Functional Groups and Properties - MCAT Biology
Card 0 of 20
Drain cleaners are a common household staple, used to open clogged drains in bathtubs and sinks. Human hair is a common culprit that clogs pipes, and hair is made predominately of protein. Drain cleaners are effective at breaking down proteins that have accumulated in plumbing. Drain cleaners can be either acidic or basic, and are also effective at breaking down fats that have accumulated with proteins.
A typical reaction—reaction 1—which would be expected for a drain cleaner on contact with human hair, would be as follows in an aqueous solution:
Another reaction that may occur, reaction 2, would take place as follows in an aqueous solution:
The NH4 molecule produced in Reaction 2 must have __________.
Drain cleaners are a common household staple, used to open clogged drains in bathtubs and sinks. Human hair is a common culprit that clogs pipes, and hair is made predominately of protein. Drain cleaners are effective at breaking down proteins that have accumulated in plumbing. Drain cleaners can be either acidic or basic, and are also effective at breaking down fats that have accumulated with proteins.
A typical reaction—reaction 1—which would be expected for a drain cleaner on contact with human hair, would be as follows in an aqueous solution:
Another reaction that may occur, reaction 2, would take place as follows in an aqueous solution:
The NH4 molecule produced in Reaction 2 must have __________.
The additional H present on ammonia (NH3) requires the generation of the a positive charge on the molecule. This also must be created to balance the negative charge created on the associated anion product.
The additional H present on ammonia (NH3) requires the generation of the a positive charge on the molecule. This also must be created to balance the negative charge created on the associated anion product.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Drain cleaners a common household staple, used to open clogged drains in bathtubs and sinks. Human hair is a common culprit that clogs pipes, and hair is made predominately of protein. Drain cleaners are effective at breaking down proteins that have accumulated in plumbing. Drain cleaners can be either acidic or basic, and are also effective at breaking down fats that have accumulated with proteins.
A typical reaction—reaction 1—which would be expected for a drain cleaner on contact with human hair, would be as follows in an aqueous solution:
Another reaction that may occur, reaction 2, would take place as follows in an aqueous solution:
Compared to the organic compound produced in Reaction 2, an aldehyde __________.
Drain cleaners a common household staple, used to open clogged drains in bathtubs and sinks. Human hair is a common culprit that clogs pipes, and hair is made predominately of protein. Drain cleaners are effective at breaking down proteins that have accumulated in plumbing. Drain cleaners can be either acidic or basic, and are also effective at breaking down fats that have accumulated with proteins.
A typical reaction—reaction 1—which would be expected for a drain cleaner on contact with human hair, would be as follows in an aqueous solution:
Another reaction that may occur, reaction 2, would take place as follows in an aqueous solution:
Compared to the organic compound produced in Reaction 2, an aldehyde __________.
Aldehydes have lower acidity than carboxylic acids, but are more reduced and thus have higher overall bond energies.
Aldehydes have lower acidity than carboxylic acids, but are more reduced and thus have higher overall bond energies.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
Which of the following would be expected pKa values for carbonic acid and carbonate, respectively?
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
Which of the following would be expected pKa values for carbonic acid and carbonate, respectively?
Carbonic acid is a weak organic acid, not nearly as strong as most inorganic acids. It is still, however, an acid, and has a pKa below 7, but nowhere near as low as 1.4 * 10-14.
Carbonate is a conjugate base, and thus has an alkaline pKa around 10.3.
Carbonic acid is a weak organic acid, not nearly as strong as most inorganic acids. It is still, however, an acid, and has a pKa below 7, but nowhere near as low as 1.4 * 10-14.
Carbonate is a conjugate base, and thus has an alkaline pKa around 10.3.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
The deprotonation of carbonic acid is favored by __________.
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
The deprotonation of carbonic acid is favored by __________.
