Covalent Bonds and Hybrid Orbitals - MCAT Biology
Card 0 of 20
Drain cleaners are a common household staple, used to open clogged drains in bathtubs and sinks. Human hair is a common culprit that clogs pipes, and hair is made predominately of protein. Drain cleaners are effective at breaking down proteins that have accumulated in plumbing. Drain cleaners can be either acidic or basic, and are also effective at breaking down fats that have accumulated with proteins.
A typical reaction—reaction 1—which would be expected for a drain cleaner on contact with human hair, would be as follows in an aqueous solution:
Another reaction that may occur, reaction 2, would take place as follows in an aqueous solution:
The C–N bond in the original protein, before reaction with drain cleaner is __________.
Drain cleaners are a common household staple, used to open clogged drains in bathtubs and sinks. Human hair is a common culprit that clogs pipes, and hair is made predominately of protein. Drain cleaners are effective at breaking down proteins that have accumulated in plumbing. Drain cleaners can be either acidic or basic, and are also effective at breaking down fats that have accumulated with proteins.
A typical reaction—reaction 1—which would be expected for a drain cleaner on contact with human hair, would be as follows in an aqueous solution:
Another reaction that may occur, reaction 2, would take place as follows in an aqueous solution:
The C–N bond in the original protein, before reaction with drain cleaner is __________.
The C–N bond is a single bond, and the carbonyl bond is a double bond. Double bonds are stronger and shorter than single bonds.
The C–N bond is a single bond, and the carbonyl bond is a double bond. Double bonds are stronger and shorter than single bonds.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Drain cleaners a common household staple, used to open clogged drains in bathtubs and sinks. Human hair is a common culprit that clogs pipes, and hair is made predominately of protein. Drain cleaners are effective at breaking down proteins that have accumulated in plumbing. Drain cleaners can be either acidic or basic, and are also effective at breaking down fats that have accumulated with proteins.
A typical reaction—reaction 1—which would be expected for a drain cleaner on contact with human hair, would be as follows in an aqueous solution:
Another reaction that may occur, reaction 2, would take place as follows in an aqueous solution:
In the carbonyl bonds of the preceeding passage __________.
Drain cleaners a common household staple, used to open clogged drains in bathtubs and sinks. Human hair is a common culprit that clogs pipes, and hair is made predominately of protein. Drain cleaners are effective at breaking down proteins that have accumulated in plumbing. Drain cleaners can be either acidic or basic, and are also effective at breaking down fats that have accumulated with proteins.
A typical reaction—reaction 1—which would be expected for a drain cleaner on contact with human hair, would be as follows in an aqueous solution:
Another reaction that may occur, reaction 2, would take place as follows in an aqueous solution:
In the carbonyl bonds of the preceeding passage __________.
The carbon at the center of a carbonyl group bonds with three sigma bonds, and one pi bond. The pi bond exists above and below the plane of the sigma bond. This carbon thus shows sp2 hybridization.
The carbon at the center of a carbonyl group bonds with three sigma bonds, and one pi bond. The pi bond exists above and below the plane of the sigma bond. This carbon thus shows sp2 hybridization.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which organelle would have the most negative effect if its membrane were damaged?
Which organelle would have the most negative effect if its membrane were damaged?
The lysosomes contain an acidic environment and digestive enzymes. Damage to the membrane would allow hydrogen ions and these enzymes to escape into the cytoplasm of the cell, where they would do damage to the other cellular components.
Damage to a mitochondrion or chloroplast would affect energy production in the cell, but would not actively cause damage. Ribosomes don't have membranes.
The lysosomes contain an acidic environment and digestive enzymes. Damage to the membrane would allow hydrogen ions and these enzymes to escape into the cytoplasm of the cell, where they would do damage to the other cellular components.
Damage to a mitochondrion or chloroplast would affect energy production in the cell, but would not actively cause damage. Ribosomes don't have membranes.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
What is the predicted molecular orbital hybridization state of the carbon in carbonic acid?
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
What is the predicted molecular orbital hybridization state of the carbon in carbonic acid?
Carbons bound via one double bond are sp2 hybridized, as long as the remaining two bonds are each sigma bonds. Take the number of sigma bonds and subtract one for your exponent in the spx expression.
Carbons bound via one double bond are sp2 hybridized, as long as the remaining two bonds are each sigma bonds. Take the number of sigma bonds and subtract one for your exponent in the spx expression.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
The bond that is present between the carbon atom and the carbonyl oxygen atom in carbonc acid is best described as having which of the following?
Among the most important pH buffer systems in humans is the bicarbonate buffer, which keeps the blood at a remarkably precise 7.42 pH. The bicarbonate buffer system uses a series of important compounds and enzymes to make the system function. Figure 1 depicts the key reactions that take place.

