Protein Functions - Biochemistry
Card 0 of 20
Lysosomal enzymes are predominantly __________.
Lysosomal enzymes are predominantly __________.
The lysosome is the "stomach" of the cell. It contains many hydrolytic enzymes to digest and recycle the monomers used to form old polymers. Remember the opposite of dehydration/condensation synthesis is hydrolysis. Hydrolysis reactions use water to break bonds in polymers, yielding monomers that can be recycled and reused in anabolic pathways.
The lysosome is the "stomach" of the cell. It contains many hydrolytic enzymes to digest and recycle the monomers used to form old polymers. Remember the opposite of dehydration/condensation synthesis is hydrolysis. Hydrolysis reactions use water to break bonds in polymers, yielding monomers that can be recycled and reused in anabolic pathways.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following best describes how a lysozyme works?
Which of the following best describes how a lysozyme works?
Lysozymes speed up by many times the hydrolysis of polysaccharides, by adding the water molecule to sugars linked in its enzyme-substrate complex. If left alone without the lysozyme, this hydrolysis would occur relatively infrequently, because it requires a large activation energy which would be supplied only by rare random collisions. The amino acid cleavage enzyme which uses the ping-pong mechanism is chymotrypsin. The enzyme which breaks nucleic acid phosophodiester bonds is phosphodiesterase. Fats are hydrolyzed by lipases, not lysozymes.
Lysozymes speed up by many times the hydrolysis of polysaccharides, by adding the water molecule to sugars linked in its enzyme-substrate complex. If left alone without the lysozyme, this hydrolysis would occur relatively infrequently, because it requires a large activation energy which would be supplied only by rare random collisions. The amino acid cleavage enzyme which uses the ping-pong mechanism is chymotrypsin. The enzyme which breaks nucleic acid phosophodiester bonds is phosphodiesterase. Fats are hydrolyzed by lipases, not lysozymes.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Phosphoglucomutase is an enzyme seen in glycogen breakdown. It is responsible for converting glucose-1-phosphate ( ) to glucose-6-phosphate (
) to glucose-6-phosphate (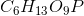 ).
).
Based on this action, to which enzyme class does phosphoglucomutase belong?
Phosphoglucomutase is an enzyme seen in glycogen breakdown. It is responsible for converting glucose-1-phosphate (
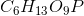
Based on this action, to which enzyme class does phosphoglucomutase belong?
Phosphoglucomutase is responsible for altering the position of the phosphate on the glucose from the "1" position to the "6" position. However, notice how the molecular formula for the product and the substrate are the same. Enzymes that rearrange the structure of a molecule in this manner are referred to as isomerase enzymes.
Phosphoglucomutase is responsible for altering the position of the phosphate on the glucose from the "1" position to the "6" position. However, notice how the molecular formula for the product and the substrate are the same. Enzymes that rearrange the structure of a molecule in this manner are referred to as isomerase enzymes.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following correctly mentions the function of a common eukaryotic ligase?
Which of the following correctly mentions the function of a common eukaryotic ligase?
Mammalian DNA ligase I has this function, and there are other DNA ligases which perform it in other animals and eukaryotes (prokaryotes also have their own DNA ligases). All the other functions mentioned are done by other classes of enzymes, not ligases (i.e. hydrolases, aminotransferases, oxidoreductases, etc.).
Mammalian DNA ligase I has this function, and there are other DNA ligases which perform it in other animals and eukaryotes (prokaryotes also have their own DNA ligases). All the other functions mentioned are done by other classes of enzymes, not ligases (i.e. hydrolases, aminotransferases, oxidoreductases, etc.).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Hemoglobin is an important component of red blood cells that allows for efficient delivery of oxygen from the lungs to tissues throughout the body. Without hemoglobin, oxygen would not be able to dissolve in the blood well enough to meet the metabolic needs of tissues. Hemoglobin is well-suited to this function because its affinity for oxygen varies depending on its chemical environment. Which of the following situations would cause a rightward shift on the oxygen dissociation curve for hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin is an important component of red blood cells that allows for efficient delivery of oxygen from the lungs to tissues throughout the body. Without hemoglobin, oxygen would not be able to dissolve in the blood well enough to meet the metabolic needs of tissues. Hemoglobin is well-suited to this function because its affinity for oxygen varies depending on its chemical environment. Which of the following situations would cause a rightward shift on the oxygen dissociation curve for hemoglobin?