Bicarbonate is the product of deprotonation of carbonic acid. Anything that stabilizes this product will encourage the deprotonation reaction, and resonance is a key stabilizing factor for bicarbonate. Stability of the conjugate base is a major contributing factor to the strength of an acid and its ability to deprotonate.
Bicarbonate is the product of deprotonation of carbonic acid. Anything that stabilizes this product will encourage the deprotonation reaction, and resonance is a key stabilizing factor for bicarbonate. Stability of the conjugate base is a major contributing factor to the strength of an acid and its ability to deprotonate.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
If a mutation rendered carbonic anhydrase nonfunctional, CO2 would not be converted to carbonic acid. What is true of CO2?
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
If a mutation rendered carbonic anhydrase nonfunctional, CO2 would not be converted to carbonic acid. What is true of CO2?
CO2 is nonpolar, and thus is more soluble in a nonpolar solvent (like a membrane) than is a polar molecule (like carbonic acid).
The pi bonds between carbon and oxygen in carbon dioxide contribute to its nonpolar character, and prevent free rotation around the bonds.
CO2 is nonpolar, and thus is more soluble in a nonpolar solvent (like a membrane) than is a polar molecule (like carbonic acid).
The pi bonds between carbon and oxygen in carbon dioxide contribute to its nonpolar character, and prevent free rotation around the bonds.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
The carbonic acid buffer system is typical of most buffers. Which of the following is true of buffers?
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
The carbonic acid buffer system is typical of most buffers. Which of the following is true of buffers?
Buffers are typically acids best at keeping a system at a pH within one pH unit of their pKa when combined with equal and copious amounts of their conjugate base.
Buffers are typically acids best at keeping a system at a pH within one pH unit of their pKa when combined with equal and copious amounts of their conjugate base.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
Which of the following is true of carbonic acid?
I. It is diprotic
II. It is planar
III. It shows no net dipole moment
IV. It has approximately 109o bond angles
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
Which of the following is true of carbonic acid?
I. It is diprotic
II. It is planar
III. It shows no net dipole moment
IV. It has approximately 109o bond angles
Carbonic acid has a central sp2 carbon; thus, it is planar with approximately 120o bond angles. This carbonyl group also exhibits a strong dipole moment, and has hydrogens on both sides of the central carbon to donate in solution.
Carbonic acid has a central sp2 carbon; thus, it is planar with approximately 120o bond angles. This carbonyl group also exhibits a strong dipole moment, and has hydrogens on both sides of the central carbon to donate in solution.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the name of the functional group that contains a vinylic hydroxyl group?
What is the name of the functional group that contains a vinylic hydroxyl group?
Enol functional groups contain a hydroxyl group bonded to a carbon involved in a double bond with another carbon (vinyl carbon). An enol will usually undergo tautomerization to become a more stable keto.
Enol functional groups contain a hydroxyl group bonded to a carbon involved in a double bond with another carbon (vinyl carbon). An enol will usually undergo tautomerization to become a more stable keto.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
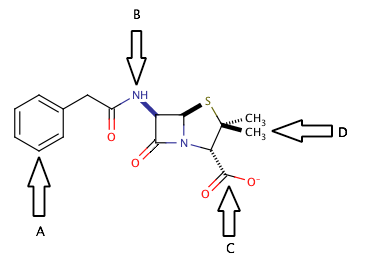
The correct answer is arrow B. An amide group is a carbonyl group with a nitrogen that is in the alpha position (directly attached to the carbonyl carbon). Penicillin has two different amide groups in its chemical structure, but only one has an arrow pointing to it in the diagram. Arrow B points to a primary secondary amide, bond to one hydrogen and two carbons. The other amide in the molecule is a tertiary amide, bond to three carbons and no hydrogens.
The correct answer is arrow B. An amide group is a carbonyl group with a nitrogen that is in the alpha position (directly attached to the carbonyl carbon). Penicillin has two different amide groups in its chemical structure, but only one has an arrow pointing to it in the diagram. Arrow B points to a primary secondary amide, bond to one hydrogen and two carbons. The other amide in the molecule is a tertiary amide, bond to three carbons and no hydrogens.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Ephedrine, whose structure is shown below, is used commonly as a stimulant and decongestant.

