Intermediates - GRE Subject Test: Chemistry
Card 0 of 6
Which of the following carbocation intermediates requires the least activation energy?
Which of the following carbocation intermediates requires the least activation energy?
The more stable the carbocation, the lower the activation energy for reaching that intermediate will be. The more substituted a carbocation is, the more stable it is. The carbocation bonded to three alkanes (tertiary carbocation) is the most stable, and thus the correct answer.
Secondary carbocations will require more energy than tertiary, and primary carbocations will require the most energy.
The more stable the carbocation, the lower the activation energy for reaching that intermediate will be. The more substituted a carbocation is, the more stable it is. The carbocation bonded to three alkanes (tertiary carbocation) is the most stable, and thus the correct answer.
Secondary carbocations will require more energy than tertiary, and primary carbocations will require the most energy.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What intermediate is involved in the conversion of compound B to compound C?

What intermediate is involved in the conversion of compound B to compound C?

The strong sulfuric acid protonates the hydroxyl group of compound B, resulting in the loss of water as a leaving group and the generation of a carbocation intermediate. Since this carbocation carbon is attached to three other carbons, this is a tertiary carbocation. It is bound to the phenyl substituent, a methyl group, and the branched carbon chain.
The strong sulfuric acid protonates the hydroxyl group of compound B, resulting in the loss of water as a leaving group and the generation of a carbocation intermediate. Since this carbocation carbon is attached to three other carbons, this is a tertiary carbocation. It is bound to the phenyl substituent, a methyl group, and the branched carbon chain.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Carbon 1:

Carbon 2:

Let's say we react the given compound with  . During the first step of the reaction, will the hydrogen be added to carbon 1 or carbon 2, why?
. During the first step of the reaction, will the hydrogen be added to carbon 1 or carbon 2, why?
Carbon 1:

Carbon 2:

Let's say we react the given compound with 
The correct answer is: carbon 1 because the intermediate will then be a secondary carbocation.
This is a case of  addition across a double bond where
addition across a double bond where  stands for any halide. The first step in this reaction is the attack of
stands for any halide. The first step in this reaction is the attack of  by the double bond. This will create two intermediates, the first being the halide anion
by the double bond. This will create two intermediates, the first being the halide anion  (so in our case
(so in our case  ), the second being a carbocation on our compound at one of the two carbons that formerly shared the double bond.
), the second being a carbocation on our compound at one of the two carbons that formerly shared the double bond.
If the hydrogen attached the carbon 2 then we would have a positive charge on carbon 1 and vice versa. A positive charge on carbon 1 is known as a primary carbocation (a carbon attached to 1 other carbon or function group), which is rarely if ever seen due to its overwhelming instability. A positive charge on carbon 2 is known as a secondary carbocation (a carbon attached to 2 other carbons or functional groups) and is much more stable than a primary carbocation.
We would want the more thermodynamically stable intermediate for our reaction to proceed, so we would want the positive charge on carbon 2 and the hydrogen attached to carbon 1.
The correct answer is: carbon 1 because the intermediate will then be a secondary carbocation.
This is a case of 




If the hydrogen attached the carbon 2 then we would have a positive charge on carbon 1 and vice versa. A positive charge on carbon 1 is known as a primary carbocation (a carbon attached to 1 other carbon or function group), which is rarely if ever seen due to its overwhelming instability. A positive charge on carbon 2 is known as a secondary carbocation (a carbon attached to 2 other carbons or functional groups) and is much more stable than a primary carbocation.
We would want the more thermodynamically stable intermediate for our reaction to proceed, so we would want the positive charge on carbon 2 and the hydrogen attached to carbon 1.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

If the carbon being pointed to was deprotonated (resulting in a positive charge on it). Would the resonance form (the positive charge being redistributed to the carbon with a bromine) be more stable than a secondary carbocation? Why?

If the carbon being pointed to was deprotonated (resulting in a positive charge on it). Would the resonance form (the positive charge being redistributed to the carbon with a bromine) be more stable than a secondary carbocation? Why?
The resonance form of this compound would put the positive charge on the carbon attached to the bromine. Unfortunately this carbon is already slightly positive due to the electron withdrawing effects of bromine due to its high electrophilicity. So this resonance form would be more unstable than a secondary carbocation due to the increased concentration of positive charge from bromine's electron withdrawal.
The resonance form of this compound would put the positive charge on the carbon attached to the bromine. Unfortunately this carbon is already slightly positive due to the electron withdrawing effects of bromine due to its high electrophilicity. So this resonance form would be more unstable than a secondary carbocation due to the increased concentration of positive charge from bromine's electron withdrawal.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following steps of free radical chlorination does not produce a free radical as a product?
Which of the following steps of free radical chlorination does not produce a free radical as a product?
The three steps of a free radical chlorination reaction are, in order, initiation, propagation, and termination.
Free radicals are produced in the initiation and propagation steps. The termination steps combine any two free radicals formed in the reaction to produce a compound that has no unpaired electrons (free radicals).
The three steps of a free radical chlorination reaction are, in order, initiation, propagation, and termination.
Free radicals are produced in the initiation and propagation steps. The termination steps combine any two free radicals formed in the reaction to produce a compound that has no unpaired electrons (free radicals).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following transformations includes an enolate intermediate?
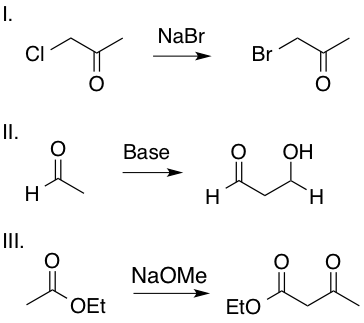
Which of the following transformations includes an enolate intermediate?

Enolates are formed by an oxygen anion bound to an alkene carbon. Reactions II and III include an enolate intermediate, as shown in the mechanisms below, whereas reaction I is a simple SN2 reaction and does not include an enolate intermediate. Enolates are highlighted in red.

Enolates are formed by an oxygen anion bound to an alkene carbon. Reactions II and III include an enolate intermediate, as shown in the mechanisms below, whereas reaction I is a simple SN2 reaction and does not include an enolate intermediate. Enolates are highlighted in red.

Compare your answer with the correct one above