Adaptive and Innate Immunity - MCAT Biology
Card 0 of 20
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy is an X-linked recessive genetic disorder, resulting in the loss of the dystrophin protein. In healthy muscle, dystrophin localizes to the sarcolemma and helps anchor the muscle fiber to the basal lamina. The loss of this protein results in progressive muscle weakness, and eventually death.
In the muscle fibers, the effects of the disease can be exacerbated by auto-immune interference. Weakness of the sarcolemma leads to damage and tears in the membrane. The body’s immune system recognizes the damage and attempts to repair it. However, since the damage exists as a chronic condition, leukocytes begin to present the damaged protein fragments as antigens, stimulating a targeted attack on the damaged parts of the muscle fiber. The attack causes inflammation, fibrosis, and necrosis, further weakening the muscle.
Studies have shown that despite the severe pathology of the muscle fibers, the innervation of the muscle is unaffected.
What is the best characterization of the immune response described in the passage?
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy is an X-linked recessive genetic disorder, resulting in the loss of the dystrophin protein. In healthy muscle, dystrophin localizes to the sarcolemma and helps anchor the muscle fiber to the basal lamina. The loss of this protein results in progressive muscle weakness, and eventually death.
In the muscle fibers, the effects of the disease can be exacerbated by auto-immune interference. Weakness of the sarcolemma leads to damage and tears in the membrane. The body’s immune system recognizes the damage and attempts to repair it. However, since the damage exists as a chronic condition, leukocytes begin to present the damaged protein fragments as antigens, stimulating a targeted attack on the damaged parts of the muscle fiber. The attack causes inflammation, fibrosis, and necrosis, further weakening the muscle.
Studies have shown that despite the severe pathology of the muscle fibers, the innervation of the muscle is unaffected.
What is the best characterization of the immune response described in the passage?
The initial response is an effort to repair physical damage, while the chronic response involves the recognition of antigens. Innate immunity refers to the body's natural untargeted defenses, such as the cells that would work to repair damage. Adaptive immunity is targeted to specific pathogens via antigen presentation. Thus, the pattern described in the passage is initially innate immunity, then adaptive immunity.
The initial response is an effort to repair physical damage, while the chronic response involves the recognition of antigens. Innate immunity refers to the body's natural untargeted defenses, such as the cells that would work to repair damage. Adaptive immunity is targeted to specific pathogens via antigen presentation. Thus, the pattern described in the passage is initially innate immunity, then adaptive immunity.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy is an X-linked recessive genetic disorder, resulting in the loss of the dystrophin protein. In healthy muscle, dystrophin localizes to the sarcolemma and helps anchor the muscle fiber to the basal lamina. The loss of this protein results in progressive muscle weakness, and eventually death.
In the muscle fibers, the effects of the disease can be exacerbated by auto-immune interference. Weakness of the sarcolemma leads to damage and tears in the membrane. The body’s immune system recognizes the damage and attempts to repair it. However, since the damage exists as a chronic condition, leukocytes begin to present the damaged protein fragments as antigens, stimulating a targeted attack on the damaged parts of the muscle fiber. The attack causes inflammation, fibrosis, and necrosis, further weakening the muscle.
Studies have shown that despite the severe pathology of the muscle fibers, the innervation of the muscle is unaffected.
Which compound is most likely responsible for initiating the inflammation response that results from the autoimmune attack?
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy is an X-linked recessive genetic disorder, resulting in the loss of the dystrophin protein. In healthy muscle, dystrophin localizes to the sarcolemma and helps anchor the muscle fiber to the basal lamina. The loss of this protein results in progressive muscle weakness, and eventually death.
In the muscle fibers, the effects of the disease can be exacerbated by auto-immune interference. Weakness of the sarcolemma leads to damage and tears in the membrane. The body’s immune system recognizes the damage and attempts to repair it. However, since the damage exists as a chronic condition, leukocytes begin to present the damaged protein fragments as antigens, stimulating a targeted attack on the damaged parts of the muscle fiber. The attack causes inflammation, fibrosis, and necrosis, further weakening the muscle.
Studies have shown that despite the severe pathology of the muscle fibers, the innervation of the muscle is unaffected.
Which compound is most likely responsible for initiating the inflammation response that results from the autoimmune attack?
Fibrin and fibrinogen are involved in wound healing and scab formation. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter in the brain. Fibrogen is not a real protein at all.
