Electricity and Magnetism
Practice Questions
AP Physics B › Electricity and Magnetism
A charge travels along a copper wire that has a resistance of 
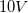
A charge travels along a copper wire that has a resistance of 
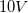
A charge travels along a copper wire that has a resistance of 
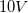
How much work is done by the electric field moving an electron along an equipotential surface with a potential of 
Which of the following changes to a copper wire will lead to the greatest decrease in voltage?
Which of the following changes to a copper wire will lead to the greatest decrease in voltage?
How much work is done by the electric field moving an electron along an equipotential surface with a potential of 
Which of the following changes to a copper wire will lead to the greatest decrease in voltage?
How much work is done by the electric field moving an electron along an equipotential surface with a potential of 
A proton traveling at 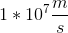


The proton’s mass is 

