Enzymes and Enzyme Inhibition - MCAT Biology
Card 0 of 20
The end product of an enzymatic reaction inhibits formation of product in an earlier step. This type of enzymatic regulation is known as __________.
The end product of an enzymatic reaction inhibits formation of product in an earlier step. This type of enzymatic regulation is known as __________.
Feedback inhibition is a type of regulation in which an enzyme product blocks an earlier part of a metabolic reaction. This allows cells to regulate resources by signaling when enough product is made.
Feedback inhibition is a type of regulation in which an enzyme product blocks an earlier part of a metabolic reaction. This allows cells to regulate resources by signaling when enough product is made.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
An unknown molecule is added to an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, immediately decreasing its rate. If the addition of more substrate has no effect, but the addition of an antibody for the unknown molecule restores the initial reaction rate, what form of inhibition is most likely occurring?
An unknown molecule is added to an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, immediately decreasing its rate. If the addition of more substrate has no effect, but the addition of an antibody for the unknown molecule restores the initial reaction rate, what form of inhibition is most likely occurring?
This question is referring specifically to the different modes of enzyme inhibition. The given fact that increasing substrate concentration does not restore enzyme function indicates that the inhibitor is binding to the enzyme at an allosteric site (eliminating competitive inhibition). The given fact that inhibitor-specific antibodies restored enzyme function indicates that the inhibition is reversible.
Uncompetitive inhibition is a specific type of noncompetitive inhibition in which the inhibitior binds to the enzyme-substrate complex. We are unable to conclude that this is the case based on the given information alone.
This question is referring specifically to the different modes of enzyme inhibition. The given fact that increasing substrate concentration does not restore enzyme function indicates that the inhibitor is binding to the enzyme at an allosteric site (eliminating competitive inhibition). The given fact that inhibitor-specific antibodies restored enzyme function indicates that the inhibition is reversible.
Uncompetitive inhibition is a specific type of noncompetitive inhibition in which the inhibitior binds to the enzyme-substrate complex. We are unable to conclude that this is the case based on the given information alone.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy is an X-linked recessive genetic disorder, resulting in the loss of the dystrophin protein. In healthy muscle, dystrophin localizes to the sarcolemma and helps anchor the muscle fiber to the basal lamina. The loss of this protein results in progressive muscle weakness, and eventually death.
In the muscle fibers, the effects of the disease can be exacerbated by auto-immune interference. Weakness of the sarcolemma leads to damage and tears in the membrane. The body’s immune system recognizes the damage and attempts to repair it; however, since the damage exists as a chronic condition, leukocytes begin to present the damaged protein fragments as antigens, stimulating a targeted attack on the damaged parts of the muscle fiber. The attack causes inflammation, fibrosis, and necrosis, further weakening the muscle.
Studies have shown that despite the severe pathology of the muscle fibers, the innervation of the muscle is unaffected.
Which of the following would best describe the dystrophin protein?
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy is an X-linked recessive genetic disorder, resulting in the loss of the dystrophin protein. In healthy muscle, dystrophin localizes to the sarcolemma and helps anchor the muscle fiber to the basal lamina. The loss of this protein results in progressive muscle weakness, and eventually death.
In the muscle fibers, the effects of the disease can be exacerbated by auto-immune interference. Weakness of the sarcolemma leads to damage and tears in the membrane. The body’s immune system recognizes the damage and attempts to repair it; however, since the damage exists as a chronic condition, leukocytes begin to present the damaged protein fragments as antigens, stimulating a targeted attack on the damaged parts of the muscle fiber. The attack causes inflammation, fibrosis, and necrosis, further weakening the muscle.
Studies have shown that despite the severe pathology of the muscle fibers, the innervation of the muscle is unaffected.
Which of the following would best describe the dystrophin protein?
