Organic Chemistry - GRE Subject Test: Chemistry
Card 0 of 20

For which of the following acid-base reactions will the equilibrium lie on the left side?
For which of the following acid-base reactions will the equilibrium lie on the left side?
The pKa value indicates how strong an acid is, and acid strength increases as pKa decreases. The side of a reaction with a lower pKa is going to dissociate more, pushing the equilibrium over to the other side. The equilibrium will thus lie on the side with the HIGHER pKa.

Since the pKa of acetic acid (4.76) is higher than the pKa of trifluoroacetic acid (0), the reaction will shift to the left to reach equilibrium.
The pKa value indicates how strong an acid is, and acid strength increases as pKa decreases. The side of a reaction with a lower pKa is going to dissociate more, pushing the equilibrium over to the other side. The equilibrium will thus lie on the side with the HIGHER pKa.
Since the pKa of acetic acid (4.76) is higher than the pKa of trifluoroacetic acid (0), the reaction will shift to the left to reach equilibrium.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of these methods can be used to synthesize a secondary alcohol?
Which of these methods can be used to synthesize a secondary alcohol?
All of these methods can successfully synthesize secondary alcohols.
Lithium aluminum hydride and sodium borohydride are strong and weaker reducing agents, respectively. Both are able to reduce ketones to secondary alcohols.
Adding water and acid to an alkene (such as propene) results in Markovnikov addition of a hydroxyl group, also creating a secondary alcohol.
Grignard reagents (organometallic halides) add to the carbonyl carbon of an aldehyde, adding an alkane group and forming an alcohol product.
All of these methods can successfully synthesize secondary alcohols.
Lithium aluminum hydride and sodium borohydride are strong and weaker reducing agents, respectively. Both are able to reduce ketones to secondary alcohols.
Adding water and acid to an alkene (such as propene) results in Markovnikov addition of a hydroxyl group, also creating a secondary alcohol.
Grignard reagents (organometallic halides) add to the carbonyl carbon of an aldehyde, adding an alkane group and forming an alcohol product.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Acetaldehyde  undergoes a Wolf-Kishner reaction, which is the addition of hydrazine
undergoes a Wolf-Kishner reaction, which is the addition of hydrazine  with subsequent addition of a base and heat. In this reaction, the aldehyde is __________, resulting in a(n) __________ product.
with subsequent addition of a base and heat. In this reaction, the aldehyde is __________, resulting in a(n) __________ product.
Acetaldehyde 

The correct answer is that the aldehyde is reduced to an alkane. In viewing the final product, we see that acetaldehyde would be reduced to ethane. The reaction of any aldehyde or ketone with hydrazine and the subsequent addition of base and heat will result in that aldehyde or ketone being reduced to an alkane, and is referred to as the Wolf-Kishner reaction. The Wolf-Kishner reagent is a commonly tested reducing agent.
The correct answer is that the aldehyde is reduced to an alkane. In viewing the final product, we see that acetaldehyde would be reduced to ethane. The reaction of any aldehyde or ketone with hydrazine and the subsequent addition of base and heat will result in that aldehyde or ketone being reduced to an alkane, and is referred to as the Wolf-Kishner reaction. The Wolf-Kishner reagent is a commonly tested reducing agent.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

What reagent(s) will successfully complete the synthesis reaction shown above?

