Genetics Principles - High School Biology
Card 0 of 20
Hemophilia is a sex-linked recessive mutation found on the X-chromosome. A healthy male mates with a female that is a carrier for the disease.
Which of the following statements is true?
Hemophilia is a sex-linked recessive mutation found on the X-chromosome. A healthy male mates with a female that is a carrier for the disease.
Which of the following statements is true?
The disease is recessive and found on the X-chromosome. Remember that males only have one X-chromosome, while females have two. As a result, males only require one mutant allele to express a recessive phenotype, while females need to have two mutant alleles in order to have hemophilia.
In this scenario, both parents are healthy, but the female is a carrier for the disease. This means that one of her alleles codes for hemophilia.
Parents: XXh x XY
Since daughters will need two copies of the mutant allele, they will all be healthy; by default they will receive the healthy X-chromosome from the father.
Daughters: XX or XXh; all healthy phenotype
Sons, however, have a 50% chance of receiving the mutant allele from the mother, because the father will always contribute the Y-chromosome to sons.
Sons: XY or XhY ; half healthy, half hemophilic
As a result, 50% of the sons will have hemophilia.
The disease is recessive and found on the X-chromosome. Remember that males only have one X-chromosome, while females have two. As a result, males only require one mutant allele to express a recessive phenotype, while females need to have two mutant alleles in order to have hemophilia.
In this scenario, both parents are healthy, but the female is a carrier for the disease. This means that one of her alleles codes for hemophilia.
Parents: XXh x XY
Since daughters will need two copies of the mutant allele, they will all be healthy; by default they will receive the healthy X-chromosome from the father.
Daughters: XX or XXh; all healthy phenotype
Sons, however, have a 50% chance of receiving the mutant allele from the mother, because the father will always contribute the Y-chromosome to sons.
Sons: XY or XhY ; half healthy, half hemophilic
As a result, 50% of the sons will have hemophilia.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Rett syndrome is a sex-linked dominant disease found on the X-chromosome. If the offspring of a certain cross have a 50% chance of receiving the disease, regardless of gender, which of the following statements is true?
Rett syndrome is a sex-linked dominant disease found on the X-chromosome. If the offspring of a certain cross have a 50% chance of receiving the disease, regardless of gender, which of the following statements is true?
Since the disease is found on the X-chromosome, we need to find the scenario in which both sons and daughters have an equal 50% probability of getting the disease. Regardless of gender, mothers will always donate one X-chromosome to the offspring. If the mother is heterozygous for the disease, she has a 50% chance of giving an offspring the diseased allele. As a result, a heterozygous mother will have children that display the disease in the observed ratio.
Parents: XXR x XY
Offspring: XX, XXR, XY, XRY
Note that this ratio of expression is only possible when the allele for the disorder is dominant; otherwise the heterozygous female would be a carrier, and not express the disorder.
Since the disease is found on the X-chromosome, we need to find the scenario in which both sons and daughters have an equal 50% probability of getting the disease. Regardless of gender, mothers will always donate one X-chromosome to the offspring. If the mother is heterozygous for the disease, she has a 50% chance of giving an offspring the diseased allele. As a result, a heterozygous mother will have children that display the disease in the observed ratio.
Parents: XXR x XY
Offspring: XX, XXR, XY, XRY
Note that this ratio of expression is only possible when the allele for the disorder is dominant; otherwise the heterozygous female would be a carrier, and not express the disorder.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Colorblindness is a sex-linked recessive condition. If a woman is a carrier for the colorblind trait has a child with a man that does not have the trait, what percent chance will their first child (regardless if it is a girl or boy) be colorblind?
Colorblindness is a sex-linked recessive condition. If a woman is a carrier for the colorblind trait has a child with a man that does not have the trait, what percent chance will their first child (regardless if it is a girl or boy) be colorblind?
