Antibodies and Antigens
Practice Questions
MCAT Biology › Antibodies and Antigens
An influenza vaccination administered through injection would be categorized as what type of immunization?
Hypersensitivity reactions occur when body tissues are affected by an abnormal immune reaction. The result is damage to normal tissues and clinical illness. A peanut allergy is an example of a hypersensitivity reaction, but there are three additional broad classes.
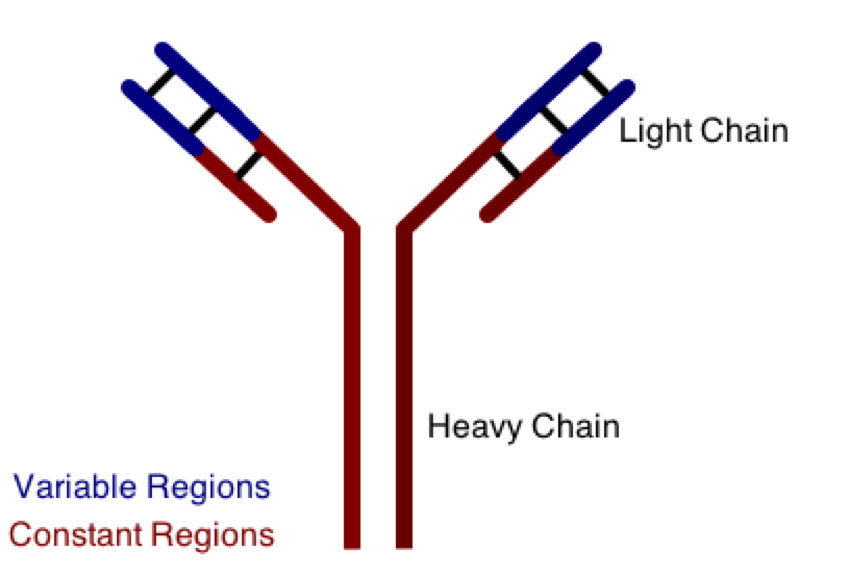
One class involves the abnormal production or deposition of antibodies. Antibodies are B-cell derived molecules that normally adhere to pathogens, rendering them unable to continue an infection. When antibodies are produced against normal tissues, however, disease can result. Figure 1 depicts a schematic structure of an antibody.
Antibodies can be divided into two peptide chains: heavy and light. Heavy chains form the backbone of the antibody, and are attached to light chains via covalent bonding. Each heavy and light chain is then further divided into constant and variable regions. Variable regions exhibit molecular variety, generating a unique chemical identity for each antibody. These unique patterns help guarantee that the body can produce antibodies to recognize many possible molecular patterns on invading pathogens.
Before antibodies enter into circulation, they exist as B-cell receptors (BCRs). BCRs are transmembrane proteins that are identical to the antibodies that exist in free circulation, with the exception of one component. Which component is likely present in BCRs, but not in antibodies in solution with blood?
Type 1 diabetes is a well-understood autoimmune disease. Autoimmune diseases result from an immune system-mediated attack on one’s own body tissues. In normal development, an organ called the thymus introduces immune cells to the body’s normal proteins. This process is called negative selection, as those immune cells that recognize normal proteins are deleted. If cells evade this process, those that recognize normal proteins enter into circulation, where they can attack body tissues. The thymus is also important for activating T-cells that recognize foreign proteins.
As the figure below shows, immune cells typically originate in the bone marrow. Some immune cells, called T-cells, then go to the thymus for negative selection. Those that survive negative selection, enter into general circulation to fight infection. Other cells, called B-cells, directly enter general circulation from the bone marrow. It is a breakdown in this carefully orchestrated process that leads to autoimmune disease, such as type 1 diabetes.

There are many ways that the body's immune system can attack its own tissues in autoimmune disease. A scientist discovers that in type 1 diabetes, antibodies play a key role in attracting lymphocytes to normal tissue, which is then damaged or destroyed. What kinds of cells typically produce antibodies?
I. T-cells
II. B-cells
III. Macrophages
Which of the following combinations might yield the necessity of blood transfusion for a new born baby?
Sexually transmitted diseases are a common problem among young people in the United States. One of the more common diseases is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which leads to inflammation and purulent discharge in the male and female reproductive tracts.
The bacterium has a number of systems to evade host defenses. Upon infection, it uses pili to adhere to host epithelium. The bacterium also uses an enzyme, gonococcal sialyltransferase, to transfer a sialyic acid residue to a gonococcal surface lipooligosaccharide (LOS). A depiction of this can be seen in Figure 1. The sialyic acid residue mimics the protective capsule found on other bacterial species.
Once infection is established, Neisseria preferentially infects columnar epithelial cells in the female reproductive tract, and leads to a loss of cilia on these cells. Damage to the reproductive tract can result in pelvic inflammatory disease, which can complicate pregnancies later in the life of the woman.

In an immune response to an organism like Neisseria, humans will often make use of antbodies. What is true of antibodies?
Which of the following statements is false concerning the humoral immune system?
Which immunoglobulin is the predominant subclass that can cross the placenta?
A patient is admitted to the hospital needing a blood transfusion. The patient has type A negative blood. Which of the following is true?
Hypersensitivity reactions occur when body tissues are affected by an abnormal immune reaction. The result is damage to normal tissues and clinical illness. A peanut allergy is an example of a hypersensitivity reaction, but there are three additional broad classes.
One class involves the abnormal production or deposition of antibodies. Antibodies are B-cell derived molecules that normally adhere to pathogens, rendering them unable to continue an infection. When antibodies are produced against normal tissues, however, disease can result. Figure 1 depicts a schematic structure of an antibody.
Antibodies can be divided into two peptide chains: heavy and light. Heavy chains form the backbone of the antibody, and are attached to light chains via covalent bonding. Each heavy and light chain is then further divided into constant and variable regions. Variable regions exhibit molecular variety, generating a unique chemical identity for each antibody. These unique patterns help guarantee that the body can produce antibodies to recognize many possible molecular patterns on invading pathogens.

Unlike B-cells, T-cells do not make antibodies. T-cells are important in the execution of cytotoxic immunity, such as neutralizing virus-infected cells. A scientist is studying the T-cell response in a mammal, and finds that his CD8+ T-cells are interacting with a surface protein found on many different types of cells in his model organism. This protein is most likely __________.
Cholera is a disease caused by vibrio cholerae, a bacteria which enters the body through the digestive tract. The bacteria is absorbed by the small intestine and enters the blood stream. Which of the following antibodies would be most effective at preventing cholera?