Histamine is the primary inflammatory molecule in the body and is released from mast cells during an immune response or trauma.
Fibrin and fibrinogen are involved in wound healing and scab formation. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter in the brain. Fibrogen is not a real protein at all.
Histamine is the primary inflammatory molecule in the body and is released from mast cells during an immune response or trauma.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following correctly matches the type of immunity to the way it was recieved?
Which of the following correctly matches the type of immunity to the way it was recieved?
Active immunity is when you are exposed to a pathogen, either through vaccination, another person with the disease, or any other means, and your body responds by producing specific antibodies with B-cells to destroy the pathogen. Passive immunity is acquired from antibody transfer, so the body does not produce its own antibodies.
Active immunity is when you are exposed to a pathogen, either through vaccination, another person with the disease, or any other means, and your body responds by producing specific antibodies with B-cells to destroy the pathogen. Passive immunity is acquired from antibody transfer, so the body does not produce its own antibodies.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of these choices is not a function of T-cells?
Which of these choices is not a function of T-cells?
The only choice that is not a function of any type of T-cell is the direct production of antibodies (which is performed by B-cells). Cytotoxic T-cells kill other cells that are bound to antigen/MHC-I complexes. Suppressor T-cells tone down the response of both B- and T-cells, and helper T-cells secrete cytokines, which increase the activity of many other immune cell types.
The only choice that is not a function of any type of T-cell is the direct production of antibodies (which is performed by B-cells). Cytotoxic T-cells kill other cells that are bound to antigen/MHC-I complexes. Suppressor T-cells tone down the response of both B- and T-cells, and helper T-cells secrete cytokines, which increase the activity of many other immune cell types.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Sexually transmitted diseases are a common problem among young people in the United States. One of the more common diseases is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which leads to inflammation and purulent discharge in the male and female reproductive tracts.
The bacterium has a number of systems to evade host defenses. Upon infection, it uses pili to adhere to host epithelium. The bacterium also uses an enzyme, gonococcal sialyltransferase, to transfer a sialyic acid residue to a gonococcal surface lipooligosaccharide (LOS). A depiction of this can be seen in Figure 1. The sialyic acid residue mimics the protective capsule found on other bacterial species.
Once infection is established, Neisseria preferentially infects columnar epithelial cells in the female reproductive tract, and leads to a loss of cilia on these cells. Damage to the reproductive tract can result in pelvic inflammatory disease, which can complicate pregnancies later in the life of the woman.

The first line of defense by a human host against a potential Neisseria infection is which of the following?
Sexually transmitted diseases are a common problem among young people in the United States. One of the more common diseases is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which leads to inflammation and purulent discharge in the male and female reproductive tracts.
The bacterium has a number of systems to evade host defenses. Upon infection, it uses pili to adhere to host epithelium. The bacterium also uses an enzyme, gonococcal sialyltransferase, to transfer a sialyic acid residue to a gonococcal surface lipooligosaccharide (LOS). A depiction of this can be seen in Figure 1. The sialyic acid residue mimics the protective capsule found on other bacterial species.
Once infection is established, Neisseria preferentially infects columnar epithelial cells in the female reproductive tract, and leads to a loss of cilia on these cells. Damage to the reproductive tract can result in pelvic inflammatory disease, which can complicate pregnancies later in the life of the woman.

The first line of defense by a human host against a potential Neisseria infection is which of the following?
Innate defenses, such as the skin or macrophages, are the first line of defense against infection. Other responses only become effective if a pathogen cannot be repelled by innate mechanisms.
Innate defenses, such as the skin or macrophages, are the first line of defense against infection. Other responses only become effective if a pathogen cannot be repelled by innate mechanisms.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Cryptosporidium is a genus of gastrointestinal parasite that infects the intestinal epithelium of mammals. Cryptosporidium is water-borne, and is an apicomplexan parasite. This phylum also includes Plasmodium, Babesia, and Toxoplasma.
Apicomplexans are unique due to their apicoplast, an apical organelle that helps penetrate mammalian epithelium. In the case of cryptosporidium, there is an interaction between the surface proteins of mammalian epithelial tissue and those of the apical portion of the cryptosporidium infective stage, or oocyst. A scientist is conducting an experiment to test the hypothesis that the oocyst secretes a peptide compound that neutralizes intestinal defense cells. These defense cells are resident in the intestinal epithelium, and defend the tissue by phagocytizing the oocysts.