First, we have to look at the genotype of the mother and father. The mother is XX, because she is a woman, while the father is XY. The mother is a carrier for the gene, which means she has the traits on one chromosome, but since it is recessive she does not express it physically (she is not colorblind). Therefore, we can denote her genotype to be X Xc (with c being the color blind trait). When we cross the mother and the father (XY), we receive the following possibilities for their children: XX , XcX, XY, XcY. The trait shows up twice, they could have a girl that is a carrier, but no female will express colorblindness from this couple. If they have a boy, there is a 50% chance that he will be color blind (remember, males only have 1 chromosome so they will inherit genes directly from their mother). But, the question is asking what percent of their children will be colorblind, regardless of it being a girl or boy, therefore the answer is 25%.
First, we have to look at the genotype of the mother and father. The mother is XX, because she is a woman, while the father is XY. The mother is a carrier for the gene, which means she has the traits on one chromosome, but since it is recessive she does not express it physically (she is not colorblind). Therefore, we can denote her genotype to be X Xc (with c being the color blind trait). When we cross the mother and the father (XY), we receive the following possibilities for their children: XX , XcX, XY, XcY. The trait shows up twice, they could have a girl that is a carrier, but no female will express colorblindness from this couple. If they have a boy, there is a 50% chance that he will be color blind (remember, males only have 1 chromosome so they will inherit genes directly from their mother). But, the question is asking what percent of their children will be colorblind, regardless of it being a girl or boy, therefore the answer is 25%.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Phil is diagnosed with X-linked muscular dystrophy (recessive). His parents do not have the disease. What is the chance that his sister also has muscular dystrophy?
Phil is diagnosed with X-linked muscular dystrophy (recessive). His parents do not have the disease. What is the chance that his sister also has muscular dystrophy?
Since Phil is male, he has one x-chromosome and one y-chromosome. Muscular dystrophy is x-linked recessive, which means his x-chromosome carries the disease allele. He must have inherited this x-chromosome from his mother because his father passed his y-chromosome. Since we know that Phil's parents are not affected, we know that his mother is a carrier of the disease. Phil's sister has two x-chromosomes: one from their mother and one from their father. In order to express a recessive trait, all copies of that gene must be the disease allele. Phil's father can only pass on a healthy x-chromosome to his daughter, and Phil's mother has a 50% chance of passing on her healthy x-chromosome. Thus, there is no chance that Phil's sister will be affected with the disease; there is a 50% chance that she is a carrier, though.
Since Phil is male, he has one x-chromosome and one y-chromosome. Muscular dystrophy is x-linked recessive, which means his x-chromosome carries the disease allele. He must have inherited this x-chromosome from his mother because his father passed his y-chromosome. Since we know that Phil's parents are not affected, we know that his mother is a carrier of the disease. Phil's sister has two x-chromosomes: one from their mother and one from their father. In order to express a recessive trait, all copies of that gene must be the disease allele. Phil's father can only pass on a healthy x-chromosome to his daughter, and Phil's mother has a 50% chance of passing on her healthy x-chromosome. Thus, there is no chance that Phil's sister will be affected with the disease; there is a 50% chance that she is a carrier, though.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Bill recently has been diagnosed with Fabry disease (X-linked recessive). Bill is planned on getting married to Emily. There is no history of Fabry disease in Emily's family. They both seek a genetic counseling for their future children. What is the percent chance of Bill and Emily having a baby girl with Fabry disease?
Bill recently has been diagnosed with Fabry disease (X-linked recessive). Bill is planned on getting married to Emily. There is no history of Fabry disease in Emily's family. They both seek a genetic counseling for their future children. What is the percent chance of Bill and Emily having a baby girl with Fabry disease?
Since Bill is has the disease and is a male, his chromosomes will appear as: XY. Since Emily does not have the disease and there is no family history of the disease, her chromosomes will appear as: XX. The chances of Bill and Emily having a baby girl is 0.5. This is because they can either have a boy (0.5) or a girl (0.5). These events are independent of each other.
