Identifying Specific Protein Structures - Biochemistry
Card 0 of 20
Which amino acid does this structure represent?

Which amino acid does this structure represent?

The amino acid's R group is composed of an ethyl group, followed by a carboxylate group, and therefore represents glutamate.
The amino acid's R group is composed of an ethyl group, followed by a carboxylate group, and therefore represents glutamate.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which amino acid does this structure represent?

Which amino acid does this structure represent?

The amino acid's chiral carbon is connected to two methyl groups followed, by a sulfur, and finally another methyl group. Therefore, the amino acid is methionine (M).
The amino acid's chiral carbon is connected to two methyl groups followed, by a sulfur, and finally another methyl group. Therefore, the amino acid is methionine (M).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The amino acid phenylalanine is pictured. If a hydroxyl group was added to the carbon in the red box, which amino acid would the new molecule most closely resemble?

The amino acid phenylalanine is pictured. If a hydroxyl group was added to the carbon in the red box, which amino acid would the new molecule most closely resemble?

The structure would most closely resembe tyrosine (pictured).

The structure would most closely resembe tyrosine (pictured).

Compare your answer with the correct one above
If the phenyl group in the pictured molecule were removed, what amino acid would the new structure most closely resemble?

If the phenyl group in the pictured molecule were removed, what amino acid would the new structure most closely resemble?

Alanine is the amino acid that would be formed by removing the phenyl group from phenylalanine (the pictured molecule).
Alanine is the amino acid that would be formed by removing the phenyl group from phenylalanine (the pictured molecule).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
If the amide group of glutamine (pictured here) was removed and a hydroxyl group was added to the carbon bound to the alpha carbon of the resulting structure, what amino acid would be formed?

If the amide group of glutamine (pictured here) was removed and a hydroxyl group was added to the carbon bound to the alpha carbon of the resulting structure, what amino acid would be formed?

Threonine (pictured here) would be formed.

Threonine (pictured here) would be formed.

Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following structures is threonine?
Which of the following structures is threonine?
Threonine is a polar uncharged amino acid with a  R-group.
R-group.
Threonine is a polar uncharged amino acid with a 
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Identify the given structure.

Identify the given structure.

Arginine is a basic amino acid. The charge on the amine in the functional group makes this structure basic. While lysine is also a basic amino acid, it has a different R-group.
Arginine is a basic amino acid. The charge on the amine in the functional group makes this structure basic. While lysine is also a basic amino acid, it has a different R-group.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following structures is methionine?
Which of the following structures is methionine?
Methionine is a non-polar amino acid. It is one of two amino acids that contain sulfur, the other is cysteine.
Methionine is a non-polar amino acid. It is one of two amino acids that contain sulfur, the other is cysteine.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Name the given structure.
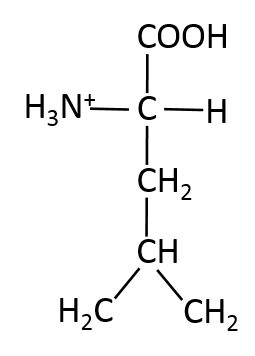
Name the given structure.

Leucine is a non-polar amino acid with a  R-group.
R-group.
Leucine is a non-polar amino acid with a 
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following structures is cysteine?
Which of the following structures is cysteine?
Cysteine is a polar amino acid with an R-group of  . It is one of two amino acids with a sulfur in the R-group, the other is methionine.
. It is one of two amino acids with a sulfur in the R-group, the other is methionine.
Cysteine is a polar amino acid with an R-group of 
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is a polar amino acid?
Which of the following is a polar amino acid?
The polarity of an amino acid is determined by the R-group. The electronegativity difference between oxygen and carbon creates a dipole with the partial positive being on carbon and the partial negative being on oxygen. The dipole makes the molecule polar.
The polarity of an amino acid is determined by the R-group. The electronegativity difference between oxygen and carbon creates a dipole with the partial positive being on carbon and the partial negative being on oxygen. The dipole makes the molecule polar.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Identify the given structure.

Identify the given structure.