What reagent(s) will successfully complete the synthesis reaction shown above?
This is an example of a Grignard reagent reaction. Because we are adding three carbons to our chain, the Grignard reagent we need must have three carbons on it. We can therefore rule out methyl grignard and ethyl grignard.
N-propyl is the straight-chained 3-carbon alkane, while isopropyl is branched. Looking at our final product, we can see the carbon chain we have added is straight-chained, and thus N-propyl Grignard is the best option. Because Grignard reagents are relatively basic, we must add an hydronium ion workup to protonate our alcohol.
This is an example of a Grignard reagent reaction. Because we are adding three carbons to our chain, the Grignard reagent we need must have three carbons on it. We can therefore rule out methyl grignard and ethyl grignard.
N-propyl is the straight-chained 3-carbon alkane, while isopropyl is branched. Looking at our final product, we can see the carbon chain we have added is straight-chained, and thus N-propyl Grignard is the best option. Because Grignard reagents are relatively basic, we must add an hydronium ion workup to protonate our alcohol.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following can reduce an alkene to an alkane?
Which of the following can reduce an alkene to an alkane?
Neither lithium aluminum hydride, nor sodium borohydride will reduce C–C double bonds.
H2/Raney nickel and H2/Pd can each (individually) reduce an alkene to an alkane. Since both H2/Raney nickel and H2/Pd can reduce the alkene, the answer is both of those reagents. This is a catalytic hydrogenation reaction, and H2/Raney nickel not only reduces C–C double bonds, but also carbonyl compounds.
Neither lithium aluminum hydride, nor sodium borohydride will reduce C–C double bonds.
H2/Raney nickel and H2/Pd can each (individually) reduce an alkene to an alkane. Since both H2/Raney nickel and H2/Pd can reduce the alkene, the answer is both of those reagents. This is a catalytic hydrogenation reaction, and H2/Raney nickel not only reduces C–C double bonds, but also carbonyl compounds.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Identify the major organic product expected from the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2-methyl-2-pentanol.
Identify the major organic product expected from the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2-methyl-2-pentanol.
The initial compound is a five-carbon alkane chain with methyl and hydroxy groups on the second carbon. Dehydration involves the hydrogenation of the hydroxy group. That group then leaves, and a double bond is formed. Zaitsev's rule states that double bonds are more stable on more highly substituted carbons. The double bond forms across carbons two and three.
The initial compound is a five-carbon alkane chain with methyl and hydroxy groups on the second carbon. Dehydration involves the hydrogenation of the hydroxy group. That group then leaves, and a double bond is formed. Zaitsev's rule states that double bonds are more stable on more highly substituted carbons. The double bond forms across carbons two and three.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
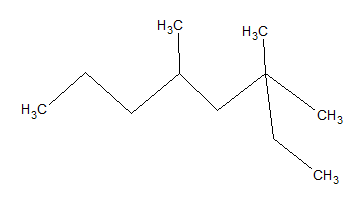
What is the IUPAC name of the given molecule?

What is the IUPAC name of the given molecule?
The longest carbon chain that can be formed is eight carbons. The base molecule is octane.
Using IUPAC rules, substituents should have the lowest possible numbers; thus, we start counting carbons from the right side rather than the left. If you count from the correct side, there are two methyl groups on carbon 3 and one on carbon 5. Thus, the name of the moleculue is 3,3,5-trimethyloctane.
The longest carbon chain that can be formed is eight carbons. The base molecule is octane.
Using IUPAC rules, substituents should have the lowest possible numbers; thus, we start counting carbons from the right side rather than the left. If you count from the correct side, there are two methyl groups on carbon 3 and one on carbon 5. Thus, the name of the moleculue is 3,3,5-trimethyloctane.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

How could you brominate the compound?

How could you brominate the compound?
The given molecule is an alkane. The only way to brominate an alkane is with bromine gas and UV light. The energy from the light serves to creat two radical bromines. These radicals are capable of bonding with alkanes. If the given compound were an alkene, either hydrobromic acid or bromine and peroxides would work.
The given molecule is an alkane. The only way to brominate an alkane is with bromine gas and UV light. The energy from the light serves to creat two radical bromines. These radicals are capable of bonding with alkanes. If the given compound were an alkene, either hydrobromic acid or bromine and peroxides would work.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The stereochemical pathway for the hydrogenation of an alkene with a metal catalyst, such as platinum, occurs via __________.
The stereochemical pathway for the hydrogenation of an alkene with a metal catalyst, such as platinum, occurs via __________.
Hydrogenation of an alkene with a metal catalyst, such as platinum, occurs via syn addition.
It is important to note the three main types of reactions for alkenes. The first type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism in which the electrophile attacks the carbocation nucleophile. This can yield syn or anti products. The second type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism that forms a bridged carbocation as the intermediate. This can yield only anti products. The third and last type of reaction is a 1-step addition. This can only yield syn products.
An example of the third type of reaction is the addition of a hydrogen with palladium, platinum, or nickel as demonstrated in the picture.