The passage tells us that "dystrophin localizes to the sarcolemma," so we know it is located at the membrane of the muscle fiber. We also know that its role is to structurally link the muscle fiber and the basal lamina. We can eliminate the choices for ion channel, signaling protein, and chemical receptor based on what we know about dystrophin's function. We are left with either fibrous protein or transmembrane protein. Though fibrous proteins also have structural roles, transmembrane protein is the best choice because we know that dystrophin is linking the muscle fiber to another structure, meaning that it must span the membrane.
The passage tells us that "dystrophin localizes to the sarcolemma," so we know it is located at the membrane of the muscle fiber. We also know that its role is to structurally link the muscle fiber and the basal lamina. We can eliminate the choices for ion channel, signaling protein, and chemical receptor based on what we know about dystrophin's function. We are left with either fibrous protein or transmembrane protein. Though fibrous proteins also have structural roles, transmembrane protein is the best choice because we know that dystrophin is linking the muscle fiber to another structure, meaning that it must span the membrane.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Of the following statements, which is true regarding the change in free energy (ΔG) of a reaction?
Of the following statements, which is true regarding the change in free energy (ΔG) of a reaction?
Gibbs Free Energy (G) is a measure of the capacity of a system to do useful work as it proceeds to equilibrium. ΔG measures the spontaneity of a reaction; a negative value for ΔG indicates a spontaneous reaction, a positive value indicates a non-spontaneous reaction, and a value of zero indicates a reaction at equilibrium. ΔG does not predict enzyme kinetics; it only predicts thermodynamics, thus, two of the answers are correct.
Gibbs Free Energy (G) is a measure of the capacity of a system to do useful work as it proceeds to equilibrium. ΔG measures the spontaneity of a reaction; a negative value for ΔG indicates a spontaneous reaction, a positive value indicates a non-spontaneous reaction, and a value of zero indicates a reaction at equilibrium. ΔG does not predict enzyme kinetics; it only predicts thermodynamics, thus, two of the answers are correct.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Drain cleaners a common household staple, used to open clogged drains in bathtubs and sinks. Human hair is a common culprit that clogs pipes, and hair is made predominately of protein. Drain cleaners are effective at breaking down proteins that have accumulated in plumbing. Drain cleaners can be either acidic or basic, and are also effective at breaking down fats that have accumulated with proteins.
A typical reaction—reaction 1—which would be expected for a drain cleaner on contact with human hair, would be as follows in an aqueous solution:
Another reaction that may occur, reaction 2, would take place as follows in an aqueous solution:
Protein that forms the hair discussed in the preceeding passage is considered strucutral protein. Functional proteins, such as enzymes, are the other major class. Which of the following is true of enzymes?
Drain cleaners a common household staple, used to open clogged drains in bathtubs and sinks. Human hair is a common culprit that clogs pipes, and hair is made predominately of protein. Drain cleaners are effective at breaking down proteins that have accumulated in plumbing. Drain cleaners can be either acidic or basic, and are also effective at breaking down fats that have accumulated with proteins.
A typical reaction—reaction 1—which would be expected for a drain cleaner on contact with human hair, would be as follows in an aqueous solution:
Another reaction that may occur, reaction 2, would take place as follows in an aqueous solution:
Protein that forms the hair discussed in the preceeding passage is considered strucutral protein. Functional proteins, such as enzymes, are the other major class. Which of the following is true of enzymes?
Enzymes are biological catalysts that function to lower activation energy via an alternative reaction pathway. They never alter the equilibrium of the reaction they impact.
Enzymes are biological catalysts that function to lower activation energy via an alternative reaction pathway. They never alter the equilibrium of the reaction they impact.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Drain cleaners a common household staple, used to open clogged drains in bathtubs and sinks. Human hair is a common culprit that clogs pipes, and hair is made predominately of protein. Drain cleaners are effective at breaking down proteins that have accumulated in plumbing. Drain cleaners can be either acidic or basic, and are also effective at breaking down fats that have accumulated with proteins.
