Inheritance Patterns, Pedigrees, and Genetic Disorders - Genetics
Card 0 of 20
The pattern of inheritance of Syndrome V has been documented in a family. According to the pedigree shown below, which mode of inheritance cannot explain the pattern?

The pattern of inheritance of Syndrome V has been documented in a family. According to the pedigree shown below, which mode of inheritance cannot explain the pattern?
This problem asks you to use concepts of inheritance and Mendelian genetics. The best approach to this problem is to rule out possiblities rather than to find the actual mode of inheritance, as the latter can be a much more difficult and time-consuming process. First off, we know that Y-linked inheritance could not explain this pattern because we see that in generation 1 (G1), the male is affected. If he is affected, all of his sons (who inherit his Y chromosome) would also be affected. There is one son in G2 who is not. Similarly, dominant X-linked inheritance could not explain this pattern; recall that the daughters inherit two copies of the X chromosome, and one is always inactivated. Were the trait X-linked dominant, then the girls of generation 3 (G3) would be affected, having received a copy of the affected gene from their father. Revisiting all other options, we see that any of the remaining inheritance patterns could possibly explain what we see.
This problem asks you to use concepts of inheritance and Mendelian genetics. The best approach to this problem is to rule out possiblities rather than to find the actual mode of inheritance, as the latter can be a much more difficult and time-consuming process. First off, we know that Y-linked inheritance could not explain this pattern because we see that in generation 1 (G1), the male is affected. If he is affected, all of his sons (who inherit his Y chromosome) would also be affected. There is one son in G2 who is not. Similarly, dominant X-linked inheritance could not explain this pattern; recall that the daughters inherit two copies of the X chromosome, and one is always inactivated. Were the trait X-linked dominant, then the girls of generation 3 (G3) would be affected, having received a copy of the affected gene from their father. Revisiting all other options, we see that any of the remaining inheritance patterns could possibly explain what we see.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Researchers are studying a disease that causes neurological deficits in humans. They have identified the disorder as autosomal dominant, but notice that about 20% of people with the dominant disease allele do not express any of the associated neurological impairment. What genetics term explains this phenomenon?
Researchers are studying a disease that causes neurological deficits in humans. They have identified the disorder as autosomal dominant, but notice that about 20% of people with the dominant disease allele do not express any of the associated neurological impairment. What genetics term explains this phenomenon?
In this example, some individuals with a certain genotype do not express the expected phenotype (symptoms of the disease) at all. The only term that properly describes this effect is reduced penetrance. Penetrance refers to the percent of individuals with a specific genotype who express the associated phenotype. In most common examples given in genetics courses, autosomal dominant diseases are 100% penetrant, meaning that all individuals with one disease allele will show symptoms to some extent. Here, however, the disease appears to show 80% penetrance.
One term often confused with penetrance is expressivity. This refers to the extent that the phenotype is expressed, and is only applicable when penetrance is 100%. If all of the individuals showed symptoms of the disease, but some showed slightly different defects than others, the disease would have variable expressivity. The other answer choices refer to unrelated genetics concepts.
In this example, some individuals with a certain genotype do not express the expected phenotype (symptoms of the disease) at all. The only term that properly describes this effect is reduced penetrance. Penetrance refers to the percent of individuals with a specific genotype who express the associated phenotype. In most common examples given in genetics courses, autosomal dominant diseases are 100% penetrant, meaning that all individuals with one disease allele will show symptoms to some extent. Here, however, the disease appears to show 80% penetrance.