Hydrogenation of an alkene with a metal catalyst, such as platinum, occurs via syn addition.
It is important to note the three main types of reactions for alkenes. The first type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism in which the electrophile attacks the carbocation nucleophile. This can yield syn or anti products. The second type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism that forms a bridged carbocation as the intermediate. This can yield only anti products. The third and last type of reaction is a 1-step addition. This can only yield syn products.
An example of the third type of reaction is the addition of a hydrogen with palladium, platinum, or nickel as demonstrated in the picture.

Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is(are) the product(s) in the Pd-catalyzed hydrogenation if 1,2-dimethylcyclopentene?
What is(are) the product(s) in the Pd-catalyzed hydrogenation if 1,2-dimethylcyclopentene?
The product for this hydrogenation is _cis-_1,2-dimethylcyclopentane.
It is important to note the three main types of reactions for alkenes. The first type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism in which the electrophile attacks the carbocation nucleophile. This can yield syn or anti products. The second type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism that forms a bridged carbocation as the intermediate. This can yield only anti products. The third and last type of reaction is a 1-step addition. This can only yield syn products.
The cis product alone forms because the reagents used were hydrogen and a metal catalyst palladium (other common metal catalysts are platinum and nickel). This type of reagent with an alkene will always be a 1-step addition that yields solely syn products. Cis-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane is the only answer that solely indicates syn products.
The product for this hydrogenation is _cis-_1,2-dimethylcyclopentane.
It is important to note the three main types of reactions for alkenes. The first type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism in which the electrophile attacks the carbocation nucleophile. This can yield syn or anti products. The second type of reaction is a 2-step mechanism that forms a bridged carbocation as the intermediate. This can yield only anti products. The third and last type of reaction is a 1-step addition. This can only yield syn products.
The cis product alone forms because the reagents used were hydrogen and a metal catalyst palladium (other common metal catalysts are platinum and nickel). This type of reagent with an alkene will always be a 1-step addition that yields solely syn products. Cis-1,2-dimethylcyclopentane is the only answer that solely indicates syn products.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

What reagent will complete this reaction?

What reagent will complete this reaction?
N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) brominates at allylic positions. Br2 will not complete this reaction with the presence of the double bond.
N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) brominates at allylic positions. Br2 will not complete this reaction with the presence of the double bond.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

What is the IUPAC name of the given diene?