0.5 (baby girl) * 1 (X-chromosome from Bill because he will not donate a Y-chromosome to a female) * 1 (X-chromosome from Emily-does not matter which X-chromosome is given since both are normal) * 0 (No matter what, the baby girl cannot have Fabry because it is an X-linked recessive disease. To get the disease, you would need XX. This is not genotypically possible with the genotypes of the parents provided).

Since Bill is has the disease and is a male, his chromosomes will appear as: XY. Since Emily does not have the disease and there is no family history of the disease, her chromosomes will appear as: XX. The chances of Bill and Emily having a baby girl is 0.5. This is because they can either have a boy (0.5) or a girl (0.5). These events are independent of each other.
0.5 (baby girl) * 1 (X-chromosome from Bill because he will not donate a Y-chromosome to a female) * 1 (X-chromosome from Emily-does not matter which X-chromosome is given since both are normal) * 0 (No matter what, the baby girl cannot have Fabry because it is an X-linked recessive disease. To get the disease, you would need XX. This is not genotypically possible with the genotypes of the parents provided).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
If a somatic cell of a diploid organism contains eight chromosomes during interphase, which of the following must be true?
If a somatic cell of a diploid organism contains eight chromosomes during interphase, which of the following must be true?
A somatic cell is a non-sex cell. During interphase (i.e. not during mitosis), a somatic cell of a diploid organism will be in its 2n state with two copies of each chromosome. A diploid somatic cell with eight chromosomes indicates that 2n=8.
When a somatic cell undergoes mitosis it first replicates its chromosomes, so in metaphase it will have sixteen chromatids. At this point, each of the eight chromosomes will be composed of two identical chromatids, for a total of sixteen.
When a germ cell begins meiosis, it also replicates the chromosomes and has sixteen chromatids until meiosis I is complete. During meiosis II, the two daughter cells from meiosis I each contain four chromosomes, each with two chromatids, for a total of eight chromatids. These chromatids are split during meiosis II, giving you four gametes that each have four chromosomes, each made of only one chromatid. This means that the gametes are haploid, since they contain only half of the original genetic material (n=4).
The transition from diploid to haploid occurs after meiosis I, since the first daughter cells only contain one copy of each chromosome after the tetrads are separated.
A somatic cell is a non-sex cell. During interphase (i.e. not during mitosis), a somatic cell of a diploid organism will be in its 2n state with two copies of each chromosome. A diploid somatic cell with eight chromosomes indicates that 2n=8.
When a somatic cell undergoes mitosis it first replicates its chromosomes, so in metaphase it will have sixteen chromatids. At this point, each of the eight chromosomes will be composed of two identical chromatids, for a total of sixteen.
When a germ cell begins meiosis, it also replicates the chromosomes and has sixteen chromatids until meiosis I is complete. During meiosis II, the two daughter cells from meiosis I each contain four chromosomes, each with two chromatids, for a total of eight chromatids. These chromatids are split during meiosis II, giving you four gametes that each have four chromosomes, each made of only one chromatid. This means that the gametes are haploid, since they contain only half of the original genetic material (n=4).
The transition from diploid to haploid occurs after meiosis I, since the first daughter cells only contain one copy of each chromosome after the tetrads are separated.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
In a dihybrid cross (AaBb x AaBb), how many total genotypes are possible in the offspring?
In a dihybrid cross (AaBb x AaBb), how many total genotypes are possible in the offspring?
The alleles for gene A assort independently from the alleles of gene B, meaning that the genotype for one does not affect the genotype of the other. Even though there are two genes, we can solve this problem by answering the question separately for the two genes.
There are three possible genotypes with respect to the A gene (AA, Aa, aa) and three possible genotypes with respect to the B gene (BB, Bb, bb). Since genes A and B assort independently, the possible offspring will be the product of the possibilities for each separate gene.