She sets up the following experiment:
As the neutralizing compound was believed to be secreted by the oocyst, the scientist collected oocysts onto growth media. The oocysts were grown among intestinal epithelial cells, and then the media was collected. The media was then added to another plate where Toxoplasma gondii was growing with intestinal epithelial cells. A second plate of Toxoplasma gondii was grown with the same type of intestinal epithelium, but no oocyst-sourced media was added.
A patient is hiking through Nepal and comes down with a case of diarrhea caused by cryptosporidium. You determine that his body was fighting this infection mainly by mounting an antibody response. Where do the cells most directly responsible for this response develop?
Cryptosporidium is a genus of gastrointestinal parasite that infects the intestinal epithelium of mammals. Cryptosporidium is water-borne, and is an apicomplexan parasite. This phylum also includes Plasmodium, Babesia, and Toxoplasma.
Apicomplexans are unique due to their apicoplast, an apical organelle that helps penetrate mammalian epithelium. In the case of cryptosporidium, there is an interaction between the surface proteins of mammalian epithelial tissue and those of the apical portion of the cryptosporidium infective stage, or oocyst. A scientist is conducting an experiment to test the hypothesis that the oocyst secretes a peptide compound that neutralizes intestinal defense cells. These defense cells are resident in the intestinal epithelium, and defend the tissue by phagocytizing the oocysts.
She sets up the following experiment:
As the neutralizing compound was believed to be secreted by the oocyst, the scientist collected oocysts onto growth media. The oocysts were grown among intestinal epithelial cells, and then the media was collected. The media was then added to another plate where Toxoplasma gondii was growing with intestinal epithelial cells. A second plate of Toxoplasma gondii was grown with the same type of intestinal epithelium, but no oocyst-sourced media was added.
A patient is hiking through Nepal and comes down with a case of diarrhea caused by cryptosporidium. You determine that his body was fighting this infection mainly by mounting an antibody response. Where do the cells most directly responsible for this response develop?
Antibodies are produced by B-cells, which develop in the bone marrow. T-cells develop in the thymus.
You can remember B for bone marrow, T for thymus.
Antibodies are produced by B-cells, which develop in the bone marrow. T-cells develop in the thymus.
You can remember B for bone marrow, T for thymus.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Cryptosporidium is a genus of gastrointestinal parasite that infects the intestinal epithelium of mammals. Cryptosporidium is water-borne, and is an apicomplexan parasite. This phylum also includes Plasmodium, Babesia, and Toxoplasma.
Apicomplexans are unique due to their apicoplast, an apical organelle that helps penetrate mammalian epithelium. In the case of cryptosporidium, there is an interaction between the surface proteins of mammalian epithelial tissue and those of the apical portion of the cryptosporidium infective stage, or oocyst. A scientist is conducting an experiment to test the hypothesis that the oocyst secretes a peptide compound that neutralizes intestinal defense cells. These defense cells are resident in the intestinal epithelium, and defend the tissue by phagocytizing the oocysts.
She sets up the following experiment:
As the neutralizing compound was believed to be secreted by the oocyst, the scientist collected oocysts onto growth media. The oocysts were grown among intestinal epithelial cells, and then the media was collected. The media was then added to another plate where Toxoplasma gondii was growing with intestinal epithelial cells. A second plate of Toxoplasma gondii was grown with the same type of intestinal epithelium, but no oocyst-sourced media was added.
In the initial stages of a cryptosporidium infection, you can observe macrophages migrating to the area of infection. This process is called chemotaxis. What is likely to be the chemical mediator responsible for chemotaxis?
Cryptosporidium is a genus of gastrointestinal parasite that infects the intestinal epithelium of mammals. Cryptosporidium is water-borne, and is an apicomplexan parasite. This phylum also includes Plasmodium, Babesia, and Toxoplasma.
Apicomplexans are unique due to their apicoplast, an apical organelle that helps penetrate mammalian epithelium. In the case of cryptosporidium, there is an interaction between the surface proteins of mammalian epithelial tissue and those of the apical portion of the cryptosporidium infective stage, or oocyst. A scientist is conducting an experiment to test the hypothesis that the oocyst secretes a peptide compound that neutralizes intestinal defense cells. These defense cells are resident in the intestinal epithelium, and defend the tissue by phagocytizing the oocysts.