Phenylalanine is a non-polar amino acid. The structure of this amino acid is literally alanine with a phenyl group attached.
Phenylalanine is a non-polar amino acid. The structure of this amino acid is literally alanine with a phenyl group attached.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is an acidic amino acid?
Which of the following is an acidic amino acid?
An acidic amino acid must have a carboxyl moiety  in its R-group. Because all amino acids contain a carboxyl moiety on the alpha carbon, that acidic group does not determine whether or not the amino acid is considered acidic.
in its R-group. Because all amino acids contain a carboxyl moiety on the alpha carbon, that acidic group does not determine whether or not the amino acid is considered acidic.
An acidic amino acid must have a carboxyl moiety 
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is a basic amino acid?
Which of the following is a basic amino acid?
Bases, according to the Bronsted-Lowry definition, are substances that accept 

Bases, according to the Bronsted-Lowry definition, are substances that accept

Compare your answer with the correct one above
Identify the given amino acid.
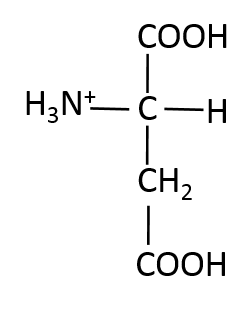
Identify the given amino acid.

Aspartic acid is an acidic amino acid, meaning it contains  in its R-group. The R-group of aspartic acid is
in its R-group. The R-group of aspartic acid is  .
.
Aspartic acid is an acidic amino acid, meaning it contains 

Compare your answer with the correct one above
Identify the given amino acid.

Identify the given amino acid.