The activity of this buffer system is mainly controlled by the renal and respiratory systems. The renal system excretes bicarbonate in the urine, while the respiratory system “blows off” carbon dioxide as needed. By balancing these two systems as needed, blood pH is maintained in such a narrow range.
The bond that is present between the carbon atom and the carbonyl oxygen atom in carbonc acid is best described as having which of the following?
The bond in question is a double bond, and thus is composed of one sigma and one pi bond.
The bond in question is a double bond, and thus is composed of one sigma and one pi bond.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Under normal circumstances, which of the following carbons will be sp3 hybridized?
Under normal circumstances, which of the following carbons will be sp3 hybridized?
Carbanions are usually sp3 hybridized. Free radical carbons, carbocations, and double bonded carbons are all sp2 hybridized.
Carbanions are usually sp3 hybridized. Free radical carbons, carbocations, and double bonded carbons are all sp2 hybridized.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
When formic acid is completely reduced, methanol is formed.
What is the hybridization of the carbon in formic acid, compared to the carbon in methanol?
When formic acid is completely reduced, methanol is formed.
What is the hybridization of the carbon in formic acid, compared to the carbon in methanol?
In order to find the hybridization of an atom, simply count the number of sigma bonds and lone pair electrons around the atom. The carbon in formic acid is double bonded to an oxygen, and has two single bonds. This means that it has sp2 hybridization. Upon being reduced to methanol, the carbon now has four single bonds surrounding it. As a result, the carbon now has sp3 hybridization.
Remember that a triple bond corresponds to sp hydrization, a double bond to sp2, and single bonds to sp3 for a carbon atom.
In order to find the hybridization of an atom, simply count the number of sigma bonds and lone pair electrons around the atom. The carbon in formic acid is double bonded to an oxygen, and has two single bonds. This means that it has sp2 hybridization. Upon being reduced to methanol, the carbon now has four single bonds surrounding it. As a result, the carbon now has sp3 hybridization.
Remember that a triple bond corresponds to sp hydrization, a double bond to sp2, and single bonds to sp3 for a carbon atom.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which compound will have the highest bond energy?
Which compound will have the highest bond energy?
In organic chemistry, the trend is that bond length is inversely proportional to bond energy. Shorter bonds result in a higher bond energy. The double bond in ethene is the shortest bond out of all the others. As a result, it has the highest bond energy.
Note that in benzene there are three double bonds and three single bonds between carbons, however, resonance means that each of these only has partial double bond character, and is therefore longer than a pure double bond.
In organic chemistry, the trend is that bond length is inversely proportional to bond energy. Shorter bonds result in a higher bond energy. The double bond in ethene is the shortest bond out of all the others. As a result, it has the highest bond energy.
Note that in benzene there are three double bonds and three single bonds between carbons, however, resonance means that each of these only has partial double bond character, and is therefore longer than a pure double bond.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The answer is arrows A and C. The carbon that is pointed to by arrow C is  hybridized. We see that its bond angles are at 120º (the full substituent points into the page) with a p-orbital that is involved in the pi bond of the carbonyl. Phenyl rings are also made up of carbons that are all
hybridized. We see that its bond angles are at 120º (the full substituent points into the page) with a p-orbital that is involved in the pi bond of the carbonyl. Phenyl rings are also made up of carbons that are all  hybridized. The nitrogen pointed to by arrow B has two electrons that are not shown, but cause the atom to be
hybridized. The nitrogen pointed to by arrow B has two electrons that are not shown, but cause the atom to be  hybridized. The methyl groups denoted by arrow D are also
hybridized. The methyl groups denoted by arrow D are also  hybridized.
hybridized.
We can quickly tell the hybridization of atoms by observing their double bonds and unbonded electrons. As a rule of thumb, any carbon, nitrogen, or oxygen involved in a double bond will be  hybridized. Any of these atoms with no double bonds will be
hybridized. Any of these atoms with no double bonds will be  hybridized. Finally, nitrogens or carbons involved in triple bonds are
hybridized. Finally, nitrogens or carbons involved in triple bonds are  hybridized.
hybridized.
The answer is arrows A and C. The carbon that is pointed to by arrow C is 



