Solubility - AP Chemistry
Card 0 of 20
Which of these WILL be soluble in water?
Which of these WILL be soluble in water?
Solubility Rules: the only soluble ionic compound listed is CsCl; the rest are insoluble due to solubility rules
Solubility Rules: the only soluble ionic compound listed is CsCl; the rest are insoluble due to solubility rules
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following will be the precipitate in the following reaction?
2KCl + Ca(OH)2 → 2KOH + CaCl2
Which of the following will be the precipitate in the following reaction?
2KCl + Ca(OH)2 → 2KOH + CaCl2
Though the solubility of calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2, is fairly low, it is a reactant and will not form a precipitate. The solid calcium hydroxide will be added to an aqueous solution of potassium chloride, KCl. During the reaction, the calcium hydroxide will transition to potassium hydroxide (KOH) and calcium chloride (CaCl2), both of which are completely soluble. At the end of the reaction, no precipitate will be observed.
Though the solubility of calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2, is fairly low, it is a reactant and will not form a precipitate. The solid calcium hydroxide will be added to an aqueous solution of potassium chloride, KCl. During the reaction, the calcium hydroxide will transition to potassium hydroxide (KOH) and calcium chloride (CaCl2), both of which are completely soluble. At the end of the reaction, no precipitate will be observed.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

If the solubility of CaF2 in the dissociation reaction above was determined to be 1.54 * 10-3M, what is the Ksp value for CaF2?
If the solubility of CaF2 in the dissociation reaction above was determined to be 1.54 * 10-3M, what is the Ksp value for CaF2?
Use the balanced reaction of the dissociation to assign values of X for the solubility of each ion. As CaF2 dissociates, each ion amount will increase by some amount; calcium will increase by X and flouride will increase by 2_X_.







Then plug in the equation to solve Ksp, using the X values assigned for each solute. Use the given value for solubility to find Ksp. Remember that NaCl si not included in the equation, as it is a pure solid.
![K_{sp}= [Ca^{2+}][F^-]^2=(X)(2X)^{2} = 4X^{3}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/119041/gif.latex)

Use the balanced reaction of the dissociation to assign values of X for the solubility of each ion. As CaF2 dissociates, each ion amount will increase by some amount; calcium will increase by X and flouride will increase by 2_X_.




Then plug in the equation to solve Ksp, using the X values assigned for each solute. Use the given value for solubility to find Ksp. Remember that NaCl si not included in the equation, as it is a pure solid.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following will form a precipitate in solution?
Which of the following will form a precipitate in solution?
Standard solubility rules tell us that group I elements and ammonium cations will always result in soluble salts. Lithium, sodium, and potassium are all group I elements, indicating that none of the given answer options will form a precipitate in solution.
Standard solubility rules tell us that group I elements and ammonium cations will always result in soluble salts. Lithium, sodium, and potassium are all group I elements, indicating that none of the given answer options will form a precipitate in solution.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
The partial pressure of an arbitrary gas,  , in an enclosed chanber with a pool of water is 7.2atm at 298K.
, in an enclosed chanber with a pool of water is 7.2atm at 298K.
The Henry's Law constant for  is
is  .
.
What is the solubility of  ?
?
The partial pressure of an arbitrary gas, 
The Henry's Law constant for 

What is the solubility of 
Henry's law can be expressed:

Where  is the Henry's Law constant, and
is the Henry's Law constant, and  is the partial pressure of the gas above the solution. We can substitute our givens into this equation:
is the partial pressure of the gas above the solution. We can substitute our givens into this equation:

Henry's law can be expressed:
Where 

Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the formula for the dissociation of  ?
?
What is the formula for the dissociation of 
 is composed of two types of ions,
is composed of two types of ions,  and
and  . When it dissociates, it forms:
. When it dissociates, it forms:




Compare your answer with the correct one above
A chemist has a fully saturated solution of chemical X, with solid X resting on the bottom. If she adds a chemical that will react with the aqueous X, what will happen to the solid?
A chemist has a fully saturated solution of chemical X, with solid X resting on the bottom. If she adds a chemical that will react with the aqueous X, what will happen to the solid?
A fully saturated solution is at equilibrium between the solid and aqueous states, but it is a dynamic equilibrium. As the reacting chemical reacts with aqueous X, more and more of the solid will dissolve into solution.
A fully saturated solution is at equilibrium between the solid and aqueous states, but it is a dynamic equilibrium. As the reacting chemical reacts with aqueous X, more and more of the solid will dissolve into solution.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Pb(OH)2 has a Ksp of 1.43 * 10-20.
What is its solubility?
Pb(OH)2 has a Ksp of 1.43 * 10-20.
What is its solubility?
Lead (II) hydroxide dissociates according to this reaction:  . Solubility is equal to the number of moles that will dissociate at equilibrium, and can be found using this reaction and the value of Ksp.
. Solubility is equal to the number of moles that will dissociate at equilibrium, and can be found using this reaction and the value of Ksp.
Ksp = \[Pb2+\]\[OH-\]2
If \[Pb2+\] = x, then \[OH-\] = 2x. They exist in a 1:2 ratio.
Ksp = 1.43 * 10-20 = x(2x)2 = 4x3
x = 1.53 x 10-7M
Lead (II) hydroxide dissociates according to this reaction: 
Ksp = \[Pb2+\]\[OH-\]2
If \[Pb2+\] = x, then \[OH-\] = 2x. They exist in a 1:2 ratio.
Ksp = 1.43 * 10-20 = x(2x)2 = 4x3
x = 1.53 x 10-7M
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following factors will generally lead a solute to dissolve more easily into a solution (i.e. increase solubility)?
Which of the following factors will generally lead a solute to dissolve more easily into a solution (i.e. increase solubility)?
Increasing the temperature of a solution will generally increase its solubility, while decreasing temperature will have the opposite effect. The common ion effect refers to the phenomenon when two compunds in a solution dissociate to produce at least one similar ion, and will make it harder for additional amounts of that ion in the solution to dissociate, decreasing solubility.
Increasing the temperature of a solution will generally increase its solubility, while decreasing temperature will have the opposite effect. The common ion effect refers to the phenomenon when two compunds in a solution dissociate to produce at least one similar ion, and will make it harder for additional amounts of that ion in the solution to dissociate, decreasing solubility.
Compare your answer with the correct one above

If the Ksp of the above dissociation is found to be 2.70 * 10-4, what is the solubility of NaCl?
If the Ksp of the above dissociation is found to be 2.70 * 10-4, what is the solubility of NaCl?
First, set up a balanced reaction and enter X for the amount of each solute that is going to be dissolved. As NaCl dissociates, each ion amount will increase by some amount, X.







Then set up the equation for the value of Ksp and enter in the value of X for each solute. Use this equation to solve for X, the solubility (in mol/L). Remember that NaCl si not included in the equation, as it is a pure solid.
![K_{sp}= [Na^{+}][Cl^{-}] = (X)(X) = X^{2}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/85510/gif.latex)


First, set up a balanced reaction and enter X for the amount of each solute that is going to be dissolved. As NaCl dissociates, each ion amount will increase by some amount, X.




Then set up the equation for the value of Ksp and enter in the value of X for each solute. Use this equation to solve for X, the solubility (in mol/L). Remember that NaCl si not included in the equation, as it is a pure solid.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
What is the formula for the dissociation of iron (II) phosphate?
What is the formula for the dissociation of iron (II) phosphate?
Iron (II) has a positive two charge:  .
.
Phosphate has a negative three charge:  .
.
The initial compound must be constructed to cancel these charges. The dissociation is:  .
.
Iron (II) has a positive two charge: 
Phosphate has a negative three charge: 
The initial compound must be constructed to cancel these charges. The dissociation is: 
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following compounds is not soluble in water?
Which of the following compounds is not soluble in water?
The key to solubility is memorizing the solubility rules. We know that all compounds of alkali metals are soluble. These include potassium, lithium, and sodium, eliminating three of the answers. We also know that all chloride salts are soluble, except those of silver, lead, and mercury. Silver chloride is, thus, not soluble.
All hydroxide compounds are generally insoluble, but alkali metals and ammonium salts will make them soluble. Alkaline earth metals make hydroxides slightly soluble.
The key to solubility is memorizing the solubility rules. We know that all compounds of alkali metals are soluble. These include potassium, lithium, and sodium, eliminating three of the answers. We also know that all chloride salts are soluble, except those of silver, lead, and mercury. Silver chloride is, thus, not soluble.
All hydroxide compounds are generally insoluble, but alkali metals and ammonium salts will make them soluble. Alkaline earth metals make hydroxides slightly soluble.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Consider the following balanced equation for the solubility of barium hydroxide in an aqueous solution.