She sets up the following experiment:
As the neutralizing compound was believed to be secreted by the oocyst, the scientist collected oocysts onto growth media. The oocysts were grown among intestinal epithelial cells, and then the media was collected. The media was then added to another plate where Toxoplasma gondii was growing with intestinal epithelial cells. A second plate of Toxoplasma gondii was grown with the same type of intestinal epithelium, but no oocyst-sourced media was added.
In the initial stages of a cryptosporidium infection, you can observe macrophages migrating to the area of infection. This process is called chemotaxis. What is likely to be the chemical mediator responsible for chemotaxis?
Cytokines and chemokines are general classes of inflammatory mediators secreted by inflammatory cells like macrophages. They not only govern inflammation, but can also recruit surrounding cells via chemotaxis.
Cytokines and chemokines are general classes of inflammatory mediators secreted by inflammatory cells like macrophages. They not only govern inflammation, but can also recruit surrounding cells via chemotaxis.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Identify the cells that correspond to the adaptive immune system and to the innate immune system.
Identify the cells that correspond to the adaptive immune system and to the innate immune system.
B-cells and T-cells are part of the adaptive immune system, while monocytes, neutrophils, and macrophages are part of the innate immune system. Activation of the adaptive immune response requires prior exposure to a pathogen and the involvement of antibodies, while the innate immune response will occur whether a pathogen has been exposed before or not.
This list only contains a few examples of immune cells for each response, and is not exhaustive.
B-cells and T-cells are part of the adaptive immune system, while monocytes, neutrophils, and macrophages are part of the innate immune system. Activation of the adaptive immune response requires prior exposure to a pathogen and the involvement of antibodies, while the innate immune response will occur whether a pathogen has been exposed before or not.
This list only contains a few examples of immune cells for each response, and is not exhaustive.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following cells is a part of the adaptive immune response?
Which of the following cells is a part of the adaptive immune response?
An adaptive immune response only occurs once a specific antigen has been presented to a T-cell by an antigen-presenting cell, which activates a highly specific immune system response. The cells most directly involved in the adaptive immune response (for the purposes of the MCAT) are helper T-cells, cytotoxic T-cells, and B-cells.
On the other hand, our immune system also evades pathogens by non-specific, innate responses which encompass a wide range of cells and biological systems. While the other three answer choices are recognzied as "immune cells", they are not involved an adaptive immune response, making them incorrect answers.
An adaptive immune response only occurs once a specific antigen has been presented to a T-cell by an antigen-presenting cell, which activates a highly specific immune system response. The cells most directly involved in the adaptive immune response (for the purposes of the MCAT) are helper T-cells, cytotoxic T-cells, and B-cells.
On the other hand, our immune system also evades pathogens by non-specific, innate responses which encompass a wide range of cells and biological systems. While the other three answer choices are recognzied as "immune cells", they are not involved an adaptive immune response, making them incorrect answers.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is not an example of innate immunity?
Which of the following is not an example of innate immunity?
All of the following are examples of non-specific defense mechanisms of the immune system, except for antibody production by B-cells. B-cells respond to specific antigens within the body via immunoglobulins located on the plasma membrane of B-cells. This type of response is known as adaptive immunity, and develops only after a particular pathogen has invaded the immune system.
All of the following are examples of non-specific defense mechanisms of the immune system, except for antibody production by B-cells. B-cells respond to specific antigens within the body via immunoglobulins located on the plasma membrane of B-cells. This type of response is known as adaptive immunity, and develops only after a particular pathogen has invaded the immune system.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
One component of the immune system is the neutrophil, a professional phagocyte that consumes invading cells. The neutrophil is ferried to the site of infection via the blood as pre-neutrophils, or monocytes, ready to differentiate as needed to defend their host.
In order to leave the blood and migrate to the tissues, where infection is active, the monocyte undergoes a process called diapedesis. Diapedesis is a process of extravasation, where the monocyte leaves the circulation by moving in between endothelial cells, enters the tissue, and matures into a neutrophil.
Diapedesis is mediated by a class of proteins called selectins, present on the monocyte membrane and the endothelium. These selectins interact, attract the monocyte to the endothelium, and allow the monocytes to roll along the endothelium until they are able to complete diapedesis by leaving the vasculature and entering the tissues.
The image below shows monocytes moving in the blood vessel, "rolling" along the vessel wall, and eventually leaving the vessel to migrate to the site of infection.

A scientist is investigating what attracts monocytes to the site of infection, thus prompting diapedesis. He finds that a class of soluble mediators are given off by infected cells. This soluble mediator is most likely __________.