A typical reaction—reaction 1—which would be expected for a drain cleaner on contact with human hair, would be as follows in an aqueous solution:
Another reaction that may occur, reaction 2, would take place as follows in an aqueous solution:
Protein that forms the hair discussed in the preceeding passage is considered strucutral protein. Functional proteins, such as enzymes, are the other major class. Which of the following is expected in an enzymatic biological reaction?
I. Faster rate than non-enzymatic reaction
II. Enzymatic coupling to hydrolysis reactions
III. More product generation relative to amount of reactant than non-enzymatic reaction
Drain cleaners a common household staple, used to open clogged drains in bathtubs and sinks. Human hair is a common culprit that clogs pipes, and hair is made predominately of protein. Drain cleaners are effective at breaking down proteins that have accumulated in plumbing. Drain cleaners can be either acidic or basic, and are also effective at breaking down fats that have accumulated with proteins.
A typical reaction—reaction 1—which would be expected for a drain cleaner on contact with human hair, would be as follows in an aqueous solution:
Another reaction that may occur, reaction 2, would take place as follows in an aqueous solution:
Protein that forms the hair discussed in the preceeding passage is considered strucutral protein. Functional proteins, such as enzymes, are the other major class. Which of the following is expected in an enzymatic biological reaction?
I. Faster rate than non-enzymatic reaction
II. Enzymatic coupling to hydrolysis reactions
III. More product generation relative to amount of reactant than non-enzymatic reaction
Enzymatic reactions will always proceed faster than if there was no enzyme present. They will also often be coupled to hydrolysis reactions to drive them forward thermodynamically, such as ATP hyrodlysis to make an otherwise unfavorable reaction proceed. The equilibrium constant of an enzymatic reaction is never different than the constant for the same reaction without enyzme, however, and thus choice III is incorrect.
Enzymatic reactions will always proceed faster than if there was no enzyme present. They will also often be coupled to hydrolysis reactions to drive them forward thermodynamically, such as ATP hyrodlysis to make an otherwise unfavorable reaction proceed. The equilibrium constant of an enzymatic reaction is never different than the constant for the same reaction without enyzme, however, and thus choice III is incorrect.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A student observes an enzymatic chemical reaction that normally takes place in human blood. She performs an experiment to see how certain conditions affect the reaction with the enzyme fully saturated with substrate. What should she do to speed the reaction up?
A student observes an enzymatic chemical reaction that normally takes place in human blood. She performs an experiment to see how certain conditions affect the reaction with the enzyme fully saturated with substrate. What should she do to speed the reaction up?
Adding more enzyme is the only way to make this reaction proceed faster. Since this is a reaction that takes place in the blood, the optimal conditions are 37 degrees Celsius and a pH of 7.4. Adding more substrate could help in certain conditions, but we know from the question that there is no free enzyme in the reaction so adding more would not help. Removing enzyme would obviously sow the reaction down.
Adding more enzyme is the only way to make this reaction proceed faster. Since this is a reaction that takes place in the blood, the optimal conditions are 37 degrees Celsius and a pH of 7.4. Adding more substrate could help in certain conditions, but we know from the question that there is no free enzyme in the reaction so adding more would not help. Removing enzyme would obviously sow the reaction down.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
In order to catalyze a reaction, an enzyme is required to __________.
In order to catalyze a reaction, an enzyme is required to __________.
Enzymes are biological catalysts that are responsible for the acceleration of the rate and specificity of many metabolic reactions. In order for rate acceleration to occur, an enzyme lowers the activation energy of a reaction. This allows for products to be formed more quickly and reactions to reach equilibrium more rapidly. Substrates bind to the active site of an enzyme and, in the presence of a large concentration of substrate, enzyme active sites become saturated and the reaction rate reaches a maximum constant. The equilibrium constant is calculated from the expression for chemical equilibrium, and is not affected by enzymes. Thus, the correct answer is to decrease the activation energy.