Listed out, these genotypes are: AABB, AABb, AaBB, AAbb, AaBb, aaBB, Aabb, aaBb, aabb.
The alleles for gene A assort independently from the alleles of gene B, meaning that the genotype for one does not affect the genotype of the other. Even though there are two genes, we can solve this problem by answering the question separately for the two genes.
There are three possible genotypes with respect to the A gene (AA, Aa, aa) and three possible genotypes with respect to the B gene (BB, Bb, bb). Since genes A and B assort independently, the possible offspring will be the product of the possibilities for each separate gene.
Listed out, these genotypes are: AABB, AABb, AaBB, AAbb, AaBb, aaBB, Aabb, aaBb, aabb.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Traits (alleles) are separated from one another during formation of gametes and are transmitted independently of one another according to __________.
Traits (alleles) are separated from one another during formation of gametes and are transmitted independently of one another according to __________.
During metaphase of meiosis, chromosomes form tetrads at the center of the cell. These tetrads are formed from pairs of homologous chromosomes. One chromosomes came from the organism's mother and the other from its father. During alignment, these chromosomes are arranged randomly, such that each gamete will have a combination of maternal and paternal DNA from the organism. This random mixing of DNA during gamete formation is known as the law of independent assortment, and plays a key role in diversifying the genetic background of offspring that form from the gamete.
During metaphase of meiosis, chromosomes form tetrads at the center of the cell. These tetrads are formed from pairs of homologous chromosomes. One chromosomes came from the organism's mother and the other from its father. During alignment, these chromosomes are arranged randomly, such that each gamete will have a combination of maternal and paternal DNA from the organism. This random mixing of DNA during gamete formation is known as the law of independent assortment, and plays a key role in diversifying the genetic background of offspring that form from the gamete.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What are chromosomes made of?
What are chromosomes made of?
Strings of DNA coiled around histone proteins make up chromatin. Chromatin condenses into chromatids. Two chromatids line up at the centrosome during cell replication, which results in X-shaped chromosomes.
Strings of DNA coiled around histone proteins make up chromatin. Chromatin condenses into chromatids. Two chromatids line up at the centrosome during cell replication, which results in X-shaped chromosomes.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A collection of an individual’s genes—inherited alleles—is defined as which of the following?
A collection of an individual’s genes—inherited alleles—is defined as which of the following?
Genotype is defined as the sequence of genetic makeup that determines specific characteristics and traits—phenotypes—of an individual. The genome is defined as the collection of an individual’s genes and consists of DNA. A genotype is expressed when information in DNA makes RNA and protein molecules, which determine the structure and function of cells; however, a genotype can also refer to genes carried by an individual, which includes mutations. Last, phenotype refers to observable physical characteristics within an individual. Some phenotypical traits are determined by the genotype, while others are shaped by environmental factors.
Genotype is defined as the sequence of genetic makeup that determines specific characteristics and traits—phenotypes—of an individual. The genome is defined as the collection of an individual’s genes and consists of DNA. A genotype is expressed when information in DNA makes RNA and protein molecules, which determine the structure and function of cells; however, a genotype can also refer to genes carried by an individual, which includes mutations. Last, phenotype refers to observable physical characteristics within an individual. Some phenotypical traits are determined by the genotype, while others are shaped by environmental factors.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A plant with red flowers is crossed with a plant with white flowers. The resulting offspring have pink flowers. What term describes the dominance of this trait?
A plant with red flowers is crossed with a plant with white flowers. The resulting offspring have pink flowers. What term describes the dominance of this trait?
A phenotypic "blending" of two traits is referred to as incomplete dominance, indicating that neither trait is truly dominant over the other. Instead of one color overpowering expression of the other, both colors are expressed simultaneously.
Codominance suggests that both phenotypes are dominant, but cannot be expressed at the same time. The result of codominance would be regions of dominant red expression and regions of dominant white expression, resulting in spots rather than blending.