We can quickly tell the hybridization of atoms by observing their double bonds and unbonded electrons. As a rule of thumb, any carbon, nitrogen, or oxygen involved in a double bond will be 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
For a compound to be considered aromatic, it must be flat, cyclic, and conjugated and it must obey Huckel's rule. Huckel's rule states that an aromatic compound must have  pi electrons in the overlapping p orbitals in order to be aromatic (n in this formula represents any integer). Only compounds with 2, 6, 10, 14, . . . pi electrons can be considered aromatic. Compound A has 6 pi electrons, compound B has 4, and compound C has 8. This eliminates answers B and C. Answer D is not cyclic, and therefore cannot be aromatic. The only aromatic compound is answer choice A, which you should recognize as benzene.
pi electrons in the overlapping p orbitals in order to be aromatic (n in this formula represents any integer). Only compounds with 2, 6, 10, 14, . . . pi electrons can be considered aromatic. Compound A has 6 pi electrons, compound B has 4, and compound C has 8. This eliminates answers B and C. Answer D is not cyclic, and therefore cannot be aromatic. The only aromatic compound is answer choice A, which you should recognize as benzene.
For a compound to be considered aromatic, it must be flat, cyclic, and conjugated and it must obey Huckel's rule. Huckel's rule states that an aromatic compound must have 
Compare your answer with the correct one above
One component of the immune system is the neutrophil, a professional phagocyte that consumes invading cells. The neutrophil is ferried to the site of infection via the blood as pre-neutrophils, or monocytes, ready to differentiate as needed to defend their host.
In order to leave the blood and migrate to the tissues, where infection is active, the monocyte undergoes a process called diapedesis. Diapedesis is a process of extravasation, where the monocyte leaves the circulation by moving in between endothelial cells, enters the tissue, and matures into a neutrophil.
Diapedesis is mediated by a class of proteins called selectins, present on the monocyte membrane and the endothelium. These selectins interact, attract the monocyte to the endothelium, and allow the monocytes to roll along the endothelium until they are able to complete diapedesis by leaving the vasculature and entering the tissues.
The image below shows monocytes moving in the blood vessel, "rolling" along the vessel wall, and eventually leaving the vessel to migrate to the site of infection.

Neutrophils make use of radical species to digest phagocytosed material. Which of the following is true of radical reactions?
One component of the immune system is the neutrophil, a professional phagocyte that consumes invading cells. The neutrophil is ferried to the site of infection via the blood as pre-neutrophils, or monocytes, ready to differentiate as needed to defend their host.
In order to leave the blood and migrate to the tissues, where infection is active, the monocyte undergoes a process called diapedesis. Diapedesis is a process of extravasation, where the monocyte leaves the circulation by moving in between endothelial cells, enters the tissue, and matures into a neutrophil.
Diapedesis is mediated by a class of proteins called selectins, present on the monocyte membrane and the endothelium. These selectins interact, attract the monocyte to the endothelium, and allow the monocytes to roll along the endothelium until they are able to complete diapedesis by leaving the vasculature and entering the tissues.
The image below shows monocytes moving in the blood vessel, "rolling" along the vessel wall, and eventually leaving the vessel to migrate to the site of infection.