One term often confused with penetrance is expressivity. This refers to the extent that the phenotype is expressed, and is only applicable when penetrance is 100%. If all of the individuals showed symptoms of the disease, but some showed slightly different defects than others, the disease would have variable expressivity. The other answer choices refer to unrelated genetics concepts.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
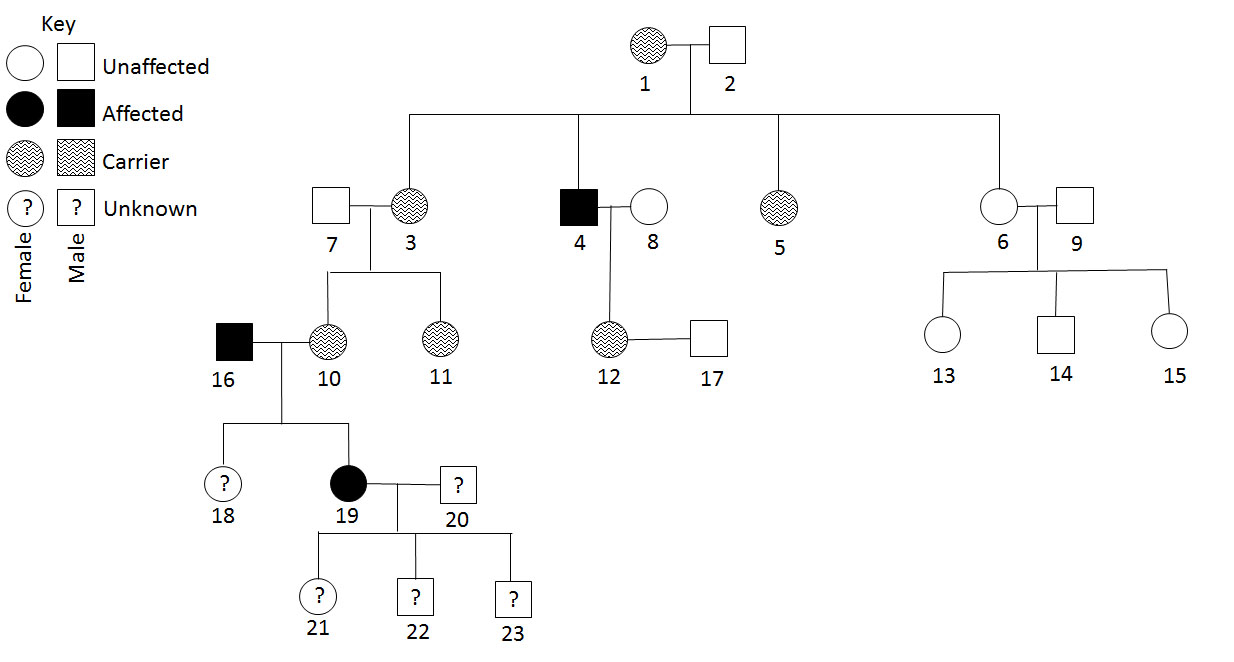
Individual 22 is male, and the trait it X-linked recessive. We know he will inherit the Y-chromosome from the unknown father, and a singular X-chromosome from the affected mother. Because the mother is affected, we know she must have two affected X-chromosomes. No matter which chromosome is passed to individual 22, he will inherit the trait.
Individual 22 is male, and the trait it X-linked recessive. We know he will inherit the Y-chromosome from the unknown father, and a singular X-chromosome from the affected mother. Because the mother is affected, we know she must have two affected X-chromosomes. No matter which chromosome is passed to individual 22, he will inherit the trait.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Rett syndrome is a sex-linked dominant disease found on the X-chromosome. If the offspring of a certain cross have a 50% chance of receiving the disease, regardless of gender, which of the following statements is true?
Rett syndrome is a sex-linked dominant disease found on the X-chromosome. If the offspring of a certain cross have a 50% chance of receiving the disease, regardless of gender, which of the following statements is true?
Since the disease is found on the X-chromosome, we need to find the scenario in which both sons and daughters have an equal 50% probability of getting the disease. Regardless of gender, mothers will always donate one X-chromosome to the offspring. If the mother is heterozygous for the disease, she has a 50% chance of giving an offspring the diseased allele. As a result, a heterozygous mother will have children that display the disease in the observed ratio.
Parents: XXR x XY
Offspring: XX, XXR, XY, XRY
Note that this ratio of expression is only possible when the allele for the disorder is dominant; otherwise the heterozygous female would be a carrier, and not express the disorder.
Since the disease is found on the X-chromosome, we need to find the scenario in which both sons and daughters have an equal 50% probability of getting the disease. Regardless of gender, mothers will always donate one X-chromosome to the offspring. If the mother is heterozygous for the disease, she has a 50% chance of giving an offspring the diseased allele. As a result, a heterozygous mother will have children that display the disease in the observed ratio.
Parents: XXR x XY
Offspring: XX, XXR, XY, XRY
Note that this ratio of expression is only possible when the allele for the disorder is dominant; otherwise the heterozygous female would be a carrier, and not express the disorder.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Two populations of the same species over time grow distant from one another. At what point will these two populations be considered different species?
Two populations of the same species over time grow distant from one another. At what point will these two populations be considered different species?