Enzymes are biological catalysts that are responsible for the acceleration of the rate and specificity of many metabolic reactions. In order for rate acceleration to occur, an enzyme lowers the activation energy of a reaction. This allows for products to be formed more quickly and reactions to reach equilibrium more rapidly. Substrates bind to the active site of an enzyme and, in the presence of a large concentration of substrate, enzyme active sites become saturated and the reaction rate reaches a maximum constant. The equilibrium constant is calculated from the expression for chemical equilibrium, and is not affected by enzymes. Thus, the correct answer is to decrease the activation energy.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Fetal hemoglobin has a higher binding affinity for oxygen than does adult hemoglobin.
In comparison to the adult oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve, the fetal oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve will __________.
Fetal hemoglobin has a higher binding affinity for oxygen than does adult hemoglobin.
In comparison to the adult oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve, the fetal oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve will __________.
Fetal hemoglobin is associated with a left-shift due to its greater binding affinity for oxygen. The Michaelis constant, Km, is defined as the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is 0.5 * Vmax. A low Km indicates high substrate affinity.
Fetal hemoglobin is associated with a left-shift due to its greater binding affinity for oxygen. The Michaelis constant, Km, is defined as the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is 0.5 * Vmax. A low Km indicates high substrate affinity.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is NOT a class of enzyme?
Which of the following is NOT a class of enzyme?
The correct answer is pyrimidine complex. A pyrimidine refers to a type of nucleotide base. Enzymes commonly have the suffix -ase at the end of their name.
The correct answer is pyrimidine complex. A pyrimidine refers to a type of nucleotide base. Enzymes commonly have the suffix -ase at the end of their name.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Functions of enzymes include all of the following except __________.
Functions of enzymes include all of the following except __________.
Enzymes are unable to shift the equilibrium of a reaction. This is a commonly confused enzyme concept, but it should be known that, chemically speaking, only adding or removing reactants and/or products can shift the equilibrium of a reaction. Although this concept is mainly seen in chemisty, known as Le Chatelier's principle, this principle is surprisingly helpful and applicable to many fields of science, including biology. All other answer choices are functions of enzymes.
Enzymes are unable to shift the equilibrium of a reaction. This is a commonly confused enzyme concept, but it should be known that, chemically speaking, only adding or removing reactants and/or products can shift the equilibrium of a reaction. Although this concept is mainly seen in chemisty, known as Le Chatelier's principle, this principle is surprisingly helpful and applicable to many fields of science, including biology. All other answer choices are functions of enzymes.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A pathway of reversible enzymatic reactions is given below. Enzymes are denoted by letters, and products by numbers.




If the enzyme C is blocked by an allosteric inhibitor, what will happen to each of the products?
A pathway of reversible enzymatic reactions is given below. Enzymes are denoted by letters, and products by numbers.
If the enzyme C is blocked by an allosteric inhibitor, what will happen to each of the products?
All upstream products, prior to the action of enzyme C, will start to increase in concentration because each enzyme is reversible. Directly, product 3 will build up and product 4 will decrease. This will lead product 5 to decrease because there is no 4 to make it. As 3 builds up, enzyme B will start working in reverse, converting it back into product 2, according to Le Chatelier's principle. Then, when 2 starts to build up, it will also be converted backwards into product 1.
All upstream products, prior to the action of enzyme C, will start to increase in concentration because each enzyme is reversible. Directly, product 3 will build up and product 4 will decrease. This will lead product 5 to decrease because there is no 4 to make it. As 3 builds up, enzyme B will start working in reverse, converting it back into product 2, according to Le Chatelier's principle. Then, when 2 starts to build up, it will also be converted backwards into product 1.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following would most greatly increase the activity of an enzyme functioning in the small intestine?
Which of the following would most greatly increase the activity of an enzyme functioning in the small intestine?
