How to find if right triangles are similar - Basic Geometry
Card 0 of 12
 ;
;  is a right angle;
is a right angle;  ;
;  ;
; 
Find  .
.




Find 
Since  and
and  is a right angle,
is a right angle,  is also a right angle.
is also a right angle.
 is the hypotenuse of the first triangle; since one of its legs
is the hypotenuse of the first triangle; since one of its legs  is half the length of that hypotenuse,
is half the length of that hypotenuse,  is 30-60-90 with
is 30-60-90 with  the shorter leg and
the shorter leg and  the longer.
the longer.
Because the two are similar triangles,  is the hypotenuse of the second triangle, and
is the hypotenuse of the second triangle, and  is its longer leg.
is its longer leg.
Therefore,  .
.
Since 







Because the two are similar triangles, 

Therefore, 
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following is sufficient to say that two right triangles are similar?
Which of the following is sufficient to say that two right triangles are similar?
If all three angles of a triangle are congruent but the sides are not, then one of the triangles is a scaled up version of the other. When this happens the proportions between the sides still remains unchanged which is the criteria for similarity.
If all three angles of a triangle are congruent but the sides are not, then one of the triangles is a scaled up version of the other. When this happens the proportions between the sides still remains unchanged which is the criteria for similarity.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following statements is true regarding the two triangles?
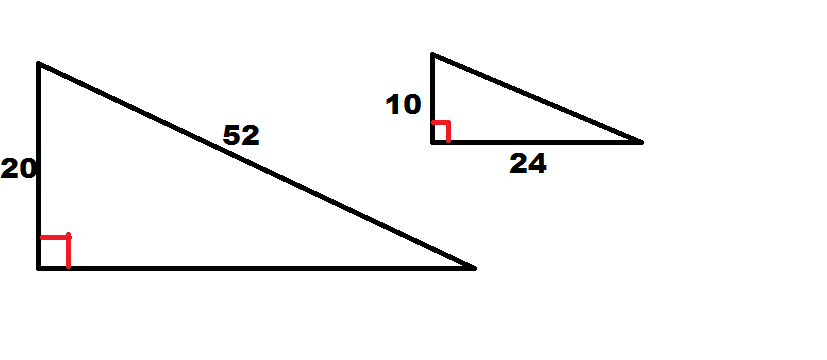
Which of the following statements is true regarding the two triangles?

Though we must do a little work, we can show these triangles are similar. First, right triangles are not necessarily always similar. They must meet the necessary criteria like any other triangles; furthermore, there is no Hypotenuse-Leg Theorem for similarity, only for congruence; therefore, we can eliminate two answer choices.
However, we can use the Pythagorean Theorem with the smaller triangle to find the missing leg. Doing so gives us a length of 48. Comparing the ratio of the shorter legs in each trangle to the ratio of the longer legs we get


In both cases, the leg of the larger triangle is twice as long as the corresponding leg in the smaller triangle. Given that the angle between the two legs is a right angle in each triangle, these angles are congruent. We now have enough evidence to conclude similarity by Side-Angle-Side.
Though we must do a little work, we can show these triangles are similar. First, right triangles are not necessarily always similar. They must meet the necessary criteria like any other triangles; furthermore, there is no Hypotenuse-Leg Theorem for similarity, only for congruence; therefore, we can eliminate two answer choices.
However, we can use the Pythagorean Theorem with the smaller triangle to find the missing leg. Doing so gives us a length of 48. Comparing the ratio of the shorter legs in each trangle to the ratio of the longer legs we get
In both cases, the leg of the larger triangle is twice as long as the corresponding leg in the smaller triangle. Given that the angle between the two legs is a right angle in each triangle, these angles are congruent. We now have enough evidence to conclude similarity by Side-Angle-Side.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Two triangles,  and
and  , are similar when:
, are similar when:
Two triangles, 

The Similar Figures Theorem holds that similar figures have both equal corresponding angles and proportional corresponding lengths. Either condition alone is not sufficient. If two figures have both equal corresponding angles and equal corresponding lengths then they are congruent, not similar.
The Similar Figures Theorem holds that similar figures have both equal corresponding angles and proportional corresponding lengths. Either condition alone is not sufficient. If two figures have both equal corresponding angles and equal corresponding lengths then they are congruent, not similar.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
 and
and  are triangles.
are triangles.