Glutamine is one of two amino acids that are amides. The nitrogen bonded to a carbon-oxygen double bond makes it an amide.
Glutamine is one of two amino acids that are amides. The nitrogen bonded to a carbon-oxygen double bond makes it an amide.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Describe the solubility of the given amino acids.
 and
and 
Describe the solubility of the given amino acids.
 and
and 
Although tyrosine is hydrophobic, it is more soluble than phenylalanine. The only difference between the two amino acids is the hydroxyl group present on tyrosine. The hydroxyl is much more acidic than the hydrogen, and so it is more likely to ionize. The ability to ionize makes it more soluble (think electrolytes).
Although tyrosine is hydrophobic, it is more soluble than phenylalanine. The only difference between the two amino acids is the hydroxyl group present on tyrosine. The hydroxyl is much more acidic than the hydrogen, and so it is more likely to ionize. The ability to ionize makes it more soluble (think electrolytes).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following statements best describes high-density lipoproteins as compared to other lipoproteins?
Which of the following statements best describes high-density lipoproteins as compared to other lipoproteins?
High-density lipoproteins have the highest proportion of protein of the five classes of blood lipoproteins: chylomicrons, very-low-density lipoproteins, intermediate-density lipoproteins, low-density lipoproteins, and high-density lipoproteins. Chylomicrons have the lowest density of the five classes of lipoproteins. This is because the have the highest proportion of triglycerides and the least lowest proportion of protein. Very-low-density lipoproteins are a bit more dense than chylomicrons; however, the relative amount of triglycerides is still high. Intermediate-density lipoproteins which are formed from the very-low-density lipoproteins have a higher density than very-low-density lipoproteins due to the fact that they have less than half of the amount of triglycerides as very-low-density lipoproteins. Low-density lipoproteins have the highest amount of cholesterol and an even lesser amount of triglycerides than intermediate-density lipoproteins. Lastly, high-density lipoproteins are the densest of the lipoproteins due to the fact that they have the highest amount of protein in relation to the amount of triglycerides they contain.
High-density lipoproteins have the highest proportion of protein of the five classes of blood lipoproteins: chylomicrons, very-low-density lipoproteins, intermediate-density lipoproteins, low-density lipoproteins, and high-density lipoproteins. Chylomicrons have the lowest density of the five classes of lipoproteins. This is because the have the highest proportion of triglycerides and the least lowest proportion of protein. Very-low-density lipoproteins are a bit more dense than chylomicrons; however, the relative amount of triglycerides is still high. Intermediate-density lipoproteins which are formed from the very-low-density lipoproteins have a higher density than very-low-density lipoproteins due to the fact that they have less than half of the amount of triglycerides as very-low-density lipoproteins. Low-density lipoproteins have the highest amount of cholesterol and an even lesser amount of triglycerides than intermediate-density lipoproteins. Lastly, high-density lipoproteins are the densest of the lipoproteins due to the fact that they have the highest amount of protein in relation to the amount of triglycerides they contain.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following statements best describes chylomicrons as compared to other lipoproteins?
Which of the following statements best describes chylomicrons as compared to other lipoproteins?
There are essentially five classes of blood lipoproteins: chylomicrons, very-low-density lipoproteins, intermediate-density lipoproteins, low-density lipoproteins, and high-density lipoproteins. Chylomicrons have the lowest density of the five classes of lipoproteins. This is because the have the highest proportion of triglycerides and the least lowest proportion of protein. Very-low-density lipoproteins are a bit more dense than chylomicrons; however, the relative amount of triglycerides is still high. Intermediate-density lipoproteins which are formed from the very-low-density lipoproteins have a higher density than very-low-density lipoproteins due to the fact that they have less than half of the amount of triglycerides as very-low-density lipoproteins. Low-density lipoproteins have the highest amount of cholesterol and an even lesser amount of triglycerides than intermediate-density lipoproteins. Lastly, high-density lipoproteins are the densest of the lipoproteins due to the fact that they have the highest amount of protein in relation to the amount of triglycerides they contain.
There are essentially five classes of blood lipoproteins: chylomicrons, very-low-density lipoproteins, intermediate-density lipoproteins, low-density lipoproteins, and high-density lipoproteins. Chylomicrons have the lowest density of the five classes of lipoproteins. This is because the have the highest proportion of triglycerides and the least lowest proportion of protein. Very-low-density lipoproteins are a bit more dense than chylomicrons; however, the relative amount of triglycerides is still high. Intermediate-density lipoproteins which are formed from the very-low-density lipoproteins have a higher density than very-low-density lipoproteins due to the fact that they have less than half of the amount of triglycerides as very-low-density lipoproteins. Low-density lipoproteins have the highest amount of cholesterol and an even lesser amount of triglycerides than intermediate-density lipoproteins. Lastly, high-density lipoproteins are the densest of the lipoproteins due to the fact that they have the highest amount of protein in relation to the amount of triglycerides they contain.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which blood lipoprotein has the highest ratio of protein to triglycerides?
Which blood lipoprotein has the highest ratio of protein to triglycerides?
Low-density lipoproteins have the highest content of cholesterol and cholesterol esters. There are essentially five classes of blood lipoproteins: chylomicrons, very-low-density lipoproteins, intermediate-density lipoproteins, low-density lipoproteins, and high-density lipoproteins. Chylomicrons have the lowest density of the five classes of lipoproteins. This is because the have the highest proportion of triglycerides and the least lowest proportion of protein. Very-low-density lipoproteins are a bit more dense than chylomicrons; however, the relative amount of triglycerides is still high. Intermediate-density lipoproteins which are formed from the very-low-density lipoproteins have a higher density than very-low-density lipoproteins due to the fact that they have less than half of the amount of triglycerides as very-low-density lipoproteins. Low-density lipoproteins have the highest amount of cholesterol and an even lesser amount of triglycerides than intermediate-density lipoproteins. Lastly, high-density lipoproteins are the densest of the lipoproteins due to the fact that they have the highest amount of protein in relation to the amount of triglycerides they contain.
Low-density lipoproteins have the highest content of cholesterol and cholesterol esters. There are essentially five classes of blood lipoproteins: chylomicrons, very-low-density lipoproteins, intermediate-density lipoproteins, low-density lipoproteins, and high-density lipoproteins. Chylomicrons have the lowest density of the five classes of lipoproteins. This is because the have the highest proportion of triglycerides and the least lowest proportion of protein. Very-low-density lipoproteins are a bit more dense than chylomicrons; however, the relative amount of triglycerides is still high. Intermediate-density lipoproteins which are formed from the very-low-density lipoproteins have a higher density than very-low-density lipoproteins due to the fact that they have less than half of the amount of triglycerides as very-low-density lipoproteins. Low-density lipoproteins have the highest amount of cholesterol and an even lesser amount of triglycerides than intermediate-density lipoproteins. Lastly, high-density lipoproteins are the densest of the lipoproteins due to the fact that they have the highest amount of protein in relation to the amount of triglycerides they contain.
Compare your answer with the correct one above