The rate of enzymatic activity can be increased in a few ways. Enzymes have optimal levels of acidity and temperature at which they function best. If this optimal level is exceeded, the enzyme will denature. Enzymes of the small intestine are adjusted to a relatively alkaline environment and will denature in acidic environments. Decreasing the temperature would decrease the rate of catalyzation. By increasing the amount of substrate, the enzyme will function faster. The level at which an enzyme's rate of catalyzation can no longer be made faster by the addition of substrate is referred to as its Vmax.
The rate of enzymatic activity can be increased in a few ways. Enzymes have optimal levels of acidity and temperature at which they function best. If this optimal level is exceeded, the enzyme will denature. Enzymes of the small intestine are adjusted to a relatively alkaline environment and will denature in acidic environments. Decreasing the temperature would decrease the rate of catalyzation. By increasing the amount of substrate, the enzyme will function faster. The level at which an enzyme's rate of catalyzation can no longer be made faster by the addition of substrate is referred to as its Vmax.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
Carbonic anhydrase is an organic enzyme. Which of the following is true of carbonic anhydrase? Assume no CO2 or bicarbonate is lost in the reaction.
I. It lowers the activation energy for the conversion of carbon dioxide to carbonic acid
II. It shifts the equilibrium toward carbon dioxide in experimental conditions
III. It modifies chemical species at its allosteric site
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
Carbonic anhydrase is an organic enzyme. Which of the following is true of carbonic anhydrase? Assume no CO2 or bicarbonate is lost in the reaction.
I. It lowers the activation energy for the conversion of carbon dioxide to carbonic acid
II. It shifts the equilibrium toward carbon dioxide in experimental conditions
III. It modifies chemical species at its allosteric site
Only choice I is correct. Carbonic anhydrase lowers the activation energy of a chemical reaction, as does any catalyst. Thermodynamics, including equilibria, are not modified by catalysts, so choice II is incorrect. Choice III is also incorrect, as an allosteric site is typically used to bind regulators of enzymes to induce conformational changes, while an active site would be where the actual catalysis takes place.
Only choice I is correct. Carbonic anhydrase lowers the activation energy of a chemical reaction, as does any catalyst. Thermodynamics, including equilibria, are not modified by catalysts, so choice II is incorrect. Choice III is also incorrect, as an allosteric site is typically used to bind regulators of enzymes to induce conformational changes, while an active site would be where the actual catalysis takes place.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
Carbonic anhydrase exhibits typical enzyme kinetics expected of similar enzymes. Which of the following is the quantity described by the value Km?
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
Carbonic anhydrase exhibits typical enzyme kinetics expected of similar enzymes. Which of the following is the quantity described by the value Km?
Reaction rates are generally impacted by the concentration of the reactants in the reaction. The Km is the amount of substrate needed to attain a concentration resulting in half of the maximum rate achievable by an ezyme catalyzed reaction.
The maximum rate will be limited by the number of enzyme moleules available, and will be reached when the enzyme active sites are saturated.
Reaction rates are generally impacted by the concentration of the reactants in the reaction. The Km is the amount of substrate needed to attain a concentration resulting in half of the maximum rate achievable by an ezyme catalyzed reaction.
The maximum rate will be limited by the number of enzyme moleules available, and will be reached when the enzyme active sites are saturated.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
A protein is discovered that inhibits carbonic anhydrase activity. It does so by reversibly binding to the active site typically occupied by carbonic acid and thus preventing carbonic acid from binding. This would most likely be what kind of inhibitor?
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
A protein is discovered that inhibits carbonic anhydrase activity. It does so by reversibly binding to the active site typically occupied by carbonic acid and thus preventing carbonic acid from binding. This would most likely be what kind of inhibitor?
Reversible binding in the active site is typical of a competitive inhibitor. Other kinds of inhibitors bind to the active site after the normal substrate has already bound, such as in uncompetitive inhibition. Alternatively, allosteric inhibitors can bind to sites other than the active site and induce a shape change that diminishes affinity for the typical substrate.