One component of the immune system is the neutrophil, a professional phagocyte that consumes invading cells. The neutrophil is ferried to the site of infection via the blood as pre-neutrophils, or monocytes, ready to differentiate as needed to defend their host.
In order to leave the blood and migrate to the tissues, where infection is active, the monocyte undergoes a process called diapedesis. Diapedesis is a process of extravasation, where the monocyte leaves the circulation by moving in between endothelial cells, enters the tissue, and matures into a neutrophil.
Diapedesis is mediated by a class of proteins called selectins, present on the monocyte membrane and the endothelium. These selectins interact, attract the monocyte to the endothelium, and allow the monocytes to roll along the endothelium until they are able to complete diapedesis by leaving the vasculature and entering the tissues.
The image below shows monocytes moving in the blood vessel, "rolling" along the vessel wall, and eventually leaving the vessel to migrate to the site of infection.

A scientist is investigating what attracts monocytes to the site of infection, thus prompting diapedesis. He finds that a class of soluble mediators are given off by infected cells. This soluble mediator is most likely __________.
Chemokines and cytokines are the main inflammatory mediators that drive a cellular response to inflammation or infection.
The JAK-STAT pathways are most linked to cell growth and division, while the hedgehog pathway (including SHH) is linked to early development. Wnt proteins are also linked to early development, but have been linked to carcinogenesis as well. Finally, fibroblast growth factor is linked with wound healing, but not with the initial immune response or recruitment.
Chemokines and cytokines are the main inflammatory mediators that drive a cellular response to inflammation or infection.
The JAK-STAT pathways are most linked to cell growth and division, while the hedgehog pathway (including SHH) is linked to early development. Wnt proteins are also linked to early development, but have been linked to carcinogenesis as well. Finally, fibroblast growth factor is linked with wound healing, but not with the initial immune response or recruitment.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
In the crusade to create a vaccine for Poliomyelitis, Jonas Salk and Albert Sabin created two separate vaccines that proved to be successful in preventing Polio onset.
The Salk vaccine, which is given by standard injection, contained virus particles inactivated by an organic solvent. This method has the advantage of inactivating each of the three Polio strains with no bias.
Albert Sabin's vaccine, given by oral inoculation via sugar water, contained live virus particles that had been genetically attenuated. With this method, each of the three Polio strains acquired separate mutations that made them unable to infect the human host cells. Strain 2 in particular contained one single nucleotide polymorphism in the internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) that prevented successful viral replication.
What type of immune response does inoculation with either vaccine stimulate?
In the crusade to create a vaccine for Poliomyelitis, Jonas Salk and Albert Sabin created two separate vaccines that proved to be successful in preventing Polio onset.
The Salk vaccine, which is given by standard injection, contained virus particles inactivated by an organic solvent. This method has the advantage of inactivating each of the three Polio strains with no bias.
Albert Sabin's vaccine, given by oral inoculation via sugar water, contained live virus particles that had been genetically attenuated. With this method, each of the three Polio strains acquired separate mutations that made them unable to infect the human host cells. Strain 2 in particular contained one single nucleotide polymorphism in the internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) that prevented successful viral replication.
What type of immune response does inoculation with either vaccine stimulate?
The adaptive immune response is responsible for encountering antigens and creating lasting immunity against it. The humoral immune response plays a role in adaptive immunity, but is more active during the secondary exposure to an antigen.
The adaptive immune response is responsible for encountering antigens and creating lasting immunity against it. The humoral immune response plays a role in adaptive immunity, but is more active during the secondary exposure to an antigen.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is not involved in innate immunity?
Which of the following is not involved in innate immunity?
Plasma cells are mature B-cells, and are not part of the innate immune response. B-cell and T-cells are part of the adaptive immune response.
The innate immune response is mainly comprised of physical barriers and phagocytes. Skin and mucous are examples of such physical barriers, while macrophages and neutrophils are examples of non-specific phagocytes.
Plasma cells are mature B-cells, and are not part of the innate immune response. B-cell and T-cells are part of the adaptive immune response.
The innate immune response is mainly comprised of physical barriers and phagocytes. Skin and mucous are examples of such physical barriers, while macrophages and neutrophils are examples of non-specific phagocytes.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is not part of the innate immune response of the body?
Which of the following is not part of the innate immune response of the body?