What is the IUPAC name of the given diene?
You must begin counting the carbons so that the first functional substituent has the lowest possible number. In this case, C1 is connected to C2 by the double bond, meaning we start counting from the left.
The longest carbon chain is seven carbons so the parent molecule is heptane. With this numbering, there are methyl groups on carbons 3 and 6 and a chlorine on carbon 5.
Substituents are named in alphabetical order and two double bonds result in a diene. Thus, the correct answer is 5-chloro-3,6-dimethyl-1,5-heptadiene.
You must begin counting the carbons so that the first functional substituent has the lowest possible number. In this case, C1 is connected to C2 by the double bond, meaning we start counting from the left.
The longest carbon chain is seven carbons so the parent molecule is heptane. With this numbering, there are methyl groups on carbons 3 and 6 and a chlorine on carbon 5.
Substituents are named in alphabetical order and two double bonds result in a diene. Thus, the correct answer is 5-chloro-3,6-dimethyl-1,5-heptadiene.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Starting with an alkyne, synthesis of a cis alkene is driven upon addition of which of the following reagents?
Starting with an alkyne, synthesis of a cis alkene is driven upon addition of which of the following reagents?
Reduction of an alkyne with hydrogen and Lindlar's catalyst will result in a cis alkene. While  is a reducing agent, when added to an alkyne, a trans alkene is formed. Potassium permanganate is an oxidizing agent and thus will not reduce the triple bond. The Grignard reagent is used to add organic substituents onto carbonyls. Addition of one equivalent of chlorine in carbon tetrachloride solvent yields a trans alkene; addition of a second equivalent of chlorine yields a tetrachloro alkane.
is a reducing agent, when added to an alkyne, a trans alkene is formed. Potassium permanganate is an oxidizing agent and thus will not reduce the triple bond. The Grignard reagent is used to add organic substituents onto carbonyls. Addition of one equivalent of chlorine in carbon tetrachloride solvent yields a trans alkene; addition of a second equivalent of chlorine yields a tetrachloro alkane.
Reduction of an alkyne with hydrogen and Lindlar's catalyst will result in a cis alkene. While 
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the best reagent for abstracting a hydrogen from ethyne?
What is the best reagent for abstracting a hydrogen from ethyne?
The triple bond in ethyne makes the hydrogens slightly more acidic than those found in ethane. A very strong base, such as the conjugate base of ammonia, would be able to abstract that hydrogen. The abstraction turns the base into ammonia. It also creates a carbanion that can be used for chain extension and alkyne synthesis.
The triple bond in ethyne makes the hydrogens slightly more acidic than those found in ethane. A very strong base, such as the conjugate base of ammonia, would be able to abstract that hydrogen. The abstraction turns the base into ammonia. It also creates a carbanion that can be used for chain extension and alkyne synthesis.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

What is the product of the compound when it reacts with two equivalents of base?

What is the product of the compound when it reacts with two equivalents of base?
For each equivalent of base, a pi bond is formed between the carbons initially bound to the bromine atoms. For each bond formed, a bromine leaving group leaves the hydrocarbon. One equivalent of base abstracts a hydrogen. The electrons from the bond to the hydrogen create a pi bond. This occurs twice, and a triple bond is formed. The result is a 5-carbon chain with a triple bond between the second and third carbons. This molecule is 2-pentyne.
For each equivalent of base, a pi bond is formed between the carbons initially bound to the bromine atoms. For each bond formed, a bromine leaving group leaves the hydrocarbon. One equivalent of base abstracts a hydrogen. The electrons from the bond to the hydrogen create a pi bond. This occurs twice, and a triple bond is formed. The result is a 5-carbon chain with a triple bond between the second and third carbons. This molecule is 2-pentyne.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Ephedrine (shown below) contains what type of amine?

Ephedrine (shown below) contains what type of amine?

A secondary amine is an amine (nitrogen atom) that is attached to two carbon-containing groups (alkyl groups or aryl groups). The nitrogen in ephedrine is attached to two alkyl groups, making it a secondary amine.
Primary amines are generally written as  . Secondary amines are generally written as
. Secondary amines are generally written as  . A tertiary amine will be bound to three different R-groups. Quaternary amines require a positive charge on the nitrogen atom to accommodate a fourth R-group.
. A tertiary amine will be bound to three different R-groups. Quaternary amines require a positive charge on the nitrogen atom to accommodate a fourth R-group.
A secondary amine is an amine (nitrogen atom) that is attached to two carbon-containing groups (alkyl groups or aryl groups). The nitrogen in ephedrine is attached to two alkyl groups, making it a secondary amine.
Primary amines are generally written as 

Compare your answer with the correct one above

What is the value of  from Huckel's rule for the given aromatic compound?
from Huckel's rule for the given aromatic compound?