Reversible binding in the active site is typical of a competitive inhibitor. Other kinds of inhibitors bind to the active site after the normal substrate has already bound, such as in uncompetitive inhibition. Alternatively, allosteric inhibitors can bind to sites other than the active site and induce a shape change that diminishes affinity for the typical substrate.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A student is conducting an experiment in which he adds an inhibitor to an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. When the student first adds the inhibitor, the reaction rate decreases, however, he can return the reaction rate to normal by adding a large quantity of substrate. What type of inhibitor is the student using?
A student is conducting an experiment in which he adds an inhibitor to an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. When the student first adds the inhibitor, the reaction rate decreases, however, he can return the reaction rate to normal by adding a large quantity of substrate. What type of inhibitor is the student using?
Only competitive inhibition can be overcome by the addition of more substrate. Competitive inhibitors work by binding to and blocking the enzyme's active site. If more substrate is added, it increases the chance that an enzyme molecule will bind to the substrate instead of the inhibitor. Noncompetitive inhibition is not affected by the amount of substrate, uncompetitive inhibition is not tested on the MCAT, and "substrate-sensitive" is not a type of inhibition.
Only competitive inhibition can be overcome by the addition of more substrate. Competitive inhibitors work by binding to and blocking the enzyme's active site. If more substrate is added, it increases the chance that an enzyme molecule will bind to the substrate instead of the inhibitor. Noncompetitive inhibition is not affected by the amount of substrate, uncompetitive inhibition is not tested on the MCAT, and "substrate-sensitive" is not a type of inhibition.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Scientists use a process called Flourescent In-Situ Hybridization, or FISH, to study genetic disorders in humans. FISH is a technique that uses spectrographic analysis to determine the presence or absence, as well as the relative abundance, of genetic material in human cells.
To use FISH, scientists apply fluorescently-labeled bits of DNA of a known color, called probes, to samples of test DNA. These probes anneal to the sample DNA, and scientists can read the colors that result using laboratory equipment. One common use of FISH is to determine the presence of extra DNA in conditions of aneuploidy, a state in which a human cell has an abnormal number of chromosomes. Chromosomes are collections of DNA, the totality of which makes up a cell’s genome. Another typical use is in the study of cancer cells, where scientists use FISH labels to ascertain if genes have moved inappropriately in a cell’s genome.
Using red fluorescent tags, scientists label probe DNA for a gene known to be expressed more heavily in cancer cells than normal cells. They then label a probe for an immediately adjacent DNA sequence with a green fluorescent tag. Both probes are then added to three dishes, shown below. In dish 1 human bladder cells are incubated with the probes, in dish 2 human epithelial cells are incubated, and in dish 3 known non-cancerous cells are used. The relative luminescence observed in regions of interest in all dishes is shown below.
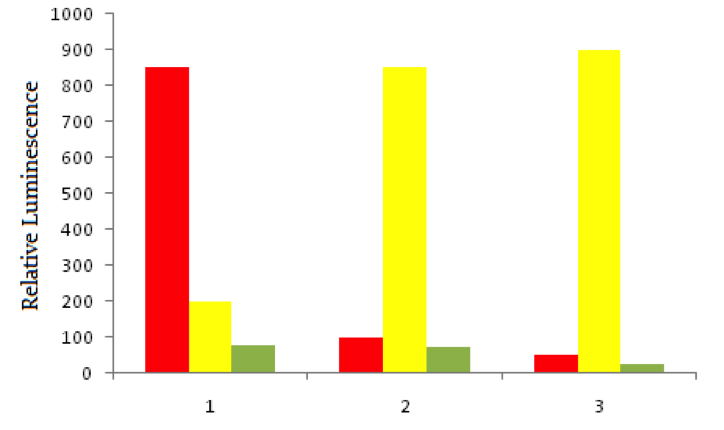
Cancer cells often invade by breaking through the collagen of a basement membrane of epithelial tissue. Considering the composition of basement membranes, which of the following compounds is most likely to be used by cancer cells for this purpose?