Neutrophils make use of radical species to digest phagocytosed material. Which of the following is true of radical reactions?
Radical reactions have an sp2, trigonal planer carbon radical intermediate. Carbon radicals are most stable as tertiary species.
Radical reactions have an sp2, trigonal planer carbon radical intermediate. Carbon radicals are most stable as tertiary species.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
2-butyne contains all of the following types of bonds except __________.
2-butyne contains all of the following types of bonds except __________.
2-butyne has the following chemical structure.

The end carbons have  hybridization (form single bonds only), while the middle two carbons have
hybridization (form single bonds only), while the middle two carbons have  hybridization (involved in a triple bond). There are no
hybridization (involved in a triple bond). There are no  hybridized carbons in this molecule.
hybridized carbons in this molecule.
2-butyne has the following chemical structure.
The end carbons have 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
The degree of unsaturation for ephedrine (shown below) is __________.

The degree of unsaturation for ephedrine (shown below) is __________.

The degree of unsaturation is equal to the number of rings plus the number of pi bonds in a molecule. Ephedrine has one ring and three pi bonds, so its degree of unsaturation is four.
To arrive at this answer, one could also use the formula below, where  is the number of carbon atoms,
is the number of carbon atoms,  is the number of hydrogen atoms,
is the number of hydrogen atoms,  is the number of halogen atoms, and
is the number of halogen atoms, and  is the number of nitrogen atoms.
is the number of nitrogen atoms.

For ephedrine,  ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  .
.

The degree of unsaturation is equal to the number of rings plus the number of pi bonds in a molecule. Ephedrine has one ring and three pi bonds, so its degree of unsaturation is four.
To arrive at this answer, one could also use the formula below, where 



For ephedrine, 



Compare your answer with the correct one above
The compound below is reacted with  . What is the final hybridization around the initially chiral center carbon when the reaction is complete?
. What is the final hybridization around the initially chiral center carbon when the reaction is complete?

The compound below is reacted with 

The initially chiral carbon has an  hybridization. Once treated with
hybridization. Once treated with  ,an oxidizing agent, the secondary alcohol in the compound is oxidized to a ketone. The central carbon is no longer a chiral center (a carbon with a double bond cannot be chiral), and the double bond (pi-bond) formed between carbon and oxygen gives the molecule an
,an oxidizing agent, the secondary alcohol in the compound is oxidized to a ketone. The central carbon is no longer a chiral center (a carbon with a double bond cannot be chiral), and the double bond (pi-bond) formed between carbon and oxygen gives the molecule an  hybridization.
hybridization.
 hybridization is formed with triple bonds, and an
hybridization is formed with triple bonds, and an  hybridization does not exist.
hybridization does not exist.
The initially chiral carbon has an 




Compare your answer with the correct one above
How many pi bonds are present in benzylamine?
How many pi bonds are present in benzylamine?
Benzylamine consists of a benzene ring with a -CH2NH2 substituent. The benzene ring contains three double bonds, and the substituent has none.
Each bond in a compound represents a sigma bond. Each additional bond represents a pi bond; thus, double binds result from one sigma and one pi bond, and triple bonds from one sigma and two pi bonds. In benzylamine, there are three double bonds and seventeen total bonds, three of which are double bonds. The compound will have a total of seventeen sigma bonds and three pi bonds.
Benzylamine consists of a benzene ring with a -CH2NH2 substituent. The benzene ring contains three double bonds, and the substituent has none.
Each bond in a compound represents a sigma bond. Each additional bond represents a pi bond; thus, double binds result from one sigma and one pi bond, and triple bonds from one sigma and two pi bonds. In benzylamine, there are three double bonds and seventeen total bonds, three of which are double bonds. The compound will have a total of seventeen sigma bonds and three pi bonds.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Compound A has a molecular formula of  . After treatment of compound A with hydrogen in the presence of a palladium and a carbon catalyst, a new compound is formed with a molecular formula of
. After treatment of compound A with hydrogen in the presence of a palladium and a carbon catalyst, a new compound is formed with a molecular formula of  . How many rings does compound A have?
. How many rings does compound A have?
Compound A has a molecular formula of 

Recall the formula for degrees of unsaturation as the sum of the number of pi bonds and the number of rings. This value is equivalent to the below formula.