What is the equilibrium expression for the balanced reaction?
Consider the following balanced equation for the solubility of barium hydroxide in an aqueous solution.
What is the equilibrium expression for the balanced reaction?
When writing the equilibrium expression for an insoluble salt, remember that pure solids and liquids are not included in the expression. Also, the coefficients for the compounds in the balanced reaction become the exponents for the compounds in the equilibrium expression.
Given a generalized chemical reaction, we can determine the equilibrium constant expression.

![K_{eq}=\frac{[C]^c[D]^d}{[A]^a[B]^b}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/94054/gif.latex)
In our reaction, the reactant is a pure solid and is not included in the equilibrium calculation.

![K_{sp}=[Ba^{2+}][OH^-]^2](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/94055/gif.latex)
When writing the equilibrium expression for an insoluble salt, remember that pure solids and liquids are not included in the expression. Also, the coefficients for the compounds in the balanced reaction become the exponents for the compounds in the equilibrium expression.
Given a generalized chemical reaction, we can determine the equilibrium constant expression.
In our reaction, the reactant is a pure solid and is not included in the equilibrium calculation.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Consider the following balanced equation for the solubility of barium hydroxide in an aqueous solution.


What is the solubility of barium hydroxide?
Consider the following balanced equation for the solubility of barium hydroxide in an aqueous solution.
What is the solubility of barium hydroxide?
In order to solve for the solubility of barium hydroxide, we need to establish an ICE table for the reaction.
I. Initially, there are no barium ions or hydroxide ions in the solution, so we can call their concentrations zero at the beginning of the reaction.
C. For every molecule of dissolved barium hydroxide, there will be one ion of barium and two ions of hydroxide. As a result, the increases in each ion can be designated  and
and  , respectively.
, respectively.
E. Finally, we plug these values into the equilibrium expression and set it equal to the solubility product constant.

![K_{sp}=[Ba^{2+}][OH^-]^2](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/94058/gif.latex)
![\small 5*10^{-3} = [x][2x]^{2}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/126927/gif.latex)

In order to solve for the solubility of barium hydroxide, we need to establish an ICE table for the reaction.
I. Initially, there are no barium ions or hydroxide ions in the solution, so we can call their concentrations zero at the beginning of the reaction.
C. For every molecule of dissolved barium hydroxide, there will be one ion of barium and two ions of hydroxide. As a result, the increases in each ion can be designated 

E. Finally, we plug these values into the equilibrium expression and set it equal to the solubility product constant.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Consider the following balanced equation for the dissociation of barium hydroxide in an aqueous solution.


A 1M solution of barium nitrate is added to the solution. What is the solubility of barium hydroxide after this addition?
Consider the following balanced equation for the dissociation of barium hydroxide in an aqueous solution.
A 1M solution of barium nitrate is added to the solution. What is the solubility of barium hydroxide after this addition?
Before we solve for the solubility, remember Le Chatelier's principle. Barium nitrate is a soluble salt that will completely dissolve in solution. This means that there will be a one molar concentration of barium ions before the salt dissolves. Since we have added to the products side of the reaction, we can predict that the equilibrium will be shifted to the left, and the barium hydroxide will be less soluble. This change in equilibrium is referred to as the common ion effect.
We will use an ICE table to determine the solubility of the salt.
I. Before the salt begins to dissolve, there is a one molar concentration of barium ions (from the barium nitrate) with no hydroxide ions in the solution.
C. Since every dissolved molecule of barium hydroxide will yield one barium ion and two hydroxide ions, the unknown increases in each ion can be designated  and
and  respectively. Notice how the barium ion increase will be added to the previously added one molar concentration in the solution.
respectively. Notice how the barium ion increase will be added to the previously added one molar concentration in the solution.
E. Now, we set the solubility expression equal to the solubility product constant.