Scientists use a process called Flourescent In-Situ Hybridization, or FISH, to study genetic disorders in humans. FISH is a technique that uses spectrographic analysis to determine the presence or absence, as well as the relative abundance, of genetic material in human cells.
To use FISH, scientists apply fluorescently-labeled bits of DNA of a known color, called probes, to samples of test DNA. These probes anneal to the sample DNA, and scientists can read the colors that result using laboratory equipment. One common use of FISH is to determine the presence of extra DNA in conditions of aneuploidy, a state in which a human cell has an abnormal number of chromosomes. Chromosomes are collections of DNA, the totality of which makes up a cell’s genome. Another typical use is in the study of cancer cells, where scientists use FISH labels to ascertain if genes have moved inappropriately in a cell’s genome.
Using red fluorescent tags, scientists label probe DNA for a gene known to be expressed more heavily in cancer cells than normal cells. They then label a probe for an immediately adjacent DNA sequence with a green fluorescent tag. Both probes are then added to three dishes, shown below. In dish 1 human bladder cells are incubated with the probes, in dish 2 human epithelial cells are incubated, and in dish 3 known non-cancerous cells are used. The relative luminescence observed in regions of interest in all dishes is shown below.

Cancer cells often invade by breaking through the collagen of a basement membrane of epithelial tissue. Considering the composition of basement membranes, which of the following compounds is most likely to be used by cancer cells for this purpose?
The basement membrane and sub-basement structures are predominately made of protein (connective tissue). To infiltrate this region, a protease would be most appropriate. The remaining choices are all enzymes, but would not be capable of digesting appropriate proteins.
The basement membrane and sub-basement structures are predominately made of protein (connective tissue). To infiltrate this region, a protease would be most appropriate. The remaining choices are all enzymes, but would not be capable of digesting appropriate proteins.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Hemoglobin is the principal oxygen-carrying protein in humans. It exists within erythrocytes, and binds up to four diatomic oxygen molecules simultaneously. Hemoglobin functions to maximize oxygen delivery to tissues, while simultaneously maximizing oxygen absorption in the lungs. Hemoglobin thus has a fundamentally contradictory set of goals. It must at once be optimized to absorb oxygen, and to offload oxygen. Natural selection has overcome this apparent contradiction by making hemoglobin exquisitely sensitive to conditions in its microenvironment.
One way in which hemoglobin accomplishes its goals is through the phenomenon of cooperativity. Cooperativity refers to the ability of hemoglobin to change its oxygen binding behavior as a function of how many other oxygen atoms are bound to the molecule.
Fetal hemoglobin shows a similar pattern of cooperativity, but has unique binding characteristics relative to adult hemoglobin. Fetal hemoglobin reaches higher saturation at lower oxygen partial pressure.
Because of cooperativity, adult and fetal oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curves appear as follows.

Beyond its ability to carry oxygen, hemoglobin is also effective as a blood buffer. The general reaction for the blood buffer system of hemoglobin is given below.
H+ + HbO2 ←→ H+Hb + O2
The observed cooperativity of oxygen binding to hemoglobin can be explained by changes in shape to the hemoglobin molecule upon oxygen attachment. What kind of change would this be considered?
Hemoglobin is the principal oxygen-carrying protein in humans. It exists within erythrocytes, and binds up to four diatomic oxygen molecules simultaneously. Hemoglobin functions to maximize oxygen delivery to tissues, while simultaneously maximizing oxygen absorption in the lungs. Hemoglobin thus has a fundamentally contradictory set of goals. It must at once be optimized to absorb oxygen, and to offload oxygen. Natural selection has overcome this apparent contradiction by making hemoglobin exquisitely sensitive to conditions in its microenvironment.
One way in which hemoglobin accomplishes its goals is through the phenomenon of cooperativity. Cooperativity refers to the ability of hemoglobin to change its oxygen binding behavior as a function of how many other oxygen atoms are bound to the molecule.