Speciation is the event that occurs when two populations of a particular species can no longer interbreed. Speciation is not defined by physical barriers or by the time that two populations are separate from one another. In fact, two populations of the same species can be apart any distance or time, and if they can still interbreed they are considered the same species even if they look completely different.
Note that carrying capacity refers to the maximum number of individuals in a population that the natural resources of the surrounding environment can support. It is, essentially, the maximum healthy population size, and is not a measure of distance as implied in the answer choice.
Speciation is the event that occurs when two populations of a particular species can no longer interbreed. Speciation is not defined by physical barriers or by the time that two populations are separate from one another. In fact, two populations of the same species can be apart any distance or time, and if they can still interbreed they are considered the same species even if they look completely different.
Note that carrying capacity refers to the maximum number of individuals in a population that the natural resources of the surrounding environment can support. It is, essentially, the maximum healthy population size, and is not a measure of distance as implied in the answer choice.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A young girl is diagnosed with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy, and her mother is pregnant with a baby boy. Which of the following must be true?
A young girl is diagnosed with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy, and her mother is pregnant with a baby boy. Which of the following must be true?
Duchenne Musclar Dystrophy is a well-studied genetic disorder, generally resulting from a frameshift mutation on the X chromosome. Its pattern of inheritance is considered X-linked recessive.
In order for a girl to have this disorder, she must possess two copies of the recessive allele (one on each X chromosome). In contrast, a boy would only need one copy of the affected allele, but it must come from the mother (he will only have one X chromosome).
Let us use  as a healthy chromosome, and
as a healthy chromosome, and  to represent the recessive allele. Since we know that the girl has the disorder, her genotype must be
to represent the recessive allele. Since we know that the girl has the disorder, her genotype must be  . She received one affected allele from the mother, and one from the father. From this information, we know that the father must have the disease. We also know that the mother either has the disease OR is a carrier.
. She received one affected allele from the mother, and one from the father. From this information, we know that the father must have the disease. We also know that the mother either has the disease OR is a carrier.
Father: 
Mother: 
The only certain conclusion that we can make is that the father has the disease.
All of the other listed answer choices are possible, but cannot be concluded with certainty unless additional information was provided.
Duchenne Musclar Dystrophy is a well-studied genetic disorder, generally resulting from a frameshift mutation on the X chromosome. Its pattern of inheritance is considered X-linked recessive.
In order for a girl to have this disorder, she must possess two copies of the recessive allele (one on each X chromosome). In contrast, a boy would only need one copy of the affected allele, but it must come from the mother (he will only have one X chromosome).
Let us use 


Father:
Mother:
The only certain conclusion that we can make is that the father has the disease.
All of the other listed answer choices are possible, but cannot be concluded with certainty unless additional information was provided.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A genetic disorder affects three generations of males in a family, but rarely affects the females. What is one possible cause of this observation?
A genetic disorder affects three generations of males in a family, but rarely affects the females. What is one possible cause of this observation?
When assessing patterns of inheritance, a genetic disorder that preferentially affects males over females will most commonly be X-linked recessive.
Females have two copies of the X chromosome (one from each parent), while males have one X chromosome (from the mother) and one Y chromosome (from the father). In a recessive allele is present on the X chromosome, a female can carry the allele without expressing it. Males, however, lack the shielding provided by a second X chromosome, and will express all recessive alleles present on their single X chromosome.
Autosomal disorders originate from non-sex chromosomes (autosomes), and do not generate any sex-linked patterns. The question also notes that females do rarely get the disease, indicating that the Y chromosome is not involved (a female will not receive the Y chromosome).
When assessing patterns of inheritance, a genetic disorder that preferentially affects males over females will most commonly be X-linked recessive.
Females have two copies of the X chromosome (one from each parent), while males have one X chromosome (from the mother) and one Y chromosome (from the father). In a recessive allele is present on the X chromosome, a female can carry the allele without expressing it. Males, however, lack the shielding provided by a second X chromosome, and will express all recessive alleles present on their single X chromosome.
Autosomal disorders originate from non-sex chromosomes (autosomes), and do not generate any sex-linked patterns. The question also notes that females do rarely get the disease, indicating that the Y chromosome is not involved (a female will not receive the Y chromosome).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Red-green colorblindness is an X-linked recessive disorder. Which of the following scenarios is not a possible method by which this disorder can be inherited?