What is the value of 
Huckel's rule states that an aromatic compound must have  delocalized electrons. The electrons in each double bond are delocalized for this molecule. There are nine double bonds, and thus eighteen delocalized electrons.
delocalized electrons. The electrons in each double bond are delocalized for this molecule. There are nine double bonds, and thus eighteen delocalized electrons.
If 4n+2=18, then n=4.
Huckel's rule states that an aromatic compound must have 
If 4n+2=18, then n=4.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following carbocation intermediates requires the least activation energy?
Which of the following carbocation intermediates requires the least activation energy?
The more stable the carbocation, the lower the activation energy for reaching that intermediate will be. The more substituted a carbocation is, the more stable it is. The carbocation bonded to three alkanes (tertiary carbocation) is the most stable, and thus the correct answer.
Secondary carbocations will require more energy than tertiary, and primary carbocations will require the most energy.
The more stable the carbocation, the lower the activation energy for reaching that intermediate will be. The more substituted a carbocation is, the more stable it is. The carbocation bonded to three alkanes (tertiary carbocation) is the most stable, and thus the correct answer.
Secondary carbocations will require more energy than tertiary, and primary carbocations will require the most energy.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What intermediate is involved in the conversion of compound B to compound C?

What intermediate is involved in the conversion of compound B to compound C?

The strong sulfuric acid protonates the hydroxyl group of compound B, resulting in the loss of water as a leaving group and the generation of a carbocation intermediate. Since this carbocation carbon is attached to three other carbons, this is a tertiary carbocation. It is bound to the phenyl substituent, a methyl group, and the branched carbon chain.
The strong sulfuric acid protonates the hydroxyl group of compound B, resulting in the loss of water as a leaving group and the generation of a carbocation intermediate. Since this carbocation carbon is attached to three other carbons, this is a tertiary carbocation. It is bound to the phenyl substituent, a methyl group, and the branched carbon chain.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Carbon 1:

Carbon 2:

Let's say we react the given compound with  . During the first step of the reaction, will the hydrogen be added to carbon 1 or carbon 2, why?
. During the first step of the reaction, will the hydrogen be added to carbon 1 or carbon 2, why?
Carbon 1:

Carbon 2:

Let's say we react the given compound with 
The correct answer is: carbon 1 because the intermediate will then be a secondary carbocation.
This is a case of  addition across a double bond where
addition across a double bond where  stands for any halide. The first step in this reaction is the attack of
stands for any halide. The first step in this reaction is the attack of  by the double bond. This will create two intermediates, the first being the halide anion
by the double bond. This will create two intermediates, the first being the halide anion  (so in our case
(so in our case  ), the second being a carbocation on our compound at one of the two carbons that formerly shared the double bond.
), the second being a carbocation on our compound at one of the two carbons that formerly shared the double bond.
If the hydrogen attached the carbon 2 then we would have a positive charge on carbon 1 and vice versa. A positive charge on carbon 1 is known as a primary carbocation (a carbon attached to 1 other carbon or function group), which is rarely if ever seen due to its overwhelming instability. A positive charge on carbon 2 is known as a secondary carbocation (a carbon attached to 2 other carbons or functional groups) and is much more stable than a primary carbocation.
We would want the more thermodynamically stable intermediate for our reaction to proceed, so we would want the positive charge on carbon 2 and the hydrogen attached to carbon 1.
The correct answer is: carbon 1 because the intermediate will then be a secondary carbocation.
This is a case of 




If the hydrogen attached the carbon 2 then we would have a positive charge on carbon 1 and vice versa. A positive charge on carbon 1 is known as a primary carbocation (a carbon attached to 1 other carbon or function group), which is rarely if ever seen due to its overwhelming instability. A positive charge on carbon 2 is known as a secondary carbocation (a carbon attached to 2 other carbons or functional groups) and is much more stable than a primary carbocation.
We would want the more thermodynamically stable intermediate for our reaction to proceed, so we would want the positive charge on carbon 2 and the hydrogen attached to carbon 1.
Compare your answer with the correct one above