Innate immunity can be considered the general immune response that attacks any oncoming pathogens. The skin, digestive enzymes, and phagocytic cells are all part of the innate immune response. Plasma cells are modified B-cells, and are part of the acquired immune response. They are responsible for synthesizing free antibodies in response to a specific identified pathogen.
Innate immunity can be considered the general immune response that attacks any oncoming pathogens. The skin, digestive enzymes, and phagocytic cells are all part of the innate immune response. Plasma cells are modified B-cells, and are part of the acquired immune response. They are responsible for synthesizing free antibodies in response to a specific identified pathogen.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Type 1 diabetes is a well-understood autoimmune disease. Autoimmune diseases result from an immune system-mediated attack on one’s own body tissues. In normal development, an organ called the thymus introduces immune cells to the body’s normal proteins. This process is called negative selection, as those immune cells that recognize normal proteins are deleted. If cells evade this process, those that recognize normal proteins enter into circulation, where they can attack body tissues. The thymus is also important for activating T-cells that recognize foreign proteins.
As the figure below shows, immune cells typically originate in the bone marrow. Some immune cells, called T-cells, then go to the thymus for negative selection. Those that survive negative selection, enter into general circulation to fight infection. Other cells, called B-cells, directly enter general circulation from the bone marrow. It is a breakdown in this carefully orchestrated process that leads to autoimmune disease, such as type 1 diabetes.

The T-cells and B-cells described in the passage are both examples of lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are involved in adaptive immunity. Which of the following are characteristics of the adaptive immune system?
I. It shows a stronger reaction to a pathogen upon a second exposure, relative to the first
II. It is the first line of defense against a pathogen in the environment
III. It involves the use of macrophages and other professional phagocytes
Type 1 diabetes is a well-understood autoimmune disease. Autoimmune diseases result from an immune system-mediated attack on one’s own body tissues. In normal development, an organ called the thymus introduces immune cells to the body’s normal proteins. This process is called negative selection, as those immune cells that recognize normal proteins are deleted. If cells evade this process, those that recognize normal proteins enter into circulation, where they can attack body tissues. The thymus is also important for activating T-cells that recognize foreign proteins.
As the figure below shows, immune cells typically originate in the bone marrow. Some immune cells, called T-cells, then go to the thymus for negative selection. Those that survive negative selection, enter into general circulation to fight infection. Other cells, called B-cells, directly enter general circulation from the bone marrow. It is a breakdown in this carefully orchestrated process that leads to autoimmune disease, such as type 1 diabetes.

The T-cells and B-cells described in the passage are both examples of lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are involved in adaptive immunity. Which of the following are characteristics of the adaptive immune system?
I. It shows a stronger reaction to a pathogen upon a second exposure, relative to the first
II. It is the first line of defense against a pathogen in the environment
III. It involves the use of macrophages and other professional phagocytes
The cells of the adaptive immune system are adaptive because they change upon exposure to a pathogen, such as a virus, and mount a stronger response upon a second exposure. Initial exposure allows for the formation of memory B-cells, which will be able to react quickly to a second exposure to the antigen.
The innate immune system, comprised of non-specific cells like macrophages, is the first line of defense against environmental pathogens and does not differ between a first and second encounter with an antigen.
The cells of the adaptive immune system are adaptive because they change upon exposure to a pathogen, such as a virus, and mount a stronger response upon a second exposure. Initial exposure allows for the formation of memory B-cells, which will be able to react quickly to a second exposure to the antigen.
The innate immune system, comprised of non-specific cells like macrophages, is the first line of defense against environmental pathogens and does not differ between a first and second encounter with an antigen.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Type 1 diabetes is a well-understood autoimmune disease. Autoimmune diseases result from an immune system-mediated attack on one’s own body tissues. In normal development, an organ called the thymus introduces immune cells to the body’s normal proteins. This process is called negative selection, as those immune cells that recognize normal proteins are deleted. If cells evade this process, those that recognize normal proteins enter into circulation, where they can attack body tissues. The thymus is also important for activating T-cells that recognize foreign proteins.
As the figure below shows, immune cells typically originate in the bone marrow. Some immune cells, called T-cells, then go to the thymus for negative selection. Those that survive negative selection, enter into general circulation to fight infection. Other cells, called B-cells, directly enter general circulation from the bone marrow. It is a breakdown in this carefully orchestrated process that leads to autoimmune disease, such as type 1 diabetes.

Which of the following constitutes a loss of innate immunity in an immunocompromised patient?
