Lymphoid Organs
Practice Questions
MCAT Biology › Lymphoid Organs
Which of these is a lymphoid organ that is active in young children, but decreases in size and importance in adulthood?
Which lymphoid organ is the site of erythrocyte, leukocyte, and lymphocyte production?
The surface of which lymphoid organ is covered with stratified squamous epithelium and located at the entrance to the oropharynx?
The lymphoid tissues are responsible for creating, storing, and processing lymphocytes, which are essentially the effector cells of the immune system. Which of the following is a lymphoid structure that is also responsible for recycling old red blood cells?
Which of the following is NOT a part of the lymphatic system?
What lymphoid organ is one of the primary sites of cancer metastasis?
Which of the following are you most likely to find in the medulla of a lymph node?
Destruction of the lymph nodes would most likely affect the immune system in which way?
Hypersensitivity reactions occur when body tissues are affected by an abnormal immune reaction. The result is damage to normal tissues and clinical illness. A peanut allergy is an example of a hypersensitivity reaction, but there are three additional broad classes.
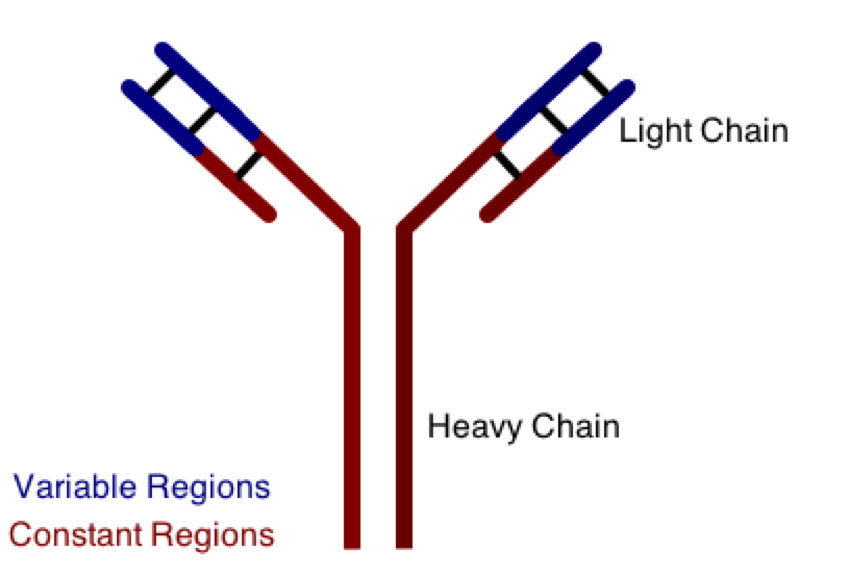
One class involves the abnormal production or deposition of antibodies. Antibodies are B-cell derived molecules that normally adhere to pathogens, rendering them unable to continue an infection. When antibodies are produced against normal tissues, however, disease can result. Figure 1 depicts a schematic structure of an antibody.
Antibodies can be divided into two peptide chains: heavy and light. Heavy chains form the backbone of the antibody, and are attached to light chains via covalent bonding. Each heavy and light chain is then further divided into constant and variable regions. Variable regions exhibit molecular variety, generating a unique chemical identity for each antibody. These unique patterns help guarantee that the body can produce antibodies to recognize many possible molecular patterns on invading pathogens.
Antibodies and antigens interact in secondary lymphoid tissue, such as the spleen. In addition to its role in promoting this interaction, what is the primary function of the spleen?
Which of the following is a primary lymphoid structure?
I. Thymus
II. Spleen
III. Lymph node