Fetal hemoglobin shows a similar pattern of cooperativity, but has unique binding characteristics relative to adult hemoglobin. Fetal hemoglobin reaches higher saturation at lower oxygen partial pressure.
Because of cooperativity, adult and fetal oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curves appear as follows.

Beyond its ability to carry oxygen, hemoglobin is also effective as a blood buffer. The general reaction for the blood buffer system of hemoglobin is given below.
H+ + HbO2 ←→ H+Hb + O2
The observed cooperativity of oxygen binding to hemoglobin can be explained by changes in shape to the hemoglobin molecule upon oxygen attachment. What kind of change would this be considered?
Hemoglobin reacts with an allosteric change to oxygen binding, because the shape of the molecule changes. In fact, oxygen is considered a "homotropic" allosteric regulator because it is the normal substrate for hemoglobin, and affects its changes on that molecule by binding to its active site.
Hemoglobin reacts with an allosteric change to oxygen binding, because the shape of the molecule changes. In fact, oxygen is considered a "homotropic" allosteric regulator because it is the normal substrate for hemoglobin, and affects its changes on that molecule by binding to its active site.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Cryptosporidium is a genus of gastrointestinal parasite that infects the intestinal epithelium of mammals. Cryptosporidium is water-borne, and is an apicomplexan parasite. This phylum also includes Plasmodium, Babesia, and Toxoplasma.
Apicomplexans are unique due to their apicoplast, an apical organelle that helps penetrate mammalian epithelium. In the case of cryptosporidium, there is an interaction between the surface proteins of mammalian epithelial tissue and those of the apical portion of the cryptosporidium infective stage, or oocyst. A scientist is conducting an experiment to test the hypothesis that the oocyst secretes a peptide compound that neutralizes intestinal defense cells. These defense cells are resident in the intestinal epithelium, and defend the tissue by phagocytizing the oocysts.
She sets up the following experiment:
As the neutralizing compound was believed to be secreted by the oocyst, the scientist collected oocysts onto growth media. The oocysts were grown among intestinal epithelial cells, and then the media was collected. The media was then added to another plate where Toxoplasma gondii was growing with intestinal epithelial cells. A second plate of Toxoplasma gondii was grown with the same type of intestinal epithelium, but no oocyst-sourced media was added.
Where is the likely site of the neutralizing toxin synthesis in cryptosporidium cells?
Cryptosporidium is a genus of gastrointestinal parasite that infects the intestinal epithelium of mammals. Cryptosporidium is water-borne, and is an apicomplexan parasite. This phylum also includes Plasmodium, Babesia, and Toxoplasma.
Apicomplexans are unique due to their apicoplast, an apical organelle that helps penetrate mammalian epithelium. In the case of cryptosporidium, there is an interaction between the surface proteins of mammalian epithelial tissue and those of the apical portion of the cryptosporidium infective stage, or oocyst. A scientist is conducting an experiment to test the hypothesis that the oocyst secretes a peptide compound that neutralizes intestinal defense cells. These defense cells are resident in the intestinal epithelium, and defend the tissue by phagocytizing the oocysts.
She sets up the following experiment:
As the neutralizing compound was believed to be secreted by the oocyst, the scientist collected oocysts onto growth media. The oocysts were grown among intestinal epithelial cells, and then the media was collected. The media was then added to another plate where Toxoplasma gondii was growing with intestinal epithelial cells. A second plate of Toxoplasma gondii was grown with the same type of intestinal epithelium, but no oocyst-sourced media was added.
Where is the likely site of the neutralizing toxin synthesis in cryptosporidium cells?
The passage specifies that the neutralizing agent is a peptide. Ribosomes synthesize peptides. Nuceloulus may have been a tempting answer, but is where ribosomes are synthesized, not peptides.
The passage specifies that the neutralizing agent is a peptide. Ribosomes synthesize peptides. Nuceloulus may have been a tempting answer, but is where ribosomes are synthesized, not peptides.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