A phenotypic "blending" of two traits is referred to as incomplete dominance, indicating that neither trait is truly dominant over the other. Instead of one color overpowering expression of the other, both colors are expressed simultaneously.
Codominance suggests that both phenotypes are dominant, but cannot be expressed at the same time. The result of codominance would be regions of dominant red expression and regions of dominant white expression, resulting in spots rather than blending.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
If red (R) and white (r) are codominant alleles that determine flower color, what phenotypes are possible for this gene?
If red (R) and white (r) are codominant alleles that determine flower color, what phenotypes are possible for this gene?
The possible genotypes for this trait are RR, Rr, and rr. To determine the answer, we must find the phenotype that corresponds to each genotype.
We know that RR is red and rr is white, since these genotypes are homozygous.
Now you must determine if Rr is red, white, or some other phenotype. Codominance means that both phenotypes show simultaneously, so the heterozygote would be both red and white, which is a distinct third phenotype. These organisms would show spots or splotches of each color.
This gives three total phenotypes: red, white, and red-white spotted.
A pink phenotype would only show in instances of incomplete dominance. When an organism is heterozygous for alleles that show incomplete dominance, an intermediate of blended phenotype will be seen.
The possible genotypes for this trait are RR, Rr, and rr. To determine the answer, we must find the phenotype that corresponds to each genotype.
We know that RR is red and rr is white, since these genotypes are homozygous.
Now you must determine if Rr is red, white, or some other phenotype. Codominance means that both phenotypes show simultaneously, so the heterozygote would be both red and white, which is a distinct third phenotype. These organisms would show spots or splotches of each color.
This gives three total phenotypes: red, white, and red-white spotted.
A pink phenotype would only show in instances of incomplete dominance. When an organism is heterozygous for alleles that show incomplete dominance, an intermediate of blended phenotype will be seen.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Yellow, blue, and red alleles all show incomplete dominance for flower color in a diploid plant species. How many phenotypes for flower color are possible in this species?
Yellow, blue, and red alleles all show incomplete dominance for flower color in a diploid plant species. How many phenotypes for flower color are possible in this species?
In the species the entire range of phenotypes will be expressed. Diploid organisms have two alleles of each gene, so the plant could be homozygous for any of the alleles or it could have any heterozygous combinations.
First, we can identify three homozygous phenotypes: YY is yellow, BB is blue, and RR is red.
Now we need to identify the heterozygous phenotypes. Since the alleles show incomplete dominance, these phenotypes will be blended. YB will be green, YR will be orange, and BR will be purple.
This gives a total of six possible allele combinations and six different phenotypes.
In the species the entire range of phenotypes will be expressed. Diploid organisms have two alleles of each gene, so the plant could be homozygous for any of the alleles or it could have any heterozygous combinations.
First, we can identify three homozygous phenotypes: YY is yellow, BB is blue, and RR is red.
Now we need to identify the heterozygous phenotypes. Since the alleles show incomplete dominance, these phenotypes will be blended. YB will be green, YR will be orange, and BR will be purple.
This gives a total of six possible allele combinations and six different phenotypes.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Two pure breeding plants are crossed. One plant has red flowers and the other has white flowers.
What phenotype(s) would be seen in the first generation if flower color exhibited incomplete dominance?
Two pure breeding plants are crossed. One plant has red flowers and the other has white flowers.
What phenotype(s) would be seen in the first generation if flower color exhibited incomplete dominance?
The genotypes of the offspring can be determined by crossing the red flowers, RR, with the white flowers, rr.
RR x rr
Offspring: all offspring are Rr.
Incomplete dominance means that neither color shows dominance in the hybrid generation. This means that instead of solid red or solid white flowers, the heterozygous plants will display a mixture of both colors. Since the entire first generation will be heterozygous for the color trait, they will all be pink (a mix of white and red).