Ephedrine contains all of the following functional groups except __________.
Ephedrine, whose structure is shown below, is used commonly as a stimulant and decongestant.

Ephedrine contains all of the following functional groups except __________.
Ephedrine contains an arene (the aromatic benzene ring), an alcohol (the -OH group), an amine (the nitrogen-based group), and an N-methyl group (-CH3 attached to nitrogen). It does not contain a ketone (C=O), or any other carboxyl groups.
Ephedrine contains an arene (the aromatic benzene ring), an alcohol (the -OH group), an amine (the nitrogen-based group), and an N-methyl group (-CH3 attached to nitrogen). It does not contain a ketone (C=O), or any other carboxyl groups.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Ephedrine (shown below) contains what type of amine?

Ephedrine (shown below) contains what type of amine?

A secondary amine is an amine (nitrogen atom) that is attached to two carbon-containing groups (alkyl groups or aryl groups). The nitrogen in ephedrine is attached to two alkyl groups, making it a secondary amine.
Primary amines are generally written as  . Secondary amines are generally written as
. Secondary amines are generally written as  . A tertiary amine will be bound to three different R-groups. Quaternary amines require a positive charge on the nitrogen atom to accommodate a fourth R-group.
. A tertiary amine will be bound to three different R-groups. Quaternary amines require a positive charge on the nitrogen atom to accommodate a fourth R-group.
A secondary amine is an amine (nitrogen atom) that is attached to two carbon-containing groups (alkyl groups or aryl groups). The nitrogen in ephedrine is attached to two alkyl groups, making it a secondary amine.
Primary amines are generally written as 

Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following functional groups would most likely act as an acid?
Which of the following functional groups would most likely act as an acid?
Carboxyl groups, or carboxylic acids, are good acids due to the resonance between the two oxygen atoms, allowing for greater stability of the conjugate base upon removal of a proton. Acetals and aldehydes can act as weak acids, but carboxyl groups will be deprotonated first.
Carboxyl groups, or carboxylic acids, are good acids due to the resonance between the two oxygen atoms, allowing for greater stability of the conjugate base upon removal of a proton. Acetals and aldehydes can act as weak acids, but carboxyl groups will be deprotonated first.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Your lab isolates a compound with the formula  . Upon further analysis, you determine that the base structure is a benzene ring with a single constituent. Which of the following could be the identity of the compound?
. Upon further analysis, you determine that the base structure is a benzene ring with a single constituent. Which of the following could be the identity of the compound?
Your lab isolates a compound with the formula 
Nitro groups and amide groups both contain oxygen components, and cannot be found in the compound described. We also know that the benzene ring only has a single constituent, meaning that it cannot be a methylamine. The compound must be benzylamine, a benzene ring with a -CH2NH2 substituent.
Nitro groups and amide groups both contain oxygen components, and cannot be found in the compound described. We also know that the benzene ring only has a single constituent, meaning that it cannot be a methylamine. The compound must be benzylamine, a benzene ring with a -CH2NH2 substituent.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Compound A, shown below, contains an example of what type of functional group?

Compound A, shown below, contains an example of what type of functional group?

Esters have the general molecular formula of  , where
, where  and
and  are carbon groups. The rightmost region of compound A shows an ester.
are carbon groups. The rightmost region of compound A shows an ester.
Ketones have the formula of  , with a carbon-oxygen double bond. Ethers have the formula of
, with a carbon-oxygen double bond. Ethers have the formula of  , with an oxygen linked by single bonds within a carbon chain. An ester resembles adjacent ketone and ether groups. Carboxylic acids have the formula
, with an oxygen linked by single bonds within a carbon chain. An ester resembles adjacent ketone and ether groups. Carboxylic acids have the formula  , resembling an ester with a hydrogen in place of a second carbon chain. Finally, the nitrile group has a formula of
, resembling an ester with a hydrogen in place of a second carbon chain. Finally, the nitrile group has a formula of  , with a triple bond between nitrogen and carbon.
, with a triple bond between nitrogen and carbon.
Compound A also contains an aromatic function group (the benzene ring) and a nitro group,  , on the far left side.
, on the far left side.
Esters have the general molecular formula of 