An oxygen dissociation curve for hemoglobin plots the percent saturation of oxygen on the  -axis vs. the partial pressure of oxygen on the
-axis vs. the partial pressure of oxygen on the  -axis. A rightward shift of the curve means that for a given oxygen saturation level, there needs to be a higher partial pressure of oxygen. Thus, a rightward shift is indicative of a decreased affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen.
-axis. A rightward shift of the curve means that for a given oxygen saturation level, there needs to be a higher partial pressure of oxygen. Thus, a rightward shift is indicative of a decreased affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen.
There are several factors that can influence hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen. One such factor is pH. At lower pH levels, hemoglobin has a more difficult time holding onto oxygen. Physiologically this makes sense, because the blood is likely to be slightly more acidic in regions where tissues are metabolically active, hence they are going to need more oxygen to sustain their metabolism. Likewise, carbon dioxide is also capable of lowering hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen. And again, this makes sense physiologically, because tissues with a high metabolism are going to be generating more carbon dioxide, which serves as a signal to allow hemoglobin to drop off more oxygen for these active tissues. And finally, an additional regulatory factor is a glycolytic intermediate called 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG). Binding of this compound to hemoglobin lowers oxygen affinity, thus higher concentrations of 2,3-BPG also cause a rightward shift of the curve.
Also note that oxygen binds hemoglobin in a cooperative fashion. This means that when one molecule of oxygen binds to hemoglobin, the other three oxygen binding sites on hemoglobin gain subsequently increased affinity for oxygen. And when a second oxygen molecule binds, the other binding sites gain more affinity, and so on. Thus, when the partial pressure of oxygen increases, hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen becomes greater.
An oxygen dissociation curve for hemoglobin plots the percent saturation of oxygen on the 

There are several factors that can influence hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen. One such factor is pH. At lower pH levels, hemoglobin has a more difficult time holding onto oxygen. Physiologically this makes sense, because the blood is likely to be slightly more acidic in regions where tissues are metabolically active, hence they are going to need more oxygen to sustain their metabolism. Likewise, carbon dioxide is also capable of lowering hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen. And again, this makes sense physiologically, because tissues with a high metabolism are going to be generating more carbon dioxide, which serves as a signal to allow hemoglobin to drop off more oxygen for these active tissues. And finally, an additional regulatory factor is a glycolytic intermediate called 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG). Binding of this compound to hemoglobin lowers oxygen affinity, thus higher concentrations of 2,3-BPG also cause a rightward shift of the curve.
Also note that oxygen binds hemoglobin in a cooperative fashion. This means that when one molecule of oxygen binds to hemoglobin, the other three oxygen binding sites on hemoglobin gain subsequently increased affinity for oxygen. And when a second oxygen molecule binds, the other binding sites gain more affinity, and so on. Thus, when the partial pressure of oxygen increases, hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen becomes greater.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following statements about ribosomes is false?
Which of the following statements about ribosomes is false?
Ribozymes are RNA molecules that catalyze specific biochemical reactions, so ribosomes (which catalyze the linking of amino acids) are indeed ribozymes. tRNA is complementary to ribosomal RNA in the sites where the two bind. Aminoacylation produces a tRNA with its 3’ end covalently linked to an amino acid. The sequence at the 3’ end is not ACA, however’ it is CCA.