Red-green colorblindness is an X-linked recessive disorder. Which of the following scenarios is not a possible method by which this disorder can be inherited?
X-linked disorders are inherited when a parent passes on his or her X-chromosome. Since females have two X-chromosomes, they are less likely to exhibit symptoms of a recessive disorder than males, who have only one. Females are capable of carrying a recessive X-linked trait without expressing it, while males are not. A male must inherit his Y-chromosome from the father and an X-chromosome from the mother, while a female must inherit X-chromosomes from both parents.
If a genotypically healthy mother and a colorblind father have a son, then this child must inherit an X-chromosome from the mother and a Y-chromosome from the father. The mother's chromosome are both genotypically normal, and do not possess the colorblind allele. This means that the son cannot possibly inherit a colorblind allele if the mother is genotypically normal.
All other presented answer represent scenarios that are possible.
X-linked disorders are inherited when a parent passes on his or her X-chromosome. Since females have two X-chromosomes, they are less likely to exhibit symptoms of a recessive disorder than males, who have only one. Females are capable of carrying a recessive X-linked trait without expressing it, while males are not. A male must inherit his Y-chromosome from the father and an X-chromosome from the mother, while a female must inherit X-chromosomes from both parents.
If a genotypically healthy mother and a colorblind father have a son, then this child must inherit an X-chromosome from the mother and a Y-chromosome from the father. The mother's chromosome are both genotypically normal, and do not possess the colorblind allele. This means that the son cannot possibly inherit a colorblind allele if the mother is genotypically normal.
All other presented answer represent scenarios that are possible.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is an example of codominance?
Which of the following is an example of codominance?
Codominance is evidenced when the phenotypes of both parents show up in the offspring. A dog that has fur that consists of colors of both parents will be an example of codominance. Only one trait can be expressed at a time, since they are both dominant phenotypes. This results in regions of one dominant allele and regions of the other, showing a spotted or mottled pattern.
Incomplete dominance occurs when neither trait is truly dominant over the other. This means that both traits can be expressed in the same regions, resulting a blending of two phenotypes. If a white and black dog produce a gray offspring, this is an example of incomplete dominance.
The answer that suggests a red offspring from a black parent and tan parent could result from one of two scenarios. The first possibility is that there are three alleles for color, with red recessive to both black and tan. Both parents carry the red allele, but do not display it, and then pass it to the offspring. Something similar happens with the O blood type. The other possibility is that red color is a new mutation.
Codominance is evidenced when the phenotypes of both parents show up in the offspring. A dog that has fur that consists of colors of both parents will be an example of codominance. Only one trait can be expressed at a time, since they are both dominant phenotypes. This results in regions of one dominant allele and regions of the other, showing a spotted or mottled pattern.
Incomplete dominance occurs when neither trait is truly dominant over the other. This means that both traits can be expressed in the same regions, resulting a blending of two phenotypes. If a white and black dog produce a gray offspring, this is an example of incomplete dominance.
The answer that suggests a red offspring from a black parent and tan parent could result from one of two scenarios. The first possibility is that there are three alleles for color, with red recessive to both black and tan. Both parents carry the red allele, but do not display it, and then pass it to the offspring. Something similar happens with the O blood type. The other possibility is that red color is a new mutation.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
If a disease is sex-linked, which chromosome is it carried on? Which gender is more affected by sex-linked diseases?
If a disease is sex-linked, which chromosome is it carried on? Which gender is more affected by sex-linked diseases?
Sex linked disorders are carried mutations on the X-chromosome. Men are more likely to be affected by sex-linked disorders because of their genetic makeup. Men contain one X-chromosome and one Y-chromosome. Therefore, if there is a mutation on the X-chromosome, it is likely to be passed to the male and expressed. On the other hand, women have two X-chromosomes. They are less likely to express the mutated X-chromosome because they have two copies.
Sex linked disorders are carried mutations on the X-chromosome. Men are more likely to be affected by sex-linked disorders because of their genetic makeup. Men contain one X-chromosome and one Y-chromosome. Therefore, if there is a mutation on the X-chromosome, it is likely to be passed to the male and expressed. On the other hand, women have two X-chromosomes. They are less likely to express the mutated X-chromosome because they have two copies.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is a Barr body?
What is a Barr body?
A Barr body is an inactivated X-chromosome found in females. Females have two X chromosomes (XX) while males have one X-chromosome and one Y-chromosome (XY). Only one X-chromosome is expressed in females, and the other is "unexpressed". The inactivated X-chromosome in females is termed a Barr body.