The genotypes of the offspring can be determined by crossing the red flowers, RR, with the white flowers, rr.
RR x rr
Offspring: all offspring are Rr.
Incomplete dominance means that neither color shows dominance in the hybrid generation. This means that instead of solid red or solid white flowers, the heterozygous plants will display a mixture of both colors. Since the entire first generation will be heterozygous for the color trait, they will all be pink (a mix of white and red).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Black fur (A) is codominant with white fur (a) and brown eyes (B) are dominant to blue eyes (b) in mice. Two mice are heterozygous for both traits. If these mice are crossed, what color of fur will the offspring with genotype Aa express?
Black fur (A) is codominant with white fur (a) and brown eyes (B) are dominant to blue eyes (b) in mice. Two mice are heterozygous for both traits. If these mice are crossed, what color of fur will the offspring with genotype Aa express?
Codominance means that more than one type of dominant allele for the same gene is present. If both black and white fur are dominant, then heterozygous (Aa) offspring would be spotted with black and white.
Note this is a different expression pattern from incomplete dominance, in which a blending of phenotypes occurs.
Codominance means that more than one type of dominant allele for the same gene is present. If both black and white fur are dominant, then heterozygous (Aa) offspring would be spotted with black and white.
Note this is a different expression pattern from incomplete dominance, in which a blending of phenotypes occurs.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Two mice are heterozygous for both fur color and eye color. If these mice were crossed and all offspring have dark brown, almost-black fur, what is the best explanation?
Two mice are heterozygous for both fur color and eye color. If these mice were crossed and all offspring have dark brown, almost-black fur, what is the best explanation?
Incomplete dominance is when more than one type of dominant allele for the same gene is present. If black and brown alleles are incompletely dominant, they "compete" for expression, which produces offspring with a combination of the two colors.
Note that this pattern difference from codominance, in which the phenotypes will be present in separate spots of blotches.
Incomplete dominance is when more than one type of dominant allele for the same gene is present. If black and brown alleles are incompletely dominant, they "compete" for expression, which produces offspring with a combination of the two colors.
Note that this pattern difference from codominance, in which the phenotypes will be present in separate spots of blotches.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is an example of codominance?
Which of the following is an example of codominance?
Codominance is evidenced when the phenotypes of both parents show up in the offspring. A dog that has fur that consists of colors of both parents will be an example of codominance. Only one trait can be expressed at a time, since they are both dominant phenotypes. This results in regions of one dominant allele and regions of the other, showing a spotted or mottled pattern.
Incomplete dominance occurs when neither trait is truly dominant over the other. This means that both traits can be expressed in the same regions, resulting a blending of two phenotypes. If a white and black dog produce a gray offspring, this is an example of incomplete dominance.
The answer that suggests a red offspring from a black parent and tan parent could result from one of two scenarios. The first possibility is that there are three alleles for color, with red recessive to both black and tan. Both parents carry the red allele, but do not display it, and then pass it to the offspring. Something similar happens with the O blood type. The other possibility is that red color is a new mutation.
Codominance is evidenced when the phenotypes of both parents show up in the offspring. A dog that has fur that consists of colors of both parents will be an example of codominance. Only one trait can be expressed at a time, since they are both dominant phenotypes. This results in regions of one dominant allele and regions of the other, showing a spotted or mottled pattern.
Incomplete dominance occurs when neither trait is truly dominant over the other. This means that both traits can be expressed in the same regions, resulting a blending of two phenotypes. If a white and black dog produce a gray offspring, this is an example of incomplete dominance.
The answer that suggests a red offspring from a black parent and tan parent could result from one of two scenarios. The first possibility is that there are three alleles for color, with red recessive to both black and tan. Both parents carry the red allele, but do not display it, and then pass it to the offspring. Something similar happens with the O blood type. The other possibility is that red color is a new mutation.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A F1 generation flower has red and white petals. One parent flower was red and the other was white. This is an example of which of the following forms of inheritance?