Ketones have the formula of 



Compound A also contains an aromatic function group (the benzene ring) and a nitro group, 
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following statements about amide bonds is NOT true?
Which of the following statements about amide bonds is NOT true?
Amides have a structure of a ketone group adjacent to an amine group.
In an amide bond, all of the atoms (the nitrogen, the carbonyl oxygen, and carbonyl carbon) are  hybridized because of resonance; the lone pair on nitrogen can delocalize into the carbonyl pi bond. The amide bond is polar, mildly acidic, with a secondary amide having the structure shown. Finally, amides are often formed by a condensation reaction between a carboxylic acid and an amine, which produces water as a byproduct.
hybridized because of resonance; the lone pair on nitrogen can delocalize into the carbonyl pi bond. The amide bond is polar, mildly acidic, with a secondary amide having the structure shown. Finally, amides are often formed by a condensation reaction between a carboxylic acid and an amine, which produces water as a byproduct.
Amides have a structure of a ketone group adjacent to an amine group.
In an amide bond, all of the atoms (the nitrogen, the carbonyl oxygen, and carbonyl carbon) are 
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Carboxylic acids typically have higher boiling points than aldehydes and ketones. This is because carboxylic acids have which of the following properties?
Carboxylic acids typically have higher boiling points than aldehydes and ketones. This is because carboxylic acids have which of the following properties?
Carboxylic acids are able to create hydrogen bonds with one another. This forms a dimer, which doubles the effective molecular weight and greatly increases the boiling point of carboxylic acids. Aldehydes and ketones are not able to form hydrogen bonds with one another, so their boiling points are dependent on each individual molecule's molecular weight. As a result, their boiling points are not as high as the corresponding carboxylic acids'. Note that carboxylic acids cannot form intramolecular hydrogen bonds.
Carboxylic acids are able to create hydrogen bonds with one another. This forms a dimer, which doubles the effective molecular weight and greatly increases the boiling point of carboxylic acids. Aldehydes and ketones are not able to form hydrogen bonds with one another, so their boiling points are dependent on each individual molecule's molecular weight. As a result, their boiling points are not as high as the corresponding carboxylic acids'. Note that carboxylic acids cannot form intramolecular hydrogen bonds.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following compounds will be the most reactive with an alcohol to form an ester product?
Which of the following compounds will be the most reactive with an alcohol to form an ester product?
All of the options, except for the carboxylic acid itself, are derivatives of a carboxylic acid. These derivatives differ in their reactivity when creating new compounds. Acid chlorides are the most reactive compounds, and amides are the least reactive out of these option. Acid chlorides and acid anhydrides frequently participate in reactions, while amides are less likely to react.
All of the options, except for the carboxylic acid itself, are derivatives of a carboxylic acid. These derivatives differ in their reactivity when creating new compounds. Acid chlorides are the most reactive compounds, and amides are the least reactive out of these option. Acid chlorides and acid anhydrides frequently participate in reactions, while amides are less likely to react.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following compounds would you expect to undergo a nucleophilic addition reaction?
Which of the following compounds would you expect to undergo a nucleophilic addition reaction?
When dealing with carbonyl compounds, remember that a carboxylic acid and all of its derivatives will undergo nucleophilic substitution. Aldehydes and ketones will undergo nucleophilic addition. Propanal is a three-carbon aldehyde, and will thus undergo nucleophilic addition.
Acetic acid is a carboxylic acid, methyl ethanoate is an ether, and ethanamide is an amide; each of these would undergo nucleophilic substitution.
When dealing with carbonyl compounds, remember that a carboxylic acid and all of its derivatives will undergo nucleophilic substitution. Aldehydes and ketones will undergo nucleophilic addition. Propanal is a three-carbon aldehyde, and will thus undergo nucleophilic addition.
Acetic acid is a carboxylic acid, methyl ethanoate is an ether, and ethanamide is an amide; each of these would undergo nucleophilic substitution.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
In the reaction scheme below, compound A is a(n) __________ and compound B is a(n) __________.

In the reaction scheme below, compound A is a(n) __________ and compound B is a(n) __________.

Ketones, like compound A, contain an internal carbon-oxygen double bond. Alcohols, like compound B, contain a hydroxyl group (-OH). In this case, compound A is a secondary ketone and compound B is a tertiary alcohol.
Alkenes, like compound C, contain a carbon-carbon double bond.
Ketones, like compound A, contain an internal carbon-oxygen double bond. Alcohols, like compound B, contain a hydroxyl group (-OH). In this case, compound A is a secondary ketone and compound B is a tertiary alcohol.
Alkenes, like compound C, contain a carbon-carbon double bond.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A pentane molecule with which of the following functional groups will have a higher boiling point than an aldehyde of similar size?
A pentane molecule with which of the following functional groups will have a higher boiling point than an aldehyde of similar size?
Boiling point is strongly influenced by the ability of a molecule to interact with other molecules in solution (intermolecular forces). Since hydrogen bonds are the strongest intermolecular force, we are ideally looking for a functional group that will be able to form hydrogen bonds.
Alkanes and alkenes are both nonpolar and cannot form hydrogen bonds, so their boiling points are very low. Esters lack a polar hydrogen and cannot hydrogen bond with other molecules.
Alcohols, on the other hand, have a hydroxyl group that is capable of hydrogen bonding with other molecules. This gives alcohols higher boiling points than aldehydes of similar size.
Boiling point is strongly influenced by the ability of a molecule to interact with other molecules in solution (intermolecular forces). Since hydrogen bonds are the strongest intermolecular force, we are ideally looking for a functional group that will be able to form hydrogen bonds.
Alkanes and alkenes are both nonpolar and cannot form hydrogen bonds, so their boiling points are very low. Esters lack a polar hydrogen and cannot hydrogen bond with other molecules.
Alcohols, on the other hand, have a hydroxyl group that is capable of hydrogen bonding with other molecules. This gives alcohols higher boiling points than aldehydes of similar size.
Compare your answer with the correct one above