Are  and
and  similar?
similar?



Are 

The Similar Figures Theorem holds that similar figures have both equal corresponding angles and proportional corresponding lengths. In other words, we need to know both the measures of the corresponding angles and the lengths of the corresponding sides. In this case, we know only the measures of  and
and  . We don't know the measures of any of the other angles or the lengths of any of the sides, so we cannot answer the question -- they might be similar, or they might not be.
. We don't know the measures of any of the other angles or the lengths of any of the sides, so we cannot answer the question -- they might be similar, or they might not be.
It's not enough to know that both figures are right triangles, nor can we assume that angles are the same measurement because they appear to be.
Similar triangles do not have to be the same size.
The Similar Figures Theorem holds that similar figures have both equal corresponding angles and proportional corresponding lengths. In other words, we need to know both the measures of the corresponding angles and the lengths of the corresponding sides. In this case, we know only the measures of 

It's not enough to know that both figures are right triangles, nor can we assume that angles are the same measurement because they appear to be.
Similar triangles do not have to be the same size.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
 and
and  are similar triangles.
are similar triangles.





What is the length of  ?
?



What is the length of 
Since  and
and  are similar triangles, we know that they have proportional corresponding lengths. We must determine which sides correspond. Here, we know
are similar triangles, we know that they have proportional corresponding lengths. We must determine which sides correspond. Here, we know  corresponds to
corresponds to  because both line segments lie opposite
because both line segments lie opposite  angles and between
angles and between  and
and  angles. Likewise, we know
angles. Likewise, we know  corresponds to
corresponds to  because both line segments lie opposite
because both line segments lie opposite  angles and between
angles and between  and
and  angles. We can use this information to set up a proportion and solve for the length of
angles. We can use this information to set up a proportion and solve for the length of  .
.

Substitute the known values.

Cross-multiply and simplify.

 and
and  result from setting up an incorrect proportion.
result from setting up an incorrect proportion.  results from incorrectly multiplying
results from incorrectly multiplying  and
and  .
.
Since 












Substitute the known values.
Cross-multiply and simplify.





Compare your answer with the correct one above
Are these triangles similar? If so, list the scale factor.

Are these triangles similar? If so, list the scale factor.
The two triangles are similar, but we can't be sure of that until we can compare all three corresponding pairs of sides and make sure the ratios are the same. In order to do that, we first have to solve for the missing sides using the Pythagorean Theorem.




The smaller triangle is missing not the hypotenuse, c, but one of the legs, so we'll use the formula slightly differently.

 subtract 36 from both sides
subtract 36 from both sides


Now we can compare all three ratios of corresponding sides:
 one way of comparing these ratios is to simplify them.
one way of comparing these ratios is to simplify them.
We can simplify the leftmost ratio by dividing top and bottom by 3 and getting  .
.
We can simplify the middle ratio by dividing top and bottom by 4 and getting  .
.
Finally, we can simplify the ratio on the right by dividing top and bottom by 5 and getting  .
.
This means that the triangles are definitely similar, and  is the scale factor.
is the scale factor.
The two triangles are similar, but we can't be sure of that until we can compare all three corresponding pairs of sides and make sure the ratios are the same. In order to do that, we first have to solve for the missing sides using the Pythagorean Theorem.
The smaller triangle is missing not the hypotenuse, c, but one of the legs, so we'll use the formula slightly differently.

Now we can compare all three ratios of corresponding sides:

We can simplify the leftmost ratio by dividing top and bottom by 3 and getting 
We can simplify the middle ratio by dividing top and bottom by 4 and getting 
Finally, we can simplify the ratio on the right by dividing top and bottom by 5 and getting 
This means that the triangles are definitely similar, and 
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Are these right triangles similar? If so, state the scale factor.

Are these right triangles similar? If so, state the scale factor.
In order to compare these triangles and determine if they are similar, we need to know all three side lengths in both triangles. To get the missing ones, we can use Pythagorean Theorem:


 take the square root
take the square root

The other triangle is missing one of the legs rather than the hypotenuse, so we'll adjust accordingly:

 subtract 36 from both sides
subtract 36 from both sides


Now we can compare ratios of corresponding sides:

The first ratio simplifies to  , but we can't simplify the others any more than they already are. The three ratios clearly do not match, so these are not similar triangles.
, but we can't simplify the others any more than they already are. The three ratios clearly do not match, so these are not similar triangles.
In order to compare these triangles and determine if they are similar, we need to know all three side lengths in both triangles. To get the missing ones, we can use Pythagorean Theorem:

The other triangle is missing one of the legs rather than the hypotenuse, so we'll adjust accordingly:

Now we can compare ratios of corresponding sides:
The first ratio simplifies to 
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Are these triangles similar? Give a justification.