Type 1 diabetes is a well-understood autoimmune disease. Autoimmune diseases result from an immune system-mediated attack on one’s own body tissues. In normal development, an organ called the thymus introduces immune cells to the body’s normal proteins. This process is called negative selection, as those immune cells that recognize normal proteins are deleted. If cells evade this process, those that recognize normal proteins enter into circulation, where they can attack body tissues. The thymus is also important for activating T-cells that recognize foreign proteins.
As the figure below shows, immune cells typically originate in the bone marrow. Some immune cells, called T-cells, then go to the thymus for negative selection. Those that survive negative selection, enter into general circulation to fight infection. Other cells, called B-cells, directly enter general circulation from the bone marrow. It is a breakdown in this carefully orchestrated process that leads to autoimmune disease, such as type 1 diabetes.

Which of the following constitutes a loss of innate immunity in an immunocompromised patient?
The immune system comprises more than what you might initially expect. Intact skin is an important part of innate immunity, while all the other choices listed are more precisely components of the adaptive immune system. T-cells and B-cells are not involved in innate immunity.
The immune system comprises more than what you might initially expect. Intact skin is an important part of innate immunity, while all the other choices listed are more precisely components of the adaptive immune system. T-cells and B-cells are not involved in innate immunity.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Hypersensitivity reactions occur when body tissues are affected by an abnormal immune reaction. The result is damage to normal tissues and clinical illness. A peanut allergy is an example of a hypersensitivity reaction, but there are three additional broad classes.
One class involves the abnormal production or deposition of antibodies. Antibodies are B-cell derived molecules that normally adhere to pathogens, rendering them unable to continue an infection. When antibodies are produced against normal tissues, however, disease can result. Figure 1 depicts a schematic structure of an antibody.
Antibodies can be divided into two peptide chains: heavy and light. Heavy chains form the backbone of the antibody, and are attached to light chains via covalent bonding. Each heavy and light chain is then further divided into constant and variable regions. Variable regions exhibit molecular variety, generating a unique chemical identity for each antibody. These unique patterns help guarantee that the body can produce antibodies to recognize many possible molecular patterns on invading pathogens.
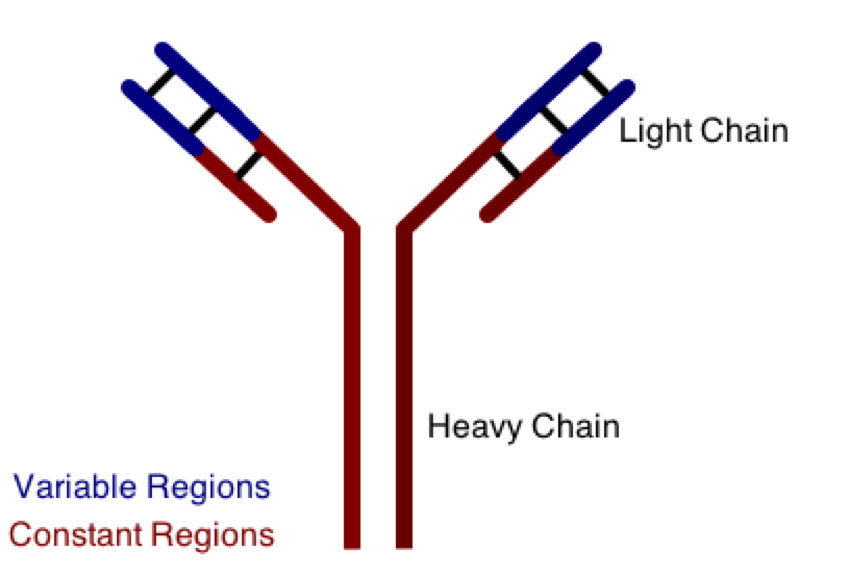
An antibody response is similar to an inflammatory response in that:
I. They are both innate immune responses
II. They are both most effective immediately following the first infection with a pathogen
III. They are both dependent on chemical mediators, such as cytokines, for function
Hypersensitivity reactions occur when body tissues are affected by an abnormal immune reaction. The result is damage to normal tissues and clinical illness. A peanut allergy is an example of a hypersensitivity reaction, but there are three additional broad classes.
One class involves the abnormal production or deposition of antibodies. Antibodies are B-cell derived molecules that normally adhere to pathogens, rendering them unable to continue an infection. When antibodies are produced against normal tissues, however, disease can result. Figure 1 depicts a schematic structure of an antibody.
