Understanding Linear-Rotational Equivalents - AP Physics B
Card 0 of 2
A wheel of radius  rolls along a flat floor and makes
rolls along a flat floor and makes  rotations over a period of time. What distance
rotations over a period of time. What distance  has the wheel traveled?
has the wheel traveled?
A wheel of radius 


In order to find the distance the wheel travels, we need a way to convert angular displacement to linear displacement. We know that the circumference of a circle (or a wheel, in this case) is  . This means that in one rotation, the wheel would travel a distance equal to its circumference.
. This means that in one rotation, the wheel would travel a distance equal to its circumference.
Distance of one rotation equals: 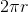 .
.
Since the wheel travels  rotations, the total distance that the wheel travels will be equal to the distance traveled by one rotation multiplied by the number of rotations.
rotations, the total distance that the wheel travels will be equal to the distance traveled by one rotation multiplied by the number of rotations.
Distance of  rotations equals:
rotations equals: 
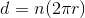
In order to find the distance the wheel travels, we need a way to convert angular displacement to linear displacement. We know that the circumference of a circle (or a wheel, in this case) is 
Distance of one rotation equals: 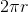
Since the wheel travels 
Distance of 
Compare your answer with the correct one above
A wheel of radius  rolls along a flat floor and makes
rolls along a flat floor and makes  rotations over a period of time. What distance
rotations over a period of time. What distance  has the wheel traveled?
has the wheel traveled?
A wheel of radius 


In order to find the distance the wheel travels, we need a way to convert angular displacement to linear displacement. We know that the circumference of a circle (or a wheel, in this case) is  . This means that in one rotation, the wheel would travel a distance equal to its circumference.
. This means that in one rotation, the wheel would travel a distance equal to its circumference.
Distance of one rotation equals: 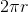 .
.
Since the wheel travels  rotations, the total distance that the wheel travels will be equal to the distance traveled by one rotation multiplied by the number of rotations.
rotations, the total distance that the wheel travels will be equal to the distance traveled by one rotation multiplied by the number of rotations.
Distance of  rotations equals:
rotations equals: 
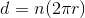
In order to find the distance the wheel travels, we need a way to convert angular displacement to linear displacement. We know that the circumference of a circle (or a wheel, in this case) is 
Distance of one rotation equals: 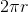
Since the wheel travels 
Distance of 
Compare your answer with the correct one above