood cells. The thymus is the primary site for T-cell differentiation. The mature T-cells leave the thymus and travel to the spleen, lymph nodes, and other lymphoid tissue where they control cell-mediated immune responses.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The lymphoid tissues are responsible for creating, storing, and processing lymphocytes, which are essentially the effector cells of the immune system. Which of the following is a lymphoid structure that is also responsible for recycling old red blood cells?
The lymphoid tissues are responsible for creating, storing, and processing lymphocytes, which are essentially the effector cells of the immune system. Which of the following is a lymphoid structure that is also responsible for recycling old red blood cells?
The spleen is a lymphoid structure that contains resident lymphocytes that produce antiobodies, as well as T-cells that are released into the bloodstream. It also contains resident macrophages, which are responsible for removing and degrading microbes and worn-out red blood cells.
The spleen is a lymphoid structure that contains resident lymphocytes that produce antiobodies, as well as T-cells that are released into the bloodstream. It also contains resident macrophages, which are responsible for removing and degrading microbes and worn-out red blood cells.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is not a function of the lymphatic system?
Which of the following is not a function of the lymphatic system?
The liver is primarily responsible for the detoxification of the blood.
All other listed options are the primary roles of the lymphatic system. Digested fats are emulsified in the small intestine, then transported via lymph (rather than blood). They enter the blood stream through the subclavian vein. The lymph also contains a large number of lymphocytes, or white blood cells, which can screen for microbes. Excess interstitial fluid is transferred to the lymph via leaky capillaries. The thymus, a primary lymphoid organ, is responsible for T-cell maturation.
The liver is primarily responsible for the detoxification of the blood.
All other listed options are the primary roles of the lymphatic system. Digested fats are emulsified in the small intestine, then transported via lymph (rather than blood). They enter the blood stream through the subclavian vein. The lymph also contains a large number of lymphocytes, or white blood cells, which can screen for microbes. Excess interstitial fluid is transferred to the lymph via leaky capillaries. The thymus, a primary lymphoid organ, is responsible for T-cell maturation.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Type 1 diabetes is a well-understood autoimmune disease. Autoimmune diseases result from an immune system-mediated attack on one’s own body tissues. In normal development, an organ called the thymus introduces immune cells to the body’s normal proteins. This process is called negative selection, as those immune cells that recognize normal proteins are deleted. If cells evade this process, those that recognize normal proteins enter into circulation, where they can attack body tissues. The thymus is also important for activating T-cells that recognize foreign proteins.
As the figure below shows, immune cells typically originate in the bone marrow. Some immune cells, called T-cells, then go to the thymus for negative selection. Those that survive negative selection, enter into general circulation to fight infection. Other cells, called B-cells, directly enter general circulation from the bone marrow. It is a breakdown in this carefully orchestrated process that leads to autoimmune disease, such as type 1 diabetes.

B-cells are primarily activated in lymph nodes, similar in some respects to T-cell activation in the thymus. Which of the following is true of the lymphatic system?
I. It drains excess fluid from interstitial spaces
II. It has one-way valves similar to those in veins
III. It is actively pumped by skeletal muscle contraction
Type 1 diabetes is a well-understood autoimmune disease. Autoimmune diseases result from an immune system-mediated attack on one’s own body tissues. In normal development, an organ called the thymus introduces immune cells to the body’s normal proteins. This process is called negative selection, as those immune cells that recognize normal proteins are deleted. If cells evade this process, those that recognize normal proteins enter into circulation, where they can attack body tissues. The thymus is also important for activating T-cells that recognize foreign proteins.
As the figure below shows, immune cells typically originate in the bone marrow. Some immune cells, called T-cells, then go to the thymus for negative selection. Those that survive negative selection, enter into general circulation to fight infection. Other cells, called B-cells, directly enter general circulation from the bone marrow. It is a breakdown in this carefully orchestrated process that leads to autoimmune disease, such as type 1 diabetes.

B-cells are primarily activated in lymph nodes, similar in some respects to T-cell activation in the thymus. Which of the following is true of the lymphatic system?
I. It drains excess fluid from interstitial spaces
II. It has one-way valves similar to those in veins
III. It is actively pumped by skeletal muscle contraction
All of these statements are true of the lymphatic system. Without a dedicated pump of its own, it relies on skeletal muscle contraction in adjacent muscles and the presence of one-way valves to remove excess interstitial fluid and bring it to lymph nodes, where the immune system can be activated.
All of these statements are true of the lymphatic system. Without a dedicated pump of its own, it relies on skeletal muscle contraction in adjacent muscles and the presence of one-way valves to remove excess interstitial fluid and bring it to lymph nodes, where the immune system can be activated.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is not a function of the lymphatic system?
Which of the following is not a function of the lymphatic system?
The lymphatic system has many purposes, including draining the 10% of interstitial fluid that is not reabsorbed by the capillaries, housing the lymph nodes that produce B-cells, and serving as a migration site for macrophages that present antigens to B-cells to initiate an immune system reaction.
The bone marrow is responsible for producing red blood cells, and for allowing B-cells to mature.
The lymphatic system has many purposes, including draining the 10% of interstitial fluid that is not reabsorbed by the capillaries, housing the lymph nodes that produce B-cells, and serving as a migration site for macrophages that present antigens to B-cells to initiate an immune system reaction.
The bone marrow is responsible for producing red blood cells, and for allowing B-cells to mature.
Compare your answer with the correct one above