Ribozymes are RNA molecules that catalyze specific biochemical reactions, so ribosomes (which catalyze the linking of amino acids) are indeed ribozymes. tRNA is complementary to ribosomal RNA in the sites where the two bind. Aminoacylation produces a tRNA with its 3’ end covalently linked to an amino acid. The sequence at the 3’ end is not ACA, however’ it is CCA.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What term is used to describe enzymes that have different chemical structures but which catalyze the same reactions?
What term is used to describe enzymes that have different chemical structures but which catalyze the same reactions?
The correct answer choice is isozymes, also called isoenzymes. Even though these enzymes can catalyze the same reaction, they often have differences in their kinetic parameters or in the way they're regulated. Coenzymes are a type of cofactor. They are generally complex organic molecules that are usually derived from vitamins, and they serve the purpose of assisting the enzyme to which they are bound. Examples include pyridoxal phosphate, biotin, coenzyme A, etc. Apoenzymes are enzymes that normally require a cofactor, but are in a state in which they lack that cofactor. Holoenzymes are apoenzymes that have their cofactor bound.
The correct answer choice is isozymes, also called isoenzymes. Even though these enzymes can catalyze the same reaction, they often have differences in their kinetic parameters or in the way they're regulated. Coenzymes are a type of cofactor. They are generally complex organic molecules that are usually derived from vitamins, and they serve the purpose of assisting the enzyme to which they are bound. Examples include pyridoxal phosphate, biotin, coenzyme A, etc. Apoenzymes are enzymes that normally require a cofactor, but are in a state in which they lack that cofactor. Holoenzymes are apoenzymes that have their cofactor bound.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is true about chromoproteins?
Which of the following is true about chromoproteins?
Heme normally binds to iron. Myoglobin is mostly concentrated in muscles, and after a muscle injury can be present in blood. Myoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen than hemoglobin; myoglobin’s oxygen saturation curve is hyperbolic, whereas hemoglobin’s is sigmoidal. Hemoglobin F (fetal hemoglobin) has a higher oxygen affinity than hemoglobin A (adult hemoglobin). This improves the transfer of oxygen from the circulation of the mother to that of the fetus.
Heme normally binds to iron. Myoglobin is mostly concentrated in muscles, and after a muscle injury can be present in blood. Myoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen than hemoglobin; myoglobin’s oxygen saturation curve is hyperbolic, whereas hemoglobin’s is sigmoidal. Hemoglobin F (fetal hemoglobin) has a higher oxygen affinity than hemoglobin A (adult hemoglobin). This improves the transfer of oxygen from the circulation of the mother to that of the fetus.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is not a characteristic of chymotrypsin?
Which of the following is not a characteristic of chymotrypsin?
Chymotrypsin is a digestive enzyme that breaks down proteins (proteolysis). It has a catalytic triad of serine, histidine, and aspartate. The hydroxyl group on serine acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl group on the amino acid, forming a tetrahedral intermediate. Histidine acts as a base, which cleaves the peptide bond. Aspartate acts as an acid, which restores the active site. Since this catalytic triad has a defined nucleophile, base, and acid, we know that there will not be an additional thiol nucleophile. Thiol nucleophiles are found in cysteine proteases.
Chymotrypsin is a digestive enzyme that breaks down proteins (proteolysis). It has a catalytic triad of serine, histidine, and aspartate. The hydroxyl group on serine acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl group on the amino acid, forming a tetrahedral intermediate. Histidine acts as a base, which cleaves the peptide bond. Aspartate acts as an acid, which restores the active site. Since this catalytic triad has a defined nucleophile, base, and acid, we know that there will not be an additional thiol nucleophile. Thiol nucleophiles are found in cysteine proteases.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Generally speaking, proteins have many important functions in living organisms. Which of the following is not a potential function of proteins?
Generally speaking, proteins have many important functions in living organisms. Which of the following is not a potential function of proteins?