A F1 generation flower has red and white petals. One parent flower was red and the other was white. This is an example of which of the following forms of inheritance?
In the example above, the flower has both red and white petals due to co-dominant inheritance pattern of the red and white petal alleles. If the flower’s phenotype was determined by incomplete dominance, the F1 hybrids would be in-between the parental phenotypes (i.e. if a red petal parent was crossed with a white petal parent, then the F1 generation would be pink). Polygenic inheritance occurs when two or more genes control one characteristic, such as skin color, eye color, and adult height.
In the example above, the flower has both red and white petals due to co-dominant inheritance pattern of the red and white petal alleles. If the flower’s phenotype was determined by incomplete dominance, the F1 hybrids would be in-between the parental phenotypes (i.e. if a red petal parent was crossed with a white petal parent, then the F1 generation would be pink). Polygenic inheritance occurs when two or more genes control one characteristic, such as skin color, eye color, and adult height.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A sugar flower has white petals, and is homozygous for this trait. Another sugar flower is homozygous for red petals. The white and red sugar flowers are crossed, and produce offspring with pink petals. Which of the following terms describes this type of inheritance?
A sugar flower has white petals, and is homozygous for this trait. Another sugar flower is homozygous for red petals. The white and red sugar flowers are crossed, and produce offspring with pink petals. Which of the following terms describes this type of inheritance?
Incomplete dominance is described by a phenotype that is not completely dominant over another. Therefore, it will be a "blending" of colors in the case of this question, therefore the petals are pink. Codominance is when both dominant traits are expressed, therefore if white was considered dominant and red was also a dominant trait, the petals would have spots of white and red, with no pink. Polygenic inheritance is described by one characteristic influenced by multiple genes, which is not the case in this problem. Finally, epistasis involves the suppression of genes, however in this problem color is not suppressed.
Incomplete dominance is described by a phenotype that is not completely dominant over another. Therefore, it will be a "blending" of colors in the case of this question, therefore the petals are pink. Codominance is when both dominant traits are expressed, therefore if white was considered dominant and red was also a dominant trait, the petals would have spots of white and red, with no pink. Polygenic inheritance is described by one characteristic influenced by multiple genes, which is not the case in this problem. Finally, epistasis involves the suppression of genes, however in this problem color is not suppressed.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
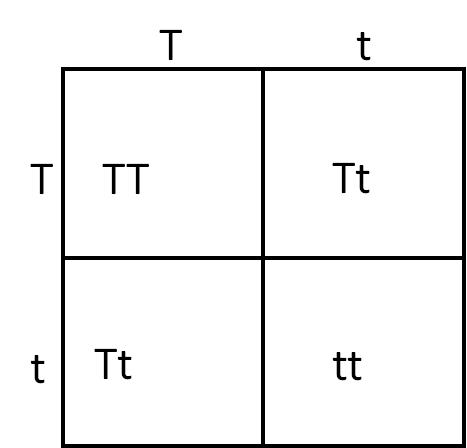
The trait "tall" is dominant (T) while "short" is recessive (t). If two parents are both heterozygous for the trait and have a child, what is the probability that the child would be phenotypically short?
The trait "tall" is dominant (T) while "short" is recessive (t). If two parents are both heterozygous for the trait and have a child, what is the probability that the child would be phenotypically short?
The problem can be solved using the following Punnett square. Since short is recessive, the only genotype that will result in a short appearance is tt. tt occurs one time on the Punnett square, out of four possible combinations; therefore, there is a 1-in-4 chance of giving birth to a short child, or 25%.
The problem can be solved using the following Punnett square. Since short is recessive, the only genotype that will result in a short appearance is tt. tt occurs one time on the Punnett square, out of four possible combinations; therefore, there is a 1-in-4 chance of giving birth to a short child, or 25%.
Compare your answer with the correct one above