Antibodies can be divided into two peptide chains: heavy and light. Heavy chains form the backbone of the antibody, and are attached to light chains via covalent bonding. Each heavy and light chain is then further divided into constant and variable regions. Variable regions exhibit molecular variety, generating a unique chemical identity for each antibody. These unique patterns help guarantee that the body can produce antibodies to recognize many possible molecular patterns on invading pathogens.

An antibody response is similar to an inflammatory response in that:
I. They are both innate immune responses
II. They are both most effective immediately following the first infection with a pathogen
III. They are both dependent on chemical mediators, such as cytokines, for function
Cytokines are important immune mediators, and are components of both adaptive and innate immunity. B- and T-lymphocytes are mediators of adaptive immunity, while inflammation is a non-specific innate immune response to a pathogen. While innate immunity, such as the inflammatory response, is active immediately following an infection, adaptive immunity requires a previous exposure to the pathogen to become most effective. The body must already recognize the invading antigen in order to activate the antibody response.
Statement I is false, statement II is false, and statement III is true.
Cytokines are important immune mediators, and are components of both adaptive and innate immunity. B- and T-lymphocytes are mediators of adaptive immunity, while inflammation is a non-specific innate immune response to a pathogen. While innate immunity, such as the inflammatory response, is active immediately following an infection, adaptive immunity requires a previous exposure to the pathogen to become most effective. The body must already recognize the invading antigen in order to activate the antibody response.
Statement I is false, statement II is false, and statement III is true.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is not a component of innate immunity?
Which of the following is not a component of innate immunity?
The innate immune system defends against pathogens, even without identifying what the pathogens are. Innate immunity includes physical and chemical barriers, such as the skin and stomach acid, which can kill some bacteria or prevent their entry into the body. Macrophages are responsible for phagocytosis of foreign pathogens without antibody mediation. Mast cells release histamine in response to infection or injury. Plasma cells, however, are mature B-cells that secrete antibodies in response to initiation of the adaptive immune response.
The innate immune system defends against pathogens, even without identifying what the pathogens are. Innate immunity includes physical and chemical barriers, such as the skin and stomach acid, which can kill some bacteria or prevent their entry into the body. Macrophages are responsible for phagocytosis of foreign pathogens without antibody mediation. Mast cells release histamine in response to infection or injury. Plasma cells, however, are mature B-cells that secrete antibodies in response to initiation of the adaptive immune response.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is not part of the adaptive immune response?
Which of the following is not part of the adaptive immune response?
The adaptive immune system responds specifically to antigens on the bacteria, virus, or parasite surface. The adaptive immune response includes B- and T-cells, eosinophils, and basophils.
Monocytes differentiate into macrophages in response to infection or injury; they do not respond to specific antigens, and are not involved in the adaptive immune response.
Macrophages phagocytose viruses and bacteria and present their antigens to helper T-cells. Helper T-cells identify the presented antigen and activate B-cells to produce antibodies against the specific antigens. Eosinophils, basophils, additional macrophages, and killer T-cells can then respond to the antibodies to help defend against invading bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
The adaptive immune system responds specifically to antigens on the bacteria, virus, or parasite surface. The adaptive immune response includes B- and T-cells, eosinophils, and basophils.
Monocytes differentiate into macrophages in response to infection or injury; they do not respond to specific antigens, and are not involved in the adaptive immune response.
Macrophages phagocytose viruses and bacteria and present their antigens to helper T-cells. Helper T-cells identify the presented antigen and activate B-cells to produce antibodies against the specific antigens. Eosinophils, basophils, additional macrophages, and killer T-cells can then respond to the antibodies to help defend against invading bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
In the event of re-infection with the same pathogen, which immune cell allows for a quick response?
In the event of re-infection with the same pathogen, which immune cell allows for a quick response?
Memory B-cells are differentiated B-cells that specifically allow for a quick response to re-infection with the same antigen. The memory B-cells proliferate after coming into contact with an antigen that they recognize, spawning plasma cells that can secrete antibodies into circulation. Helper T-cells activate immature B-cells, while natural killer cells release perforin to kill invading bacteria.
Memory B-cells are differentiated B-cells that specifically allow for a quick response to re-infection with the same antigen. The memory B-cells proliferate after coming into contact with an antigen that they recognize, spawning plasma cells that can secrete antibodies into circulation. Helper T-cells activate immature B-cells, while natural killer cells release perforin to kill invading bacteria.
Compare your answer with the correct one above