A Barr body is an inactivated X-chromosome found in females. Females have two X chromosomes (XX) while males have one X-chromosome and one Y-chromosome (XY). Only one X-chromosome is expressed in females, and the other is "unexpressed". The inactivated X-chromosome in females is termed a Barr body.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
You are a dog breeder and want to figure out the genotype of the female brown dog you have. Brown is the dominant phenotype, while white is the recessive. You decide to breed her with a male who is also brown and has strictly dominant brown alleles. If the female is heterozygous, what percentage of her litter should be white?
You are a dog breeder and want to figure out the genotype of the female brown dog you have. Brown is the dominant phenotype, while white is the recessive. You decide to breed her with a male who is also brown and has strictly dominant brown alleles. If the female is heterozygous, what percentage of her litter should be white?
Since the father has only dominant alleles for the brown phenotype, all of the litter will be brown. However, half the litter should carry the recessive allele. The punnet square below shows the dad's genotype on top and the mom's genotype on the left. The outcome is that half the progeny will have the genotype BB and half will have the genotype Bb. Therefore, all offspring will have the brown phenotype.
B B
B BB BB
b Bb Bb
Since the father has only dominant alleles for the brown phenotype, all of the litter will be brown. However, half the litter should carry the recessive allele. The punnet square below shows the dad's genotype on top and the mom's genotype on the left. The outcome is that half the progeny will have the genotype BB and half will have the genotype Bb. Therefore, all offspring will have the brown phenotype.
B B
B BB BB
b Bb Bb
Compare your answer with the correct one above
When a black chicken and a white chicken are crossed together, all of the offspring are grey chickens. What type of genetic inheritance is represented in this example?
When a black chicken and a white chicken are crossed together, all of the offspring are grey chickens. What type of genetic inheritance is represented in this example?
This example represents the incomplete dominance crossing a black chicken with a white chicken resulted in the offspring taking on a third phenotype that is an intermediate, blended phenotype of both parents' phenotypes.
This example represents the incomplete dominance crossing a black chicken with a white chicken resulted in the offspring taking on a third phenotype that is an intermediate, blended phenotype of both parents' phenotypes.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
When a black chicken and a white chicken are crossed, all of the offspring have black and white spots. What type of genetic inheritance is represented here?
When a black chicken and a white chicken are crossed, all of the offspring have black and white spots. What type of genetic inheritance is represented here?
This is an example of codominance -- crossing a black chicken with a white chicken results in the offspring taking on a third phenotype where both of the parents' phenotypes appear together. This is different than incomplete dominance, in which the offspring take on a third phenotype that is a "blend" of the parents' phenotypes (gray chickens as opposed to spotted chickens).
This is an example of codominance -- crossing a black chicken with a white chicken results in the offspring taking on a third phenotype where both of the parents' phenotypes appear together. This is different than incomplete dominance, in which the offspring take on a third phenotype that is a "blend" of the parents' phenotypes (gray chickens as opposed to spotted chickens).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Females have two X chromosomes, while males have only one. Most of the genes on the X chromosome, however, are expressed at the same level in both females and males. Which of the following statements regarding X chromosomes is correct?
Females have two X chromosomes, while males have only one. Most of the genes on the X chromosome, however, are expressed at the same level in both females and males. Which of the following statements regarding X chromosomes is correct?
XIST stands for X-inactivation specific transcript, which acts in the inactivation process in females since only one X will be active. The nuclei of cells in females contain the barr body. Female heterozygotes are mosaics. Calico cats are almost always female.
XIST stands for X-inactivation specific transcript, which acts in the inactivation process in females since only one X will be active. The nuclei of cells in females contain the barr body. Female heterozygotes are mosaics. Calico cats are almost always female.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Achondroplasia is an autosomal dominant disease where there is a mutation in the FGF3 gene, causing a constitutively active receptor, leading to severely shortened bones. What form of inheritance is this?
Achondroplasia is an autosomal dominant disease where there is a mutation in the FGF3 gene, causing a constitutively active receptor, leading to severely shortened bones. What form of inheritance is this?
Achondroplasia is a gain of function, because the gene is always active, therefore you are gaining more than you normally would. In loss of function, you are losing the ability to use that gene/protein, so it is under active — such as in marfan syndrome. Porphyria refers to not having enough enzymes to breakdown products, leading to a build up of the substrate. Abnormal multimeric complex is when you have a structure that involves multiple components to combine to make one; i.e. collagen type I in osteogenesis imperfects.