As stated in the question stem, proteins are super important because they perform an enormous variety of functions. Proteins can sometimes serve a structural role, such as the protein collagen which helps give some connective tissues their unique properties. They can also act as chemical messengers, as some protein hormones do such as growth hormone. Some proteins, such as antibodies, can even protect against infection by neutralizing invading pathogens such as bacteria. In addition, proteins can also exist as enzymes, which act to greatly increase the rate of specific reactions. Other proteins can act as carriers or transporters that help to facilitate the movement of some chemicals across an otherwise impermeable cell membrane. While it's true that proteins play a very important structural and functional role in the cell membrane, they are not the primary structural component. Rather, phospholipids serve as the most abundant component of cell membranes and helps to give them their unique role as "cellular barriers."
As stated in the question stem, proteins are super important because they perform an enormous variety of functions. Proteins can sometimes serve a structural role, such as the protein collagen which helps give some connective tissues their unique properties. They can also act as chemical messengers, as some protein hormones do such as growth hormone. Some proteins, such as antibodies, can even protect against infection by neutralizing invading pathogens such as bacteria. In addition, proteins can also exist as enzymes, which act to greatly increase the rate of specific reactions. Other proteins can act as carriers or transporters that help to facilitate the movement of some chemicals across an otherwise impermeable cell membrane. While it's true that proteins play a very important structural and functional role in the cell membrane, they are not the primary structural component. Rather, phospholipids serve as the most abundant component of cell membranes and helps to give them their unique role as "cellular barriers."
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of these describes the protein myoglobin?
Which of these describes the protein myoglobin?
Myoglobin and hemoglobin are not the same molecule; their functions are similar but different in several ways. Myoglobin is an oxygen-binding protein of muscle tissues. In contrast, hemoglobin is the oxygen-transport protein found in blood. Hemoglobin can bind four oxygen atoms, while myoglobin can only bind one. Both hemoglobin and myoglobin contain heme groups, with hemoglobin containing four and myoglobin containing one. These iron-containing groups are responsible for binding the oxygen atom(s).
Myoglobin and hemoglobin are not the same molecule; their functions are similar but different in several ways. Myoglobin is an oxygen-binding protein of muscle tissues. In contrast, hemoglobin is the oxygen-transport protein found in blood. Hemoglobin can bind four oxygen atoms, while myoglobin can only bind one. Both hemoglobin and myoglobin contain heme groups, with hemoglobin containing four and myoglobin containing one. These iron-containing groups are responsible for binding the oxygen atom(s).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of these is not a function of membrane proteins?
Which of these is not a function of membrane proteins?
Membrane proteins have several functions. They can act as catalysts, receptor proteins for different molecules attempting to enter/exit the cell, and also function in transport as channels or transporters. However, energy storage is a function that is carried out by carbohydrates and lipids.
Membrane proteins have several functions. They can act as catalysts, receptor proteins for different molecules attempting to enter/exit the cell, and also function in transport as channels or transporters. However, energy storage is a function that is carried out by carbohydrates and lipids.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following correctly describes an allosteric enzyme?
Which of the following correctly describes an allosteric enzyme?
Allosteric enzymes are enzymes that can be regulated by binding of a small molecule to an "allosteric site" on the enzyme. This is a location on the enzyme that is distinct from the active site, which is where the enzyme binds to its substrate.
Allosteric compounds can be either activators or repressors. Activators cause the enzyme's activity to increase, whereas repressors cause the enzyme's activity to decrease. This happens because binding of an allosteric molecule acts to change the enzyme's structural conformation, even if just slightly, which thus makes it either more active or less active.
For example, phosphofructokinase is an enzyme found in glycolysis, the metabolic pathway that breaks glucose down in cells for energy. This enzyme is a critical component of the pathway, because it is largely responsible for regulating the flux of glucose through this pathway. As such, there are many cellular metabolites that act to either increase or decrease this enzyme's activity. As an example, molecules like ATP and other intermediates of glycolysis and, subsequently, the citric acid cycle are able to decrease this enzyme's activity. Some of these metabolites include phosphoenolpyruvate and citric acid, in addition to ATP, all of which indicate that the cell has an abundant amount of energy available. AMP, on the other hand, acts to allosterically activate phosphofructokinase because it signals that the cell is low in energy. Thus, allosteric enzymes are an important component of how biochemical processes can be regulated.