![K_{sp}=[Ba^{2+}][OH^-]^2](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/110662/gif.latex)
![\small 5*10^{-3} = [1+x][2x]^{2}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/94077/gif.latex)
Since 1 is such a larger number than the value we will get for  , we can consider the value in the barium ion expression to be negligible. This allows us to simplify the equation to the following setup.
, we can consider the value in the barium ion expression to be negligible. This allows us to simplify the equation to the following setup.
![\small 5*10^{-3} = [1][2x]^{2}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/94078/gif.latex)

The solubility of barium hydroxide without the common ion effect is 0.108M. Notice how the solubility for the salt has decreased, as was predicted in the beginning by Le Chatelier's principle.
Before we solve for the solubility, remember Le Chatelier's principle. Barium nitrate is a soluble salt that will completely dissolve in solution. This means that there will be a one molar concentration of barium ions before the salt dissolves. Since we have added to the products side of the reaction, we can predict that the equilibrium will be shifted to the left, and the barium hydroxide will be less soluble. This change in equilibrium is referred to as the common ion effect.
We will use an ICE table to determine the solubility of the salt.
I. Before the salt begins to dissolve, there is a one molar concentration of barium ions (from the barium nitrate) with no hydroxide ions in the solution.
C. Since every dissolved molecule of barium hydroxide will yield one barium ion and two hydroxide ions, the unknown increases in each ion can be designated 

E. Now, we set the solubility expression equal to the solubility product constant.
Since 1 is such a larger number than the value we will get for 
The solubility of barium hydroxide without the common ion effect is 0.108M. Notice how the solubility for the salt has decreased, as was predicted in the beginning by Le Chatelier's principle.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Four different insoluble salts are added to an aqueous solution in equal amounts. Assume that the salts do not interact with one another in any way. The following list shows the salts and their solubility product constants.






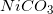

Which of the following ions will have the highest concentration in the solution?
Four different insoluble salts are added to an aqueous solution in equal amounts. Assume that the salts do not interact with one another in any way. The following list shows the salts and their solubility product constants.



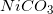
Which of the following ions will have the highest concentration in the solution?
The solubility product constants help us envision which ions will have the largest concentrations after dissolving to equilibrium.  has the largest solubility product constant, meaning it will dissolve the most out of the four options.
has the largest solubility product constant, meaning it will dissolve the most out of the four options.
Upon the dissolving of  , twice the number of fluoride ions will be released as magnesium ions; however, the solubility constant for magnesium fluoride is so much smaller, compared to the solubility constant of
, twice the number of fluoride ions will be released as magnesium ions; however, the solubility constant for magnesium fluoride is so much smaller, compared to the solubility constant of  , that it will not become the ion with the largest concentration.
, that it will not become the ion with the largest concentration.

![[F^-]<[CrO_4^{2-}]](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/119420/gif.latex)
The solubility product constants help us envision which ions will have the largest concentrations after dissolving to equilibrium. 
Upon the dissolving of 

Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following compounds is insoluble in water?
Which of the following compounds is insoluble in water?
Unless paired with an alkali metal, carbonate compounds are generally insoluble. Compounds that contain nitrate or an alkali metal will generally be soluble in water, and hydroxides are soluble when paired with heavier alkaline earth metals (such as calcium).
Unless paired with an alkali metal, carbonate compounds are generally insoluble. Compounds that contain nitrate or an alkali metal will generally be soluble in water, and hydroxides are soluble when paired with heavier alkaline earth metals (such as calcium).
Compare your answer with the correct one above
 is dissolved in water. Which of the following salts will result in a precipitate if added to the silver sulfate solution?
is dissolved in water. Which of the following salts will result in a precipitate if added to the silver sulfate solution?

This question requires an understanding of solubility guidelines and which ion combinations will result in precipitates. Virtually all ionic compounds containing ammonium, sodium, and nitrate will be soluble in water. Most ionic compounds containing chlorine are soluble, with the exceptions of silver, mercury, and lead cations.

If sodium chloride dissolves in this solution, the silver cations and chlorine anions will combine and result in a white, crystalline silver chloride precipitate.