Are these triangles similar? Give a justification.
These triangles were purposely drawn misleadingly. Just from glancing at them, the angles that appear to correspond are given different angle measures, so they don't "look" similar. However, if we subtract, we figure out that the missing angle in the triangle with the 66-degree angle must be 24 degrees, since  . Similarly, the missing angle in the triangle with the 24-degree angle must be 66 degress. This means that all 3 corresponding pairs of angles are congruent, making the triangles similar.
. Similarly, the missing angle in the triangle with the 24-degree angle must be 66 degress. This means that all 3 corresponding pairs of angles are congruent, making the triangles similar.
These triangles were purposely drawn misleadingly. Just from glancing at them, the angles that appear to correspond are given different angle measures, so they don't "look" similar. However, if we subtract, we figure out that the missing angle in the triangle with the 66-degree angle must be 24 degrees, since 
Compare your answer with the correct one above

Refer to the above figure.
True, false, or inconclusive:  .
.

Refer to the above figure.
True, false, or inconclusive: 
 is an altitude of
is an altitude of  , so it divides the triangle into two smaller triangles similar to each other - that is, if we match the shorter legs, the longer legs, and the hypotenuses, the similarity statement is
, so it divides the triangle into two smaller triangles similar to each other - that is, if we match the shorter legs, the longer legs, and the hypotenuses, the similarity statement is
 .
.



Compare your answer with the correct one above

Refer to the above diagram.
True or false: 

Refer to the above diagram.
True or false:
The distance from the origin to  is the absolute value of the
is the absolute value of the 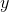 -coordinate of
-coordinate of  , which is
, which is  . Similarly,
. Similarly, 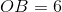 ,
,  , and
, and  . Also, since the axes intersect at right angles,
. Also, since the axes intersect at right angles,  and
and  are both right, and, consequently, congruent.
are both right, and, consequently, congruent.
According to the Side-Angle-Side Similarity Theorem (SASS), if two sides of a triangle are in proportion to the corresponding sides of a second triangle, and their included angles are congruent, the triangles are similar.
We can test the proportion statement

by substituting:

Test the truth of this statement by comparing their cross products:


The cross-products are equal, making the proportion statement true, so two pairs of sides are in proportion. Also, their included angles  and
and  are congruent. This sets up the conditions of SASS, so
are congruent. This sets up the conditions of SASS, so  .
.
The distance from the origin to 
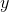


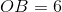




According to the Side-Angle-Side Similarity Theorem (SASS), if two sides of a triangle are in proportion to the corresponding sides of a second triangle, and their included angles are congruent, the triangles are similar.
We can test the proportion statement
by substituting:
Test the truth of this statement by comparing their cross products:
The cross-products are equal, making the proportion statement true, so two pairs of sides are in proportion. Also, their included angles 


Compare your answer with the correct one above
Given:  and
and  .
.
 and
and  are both right angles.
are both right angles.


True or false: From the given information, it follows that  .
.
Given: 



True or false: From the given information, it follows that 
If we seek to prove that  , then
, then  ,
,  , and
, and  correspond to
correspond to  ,
,  , and
, and  , respectively.
, respectively.
By the Side-Angle-Side Similarity Theorem (SASS), if two sides of a triangle are in proportion with the corresponding sides of another triangle, and the included angles are congruent, then the triangles are similar.
 and
and  , so by the Division Property of Equality,
, so by the Division Property of Equality,  . Also,
. Also,  and
and  , their respective included angles, are both right angles, so
, their respective included angles, are both right angles, so  . The conditions of SASS are met, so
. The conditions of SASS are met, so 
If we seek to prove that 






By the Side-Angle-Side Similarity Theorem (SASS), if two sides of a triangle are in proportion with the corresponding sides of another triangle, and the included angles are congruent, then the triangles are similar.






Compare your answer with the correct one above