Allosteric enzymes are enzymes that can be regulated by binding of a small molecule to an "allosteric site" on the enzyme. This is a location on the enzyme that is distinct from the active site, which is where the enzyme binds to its substrate.
Allosteric compounds can be either activators or repressors. Activators cause the enzyme's activity to increase, whereas repressors cause the enzyme's activity to decrease. This happens because binding of an allosteric molecule acts to change the enzyme's structural conformation, even if just slightly, which thus makes it either more active or less active.
For example, phosphofructokinase is an enzyme found in glycolysis, the metabolic pathway that breaks glucose down in cells for energy. This enzyme is a critical component of the pathway, because it is largely responsible for regulating the flux of glucose through this pathway. As such, there are many cellular metabolites that act to either increase or decrease this enzyme's activity. As an example, molecules like ATP and other intermediates of glycolysis and, subsequently, the citric acid cycle are able to decrease this enzyme's activity. Some of these metabolites include phosphoenolpyruvate and citric acid, in addition to ATP, all of which indicate that the cell has an abundant amount of energy available. AMP, on the other hand, acts to allosterically activate phosphofructokinase because it signals that the cell is low in energy. Thus, allosteric enzymes are an important component of how biochemical processes can be regulated.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following reaction types is not catalyzed by cobalamin enzymes?
Which of the following reaction types is not catalyzed by cobalamin enzymes?
Cobalamin enzymes are B12-dependent enzymes. This type of enzyme catalyzes methylations, intramolecular rearrangements, and reduction of ribonucleotides. However, it is not associated with the ligation of the hydrogen bonds between DNA bases.
Cobalamin enzymes are B12-dependent enzymes. This type of enzyme catalyzes methylations, intramolecular rearrangements, and reduction of ribonucleotides. However, it is not associated with the ligation of the hydrogen bonds between DNA bases.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Where does steroid synthesis and detoxification of drugs and poisons occur in a cell?
Where does steroid synthesis and detoxification of drugs and poisons occur in a cell?
Liver hepatocytes and steroid hormone producing cells of the adrenal cortex are rich in the SER. RER is the site of synthesis of secretory (exported) proteins. The golgi apparatus does many things, but in general, think of it as the distribution center and vesicular trafficking. It organizes and directs where everything should go. The nucleolus is unrelated to this topic, but it does produce ribosomes.
Liver hepatocytes and steroid hormone producing cells of the adrenal cortex are rich in the SER. RER is the site of synthesis of secretory (exported) proteins. The golgi apparatus does many things, but in general, think of it as the distribution center and vesicular trafficking. It organizes and directs where everything should go. The nucleolus is unrelated to this topic, but it does produce ribosomes.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following lists the cytoskeletal filaments in order of increasing diameter?
Which of the following lists the cytoskeletal filaments in order of increasing diameter?
Actin filaments, also known as microfilaments, are flexible and bundle up, and are 5-9nm in diameter. Intermediate filaments, which can strengthen cells, are about 10nm. Microtubules, rigid and attached on one end to a centrosome, are 25nm.
Actin filaments, also known as microfilaments, are flexible and bundle up, and are 5-9nm in diameter. Intermediate filaments, which can strengthen cells, are about 10nm. Microtubules, rigid and attached on one end to a centrosome, are 25nm.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Enzymes can be regulated in a multitude of ways. One such way is by covalent modification, in which functional groups are attached to or removed from the enzyme. One such functional group that can be added to an enzyme is a phosphate group. Depending on the enzyme, addition of a phosphate group may increase or decrease that enzyme's activity. Which of the following is the general name of an enzyme that functions to add phosphate groups to its substrate?