This question requires an understanding of solubility guidelines and which ion combinations will result in precipitates. Virtually all ionic compounds containing ammonium, sodium, and nitrate will be soluble in water. Most ionic compounds containing chlorine are soluble, with the exceptions of silver, mercury, and lead cations.
If sodium chloride dissolves in this solution, the silver cations and chlorine anions will combine and result in a white, crystalline silver chloride precipitate.
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Which of the following ionic compounds is soluble in water?
I. 
II. 
III. 
Which of the following ionic compounds is soluble in water?
I.
II.
III.
Solubility rules determine which ionic compounds are soluble. All nitrates and group I compounds (those containing alkali metals) are soluble. This means that compounds I and II must be soluble; compound I is a nitrate and compound II contains sodium, an alkali metal.
Compound III, calcium fluoride, is not soluble. Most fluoride compounds are soluble, with the exceptions of:  .
.
Solubility rules determine which ionic compounds are soluble. All nitrates and group I compounds (those containing alkali metals) are soluble. This means that compounds I and II must be soluble; compound I is a nitrate and compound II contains sodium, an alkali metal.
Compound III, calcium fluoride, is not soluble. Most fluoride compounds are soluble, with the exceptions of: 
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Out of the compounds shown, which one is least soluble in water?
Out of the compounds shown, which one is least soluble in water?
This question is asking us to identify a compound that is the least soluble in the solvent water. To be able to answer this question, it's important to understand that, as a general rule of thumb, like dissolves like. In other words, since water is a polar molecule, the compounds that will best dissolve in water are those that are themselves either polar or carry a net charge.
 is expected to be soluble because it is polarized. With a lone electron pair on the nitrogen atom and the large electronegativity difference between the nitrogen and each of the three hydrogen atoms, ammonia will easily dissolve within water.
is expected to be soluble because it is polarized. With a lone electron pair on the nitrogen atom and the large electronegativity difference between the nitrogen and each of the three hydrogen atoms, ammonia will easily dissolve within water.
Likewise,  is expected to dissolve in water because it can ionize. Once dissolved in water,
is expected to dissolve in water because it can ionize. Once dissolved in water,  can dissociate to become
can dissociate to become  and
and  . And since each of these molecules carry a charge and are thus very stabilized within the polar environment that water provides, the dissociation process is extremely favorable.
. And since each of these molecules carry a charge and are thus very stabilized within the polar environment that water provides, the dissociation process is extremely favorable.
For much the same reasons,  is also soluble in water. It can dissociate into one
is also soluble in water. It can dissociate into one  and two
and two  , making it dissolve readily in water.
, making it dissolve readily in water.
But what about  ? The difference in electronegativity between carbon and chlorine is high, so the compound is expected to be polar, right? Well, not exactly. There is a very important distinction to be made here. Just because a bond within a molecule is polar doesn't mean that the molecule itself is polar. Sure, the bond between carbon and chlorine is indeed polar. But remember, we also need to take the shape of the molecule into account.
? The difference in electronegativity between carbon and chlorine is high, so the compound is expected to be polar, right? Well, not exactly. There is a very important distinction to be made here. Just because a bond within a molecule is polar doesn't mean that the molecule itself is polar. Sure, the bond between carbon and chlorine is indeed polar. But remember, we also need to take the shape of the molecule into account.  is a tetrahedral molecule. As a result, each of the chlorine atoms point away from the central carbon atom in the shape of a tetrahedron. Because of this, all of the individual carbon-chlorine dipoles (from each bond) cancels each other out. As a result of this, the net dipole moment on this compound becomes zero, and thus has no polarity. And since the polarity on this compound is zero, it would not be expected to dissolve very well in water.
is a tetrahedral molecule. As a result, each of the chlorine atoms point away from the central carbon atom in the shape of a tetrahedron. Because of this, all of the individual carbon-chlorine dipoles (from each bond) cancels each other out. As a result of this, the net dipole moment on this compound becomes zero, and thus has no polarity. And since the polarity on this compound is zero, it would not be expected to dissolve very well in water.
This question is asking us to identify a compound that is the least soluble in the solvent water. To be able to answer this question, it's important to understand that, as a general rule of thumb, like dissolves like. In other words, since water is a polar molecule, the compounds that will best dissolve in water are those that are themselves either polar or carry a net charge.

Likewise, 



For much the same reasons, 


But what about 

Compare your answer with the correct one above