C is the number of carbons, H is the number of hydrogens, X is the number of halogens, and N is the number of nitrogens. Using this formula, compound A has four degrees of unsaturation, while the product only has two.


The reaction described is a hydrogenation reaction, which will reduce double bonds. The reaction saturates two pi bonds of compound A, meaning the remaining degrees of unsaturation in that compound have to come from two rings. Essentially, due to the reaction given, we know that the product contains no double bonds but still has two degrees of unsaturation. These unsaturation points must correspond to rings.
Recall the formula for degrees of unsaturation as the sum of the number of pi bonds and the number of rings. This value is equivalent to the below formula.
C is the number of carbons, H is the number of hydrogens, X is the number of halogens, and N is the number of nitrogens. Using this formula, compound A has four degrees of unsaturation, while the product only has two.
The reaction described is a hydrogenation reaction, which will reduce double bonds. The reaction saturates two pi bonds of compound A, meaning the remaining degrees of unsaturation in that compound have to come from two rings. Essentially, due to the reaction given, we know that the product contains no double bonds but still has two degrees of unsaturation. These unsaturation points must correspond to rings.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
How many  -bonds are in one molecule of acetic acid?
-bonds are in one molecule of acetic acid?
How many 
Acetic acid has the formula  . This compound is common enough that the IUPAC name will rarely be given, and you will need to recognize it by common name alone.
. This compound is common enough that the IUPAC name will rarely be given, and you will need to recognize it by common name alone.
Whenever two atoms are directly bonded to one another, a  -bond is formed. Even when there is a double or triple bond between two atoms, there is still one
-bond is formed. Even when there is a double or triple bond between two atoms, there is still one  -bond between the two atoms. In acetic acid, there are seven bonds between atoms. Even though the carbonyl carbon has a double bond, there is still a
-bond between the two atoms. In acetic acid, there are seven bonds between atoms. Even though the carbonyl carbon has a double bond, there is still a  -bond between the carbon and oxygen. As a result, there are seven total
-bond between the carbon and oxygen. As a result, there are seven total  -bonds in a molecule of acetic acid.
-bonds in a molecule of acetic acid.
Acetic acid has the formula 
Whenever two atoms are directly bonded to one another, a 



Compare your answer with the correct one above
What carbon hybridizations can be found in one molecule of acetic acid?
What carbon hybridizations can be found in one molecule of acetic acid?
Acetic acid has the formula  . This compound is common enough that the IUPAC name will rarely be given, and you will need to recognize it by common name alone.
. This compound is common enough that the IUPAC name will rarely be given, and you will need to recognize it by common name alone.
Acetic acid has two carbons in the molecule. The carbonyl carbon is the carbon that is double bonded to oxygen. This double bond gives the carbonyl carbon hybridization. The other carbon has four atoms attached to it, which gives it
hybridization. The other carbon has four atoms attached to it, which gives it  hybridization. Remember that the hybridization of an atom is dependent on the total number of bonded atoms, plus the number of lone electron pairs.
hybridization. Remember that the hybridization of an atom is dependent on the total number of bonded atoms, plus the number of lone electron pairs.
Acetic acid has the formula 
Acetic acid has two carbons in the molecule. The carbonyl carbon is the carbon that is double bonded to oxygen. This double bond gives the carbonyl carbon

Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following statements about the character of a bond is true?
Which of the following statements about the character of a bond is true?
The character of a hybrid orbital is defined as the extent to which it resembles the unhybridized orbitals that created it. For example, an  orbital has half "s" character and half "p" character and results from a triple bond. Remember that the more "s" character a bond has, the stronger, shorter, and more stable the bond will be.
orbital has half "s" character and half "p" character and results from a triple bond. Remember that the more "s" character a bond has, the stronger, shorter, and more stable the bond will be.  and
and  hybridizations result in longer, weaker bonds (double bonds and single bond, respectively) due to increased contributions of "p" character.
hybridizations result in longer, weaker bonds (double bonds and single bond, respectively) due to increased contributions of "p" character.
The character of a hybrid orbital is defined as the extent to which it resembles the unhybridized orbitals that created it. For example, an 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
The concept of genomic imprinting is important in human genetics. In genomic imprinting, a certain region of DNA is only expressed by one of the two chromosomes that make up a typical homologous pair. In healthy individuals, genomic imprinting results in the silencing of genes in a certain section of the maternal chromosome 15. The DNA in this part of the chromosome is "turned off" by the addition of methyl groups to the DNA molecule. Healthy people will thus only have expression of this section of chromosome 15 from paternally-derived DNA.
The two classic human diseases that illustrate defects in genomic imprinting are Prader-Willi and Angelman Syndromes. In Prader-Willi Syndrome, the section of paternal chromosome 15 that is usually expressed is disrupted, such as by a chromosomal deletion. In Angelman Syndrome, maternal genes in this section are deleted, while paternal genes are silenced. Prader-Willi Syndrome is thus closely linked to paternal inheritance, while Angelman Syndrome is linked to maternal inheritance.
Figure 1 shows the chromosome 15 homologous pair for a child with Prader-Willi Syndrome. The parental chromosomes are also shown. The genes on the mother’s chromosomes are silenced normally, as represented by the black boxes. At once, there is also a chromosomal deletion on one of the paternal chromosomes. The result is that the child does not have any genes expressed that are normally found on that region of this chromosome.
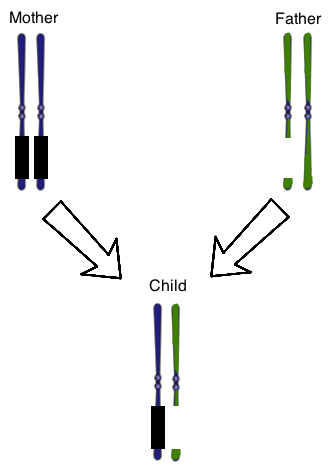
The passage indicates that genomic imprinting relies on silencing genes by adding methyl groups to DNA sequences. Which of the following is true of methyl groups?
The concept of genomic imprinting is important in human genetics. In genomic imprinting, a certain region of DNA is only expressed by one of the two chromosomes that make up a typical homologous pair. In healthy individuals, genomic imprinting results in the silencing of genes in a certain section of the maternal chromosome 15. The DNA in this part of the chromosome is "turned off" by the addition of methyl groups to the DNA molecule. Healthy people will thus only have expression of this section of chromosome 15 from paternally-derived DNA.
The two classic human diseases that illustrate defects in genomic imprinting are Prader-Willi and Angelman Syndromes. In Prader-Willi Syndrome, the section of paternal chromosome 15 that is usually expressed is disrupted, such as by a chromosomal deletion. In Angelman Syndrome, maternal genes in this section are deleted, while paternal genes are silenced. Prader-Willi Syndrome is thus closely linked to paternal inheritance, while Angelman Syndrome is linked to maternal inheritance.
Figure 1 shows the chromosome 15 homologous pair for a child with Prader-Willi Syndrome. The parental chromosomes are also shown. The genes on the mother’s chromosomes are silenced normally, as represented by the black boxes. At once, there is also a chromosomal deletion on one of the paternal chromosomes. The result is that the child does not have any genes expressed that are normally found on that region of this chromosome.

The passage indicates that genomic imprinting relies on silencing genes by adding methyl groups to DNA sequences. Which of the following is true of methyl groups?
Methyl groups are  substituents, and thus have a central carbon with four single bonds, one of which is a covalent attachment to the DNA substrate:
substituents, and thus have a central carbon with four single bonds, one of which is a covalent attachment to the DNA substrate:  . A central carbon with four bonds will be
. A central carbon with four bonds will be  hybridized.
hybridized.
Note that methylation is a covalent interaction, making it much more permanent than dipole interactions between DNA and histones. This allows methylation to have long-term effects, and is one of the principles of epigenetic regulation and inheritance.
Methyl groups are 


Note that methylation is a covalent interaction, making it much more permanent than dipole interactions between DNA and histones. This allows methylation to have long-term effects, and is one of the principles of epigenetic regulation and inheritance.
Compare your answer with the correct one above



 hybridized?
hybridized?