Enzymes can be regulated in a multitude of ways. One such way is by covalent modification, in which functional groups are attached to or removed from the enzyme. One such functional group that can be added to an enzyme is a phosphate group. Depending on the enzyme, addition of a phosphate group may increase or decrease that enzyme's activity. Which of the following is the general name of an enzyme that functions to add phosphate groups to its substrate?
The correct answer is a kinase. Kinases are enzymes that couple the hydrolysis of ATP to the addition of a phosphate group to its substrate.
Phosphatase enzymes basically function oppositely to how kinases work. Phosphatases use water to hydrolyze phosphate groups off of their substrate.
Isomerase enzymes function to interconvert the structure of molecules from one isomer to another. This means that the substrate will remain with the same molecular formula, but it will have a difference in the connectivity of its bonds.
Ligases are enzymes that work by joining two molecules together.
Oxidoreductases are enzymes that act by catalyzing oxidation and reduction reactions, which involve the transfer of electrons from one molecule to another.
The correct answer is a kinase. Kinases are enzymes that couple the hydrolysis of ATP to the addition of a phosphate group to its substrate.
Phosphatase enzymes basically function oppositely to how kinases work. Phosphatases use water to hydrolyze phosphate groups off of their substrate.
Isomerase enzymes function to interconvert the structure of molecules from one isomer to another. This means that the substrate will remain with the same molecular formula, but it will have a difference in the connectivity of its bonds.
Ligases are enzymes that work by joining two molecules together.
Oxidoreductases are enzymes that act by catalyzing oxidation and reduction reactions, which involve the transfer of electrons from one molecule to another.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
In the last step of glycolysis, what is the name of the enzyme that converts phosphoenolpyruvate into pyruvate?
In the last step of glycolysis, what is the name of the enzyme that converts phosphoenolpyruvate into pyruvate?
The last step of glycolysis, which involves the conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate into pyruvate, is catalyzed by the enzyme pyruvate kinase, yielding one pyruvate molecule and 1 ATP. The other kinases are involved in different steps of glycolysis.
The last step of glycolysis, which involves the conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate into pyruvate, is catalyzed by the enzyme pyruvate kinase, yielding one pyruvate molecule and 1 ATP. The other kinases are involved in different steps of glycolysis.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following enzymes catalyzes a reaction that is the functional opposite of the reaction catalyzed by kinases?
Which of the following enzymes catalyzes a reaction that is the functional opposite of the reaction catalyzed by kinases?
Kinases catalyze the attachment of phosphate groups to their substrates. Phosphatases specifically remove phosphate groups from their substrates, which is the opposite of the function of kinases. The other enzymes listed do not have functions that involve removal of phosphate groups.
Kinases catalyze the attachment of phosphate groups to their substrates. Phosphatases specifically remove phosphate groups from their substrates, which is the opposite of the function of kinases. The other enzymes listed do not have functions that involve removal of phosphate groups.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is false regarding protein kinase A (PKA)?
Which of the following is false regarding protein kinase A (PKA)?
From it's name, we can assume that this kinase will add phosphate groups to its targets. The source of these phosphate groups is ATP. PKA has 2 catalytic, and 2 regulatory subunits. When PKA is activated, there is a conformational change that causes the regulatory subunits to fall off, and frees the catalytic (kinase) portions. When PKA is inhibited, the regulatory subunits bind to the catalytic subunits and prevent phosphorylation. PKA has many activators, but cAMP is one of the most robust and well studied activator. Therefore, cAMP binds to the regulatory subunits, but does not inhibit protein function.
From it's name, we can assume that this kinase will add phosphate groups to its targets. The source of these phosphate groups is ATP. PKA has 2 catalytic, and 2 regulatory subunits. When PKA is activated, there is a conformational change that causes the regulatory subunits to fall off, and frees the catalytic (kinase) portions. When PKA is inhibited, the regulatory subunits bind to the catalytic subunits and prevent phosphorylation. PKA has many activators, but cAMP is one of the most robust and well studied activator. Therefore, cAMP binds to the regulatory subunits, but does not inhibit protein function.
Compare your answer with the correct one above