Achondroplasia is a gain of function, because the gene is always active, therefore you are gaining more than you normally would. In loss of function, you are losing the ability to use that gene/protein, so it is under active — such as in marfan syndrome. Porphyria refers to not having enough enzymes to breakdown products, leading to a build up of the substrate. Abnormal multimeric complex is when you have a structure that involves multiple components to combine to make one; i.e. collagen type I in osteogenesis imperfects.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
If someone has sickle cell anemia, they are protected against malaria. What is the name of this phenomenon?
If someone has sickle cell anemia, they are protected against malaria. What is the name of this phenomenon?
Sickle cell anemia is a heterozygous genotype. Having this genotype protects against malaria, which is describing the heterozygous advantage (where having the heterozygote genotype is more favorable than being homozygous dominant or recessive). Heteroplasmy is when there is more than 1 type of organelle genome in a cell like mitochondria. Founder effect is a sudden decrease in population size. Continuous variation is a range of phenotypes from allelic variation in multiple genes.
Sickle cell anemia is a heterozygous genotype. Having this genotype protects against malaria, which is describing the heterozygous advantage (where having the heterozygote genotype is more favorable than being homozygous dominant or recessive). Heteroplasmy is when there is more than 1 type of organelle genome in a cell like mitochondria. Founder effect is a sudden decrease in population size. Continuous variation is a range of phenotypes from allelic variation in multiple genes.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A human with the genotype XX is __________.
A human with the genotype XX is __________.
Humans with the genotype XX are female, as females get two X chromosomes (one from the mother, one from the father). On the other hand, humans with the genotype XY are male, as males get a Y chromosome from the father and an X chromosome from the mother.
Humans with the genotype XX are female, as females get two X chromosomes (one from the mother, one from the father). On the other hand, humans with the genotype XY are male, as males get a Y chromosome from the father and an X chromosome from the mother.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
There are multiple mutation mediated protein coding changes that can occur during meiosis/replication. Many of the mutations lead to a disease that affects multiple systems; i.e. cardiovascular, immune, endocrinel. What is the term for when a single mutation results in more than one unrelated effect?
There are multiple mutation mediated protein coding changes that can occur during meiosis/replication. Many of the mutations lead to a disease that affects multiple systems; i.e. cardiovascular, immune, endocrinel. What is the term for when a single mutation results in more than one unrelated effect?
Pleitrophy occurs when a single mutation causes different systems that are unrelated to be affects. A modifier gene is something that can make a gene worse or better. One example are single nucleotide polymorphisms. Frameshift is an example of one of the mutations that could occur. Lionization is X inactivation that occurs in females.
Pleitrophy occurs when a single mutation causes different systems that are unrelated to be affects. A modifier gene is something that can make a gene worse or better. One example are single nucleotide polymorphisms. Frameshift is an example of one of the mutations that could occur. Lionization is X inactivation that occurs in females.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Someone has angleman syndrome, which is a disease passed from mother to offspring due to the mother having a deletion at chromosome 15, which type of epigenetic phenomenon is this?
Someone has angleman syndrome, which is a disease passed from mother to offspring due to the mother having a deletion at chromosome 15, which type of epigenetic phenomenon is this?
Genomic imprinting is when certain genes are expressed in a parent-of-origin inheritance pattern. In the example, angleman syndrome goes to the offspring if the mother has a deletion in chromosome 15. Mitochondrial inheritance is only from the mother and refers to the number of defective mitochondria that may have been inherited. Trinucleotide repeat is the expansion of 3 nucleotide repeats usually associated with Huntington's. Multifactorial inheritance has to do with polygenic (genes & environment), co inheritance, risk factors, and environmental influence.
Genomic imprinting is when certain genes are expressed in a parent-of-origin inheritance pattern. In the example, angleman syndrome goes to the offspring if the mother has a deletion in chromosome 15. Mitochondrial inheritance is only from the mother and refers to the number of defective mitochondria that may have been inherited. Trinucleotide repeat is the expansion of 3 nucleotide repeats usually associated with Huntington's. Multifactorial inheritance has to do with polygenic (genes & environment), co inheritance, risk factors, and environmental influence.
Compare your answer with the correct one above