Taylor Series - AP Calculus BC
Card 0 of 20
Let  be the fifth-degree Taylor polynomial approximation for
be the fifth-degree Taylor polynomial approximation for  , centered at
, centered at  .
.
What is the Lagrange error of the polynomial approximation to  ?
?
Let 


What is the Lagrange error of the polynomial approximation to 
The fifth degree Taylor polynomial approximating  centered at
centered at  is:
is:

The Lagrange error is the absolute value of the next term in the sequence, which is equal to  .
.
We need only evaluate this at 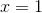 and thus we obtain
and thus we obtain 
The fifth degree Taylor polynomial approximating 

The Lagrange error is the absolute value of the next term in the sequence, which is equal to 
We need only evaluate this at 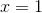
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Let  be the fifth-degree Taylor polynomial approximation for
be the fifth-degree Taylor polynomial approximation for  , centered at
, centered at  .
.
What is the Lagrange error of the polynomial approximation to  ?
?
Let 


What is the Lagrange error of the polynomial approximation to 
The fifth degree Taylor polynomial approximating  centered at
centered at  is:
is:

The Lagrange error is the absolute value of the next term in the sequence, which is equal to  .
.
We need only evaluate this at 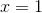 and thus we obtain
and thus we obtain 
The fifth degree Taylor polynomial approximating 

The Lagrange error is the absolute value of the next term in the sequence, which is equal to 
We need only evaluate this at 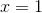
Compare your answer with the correct one above
For which of the following functions can the Maclaurin series representation be expressed in four or fewer non-zero terms?
For which of the following functions can the Maclaurin series representation be expressed in four or fewer non-zero terms?
Recall the Maclaurin series formula:


Despite being a 5th degree polynomial recall that the Maclaurin series for any polynomial is just the polynomial itself, so this function's Taylor series is identical to itself with two non-zero terms.
The only function that has four or fewer terms is  as its Maclaurin series is
as its Maclaurin series is .
.
Recall the Maclaurin series formula:
Despite being a 5th degree polynomial recall that the Maclaurin series for any polynomial is just the polynomial itself, so this function's Taylor series is identical to itself with two non-zero terms.
The only function that has four or fewer terms is 

Compare your answer with the correct one above
Let 
Find the the first three terms of the Taylor Series for  centered at
centered at  .
.
Let
Find the the first three terms of the Taylor Series for 

Using the formula of a binomial series centered at 0:
 ,
,
where we replace  with
with  and
and  , we get:
, we get:
 for the first 3 terms.
for the first 3 terms.
Then, we find the terms where,

Using the formula of a binomial series centered at 0:

where we replace 



Then, we find the terms where,
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Write the first three terms of the Taylor series for the following function about  :
:

Write the first three terms of the Taylor series for the following function about 
The general form for the Taylor series (of a function f(x)) about x=a is the following:
 .
.
Because we only want the first three terms, we simply plug in a=1, and then n=0, 1, and 2 for the first three terms (starting at n=0).
The hardest part, then, is finding the zeroth, first, and second derivative of the function given:



The derivative was found using the following rules:

Then, simply plug in the remaining information and write out the terms:

The general form for the Taylor series (of a function f(x)) about x=a is the following:

Because we only want the first three terms, we simply plug in a=1, and then n=0, 1, and 2 for the first three terms (starting at n=0).
The hardest part, then, is finding the zeroth, first, and second derivative of the function given:
The derivative was found using the following rules:
Then, simply plug in the remaining information and write out the terms:
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Write out the first four terms of the Taylor series about  for the following function:
for the following function:

Write out the first four terms of the Taylor series about 
The Taylor series about x=a of any function is given by the following:

So, we must find the zeroth, first, second, and third derivatives of the function (for n=0, 1, 2, and 3 which makes the first four terms):




The derivatives were found using the following rule:

Now, evaluated at x=a=1, and plugging in the correct n where appropriate, we get the following:

which when simplified is equal to
 .
.
The Taylor series about x=a of any function is given by the following:
So, we must find the zeroth, first, second, and third derivatives of the function (for n=0, 1, 2, and 3 which makes the first four terms):
The derivatives were found using the following rule:
Now, evaluated at x=a=1, and plugging in the correct n where appropriate, we get the following:
which when simplified is equal to

Compare your answer with the correct one above
Write out the first three terms of the Taylor series about  for the following function:
for the following function:

Write out the first three terms of the Taylor series about 
The general formula for the Taylor series about x=a for a given function is

We must find the zeroth, first, and second derivative of the function (for n=0, 1, and 2). The zeroth derivative is just the function itself.


The derivatives were found using the following rule:

Now, follow the above formula to write out the first three terms:

which simplified becomes

The general formula for the Taylor series about x=a for a given function is
We must find the zeroth, first, and second derivative of the function (for n=0, 1, and 2). The zeroth derivative is just the function itself.
The derivatives were found using the following rule:
Now, follow the above formula to write out the first three terms:
which simplified becomes
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Find the Taylor series expansion of  at
at  .
.
Find the Taylor series expansion of 

The Taylor series is defined as
 where the expression within the summation is the nth term of the Taylor polynomial.
where the expression within the summation is the nth term of the Taylor polynomial.
To find the Taylor series expansion of  at
at  , we first need to find an expression for the nth term of the Taylor polynomial.
, we first need to find an expression for the nth term of the Taylor polynomial.
The nth term of the Taylor polynomial is defined as

For,  and
and  .
.
We need to find terms in the taylor polynomial until we can determine the pattern for the nth term.

![f'(x)=\frac{d}{dx}\left [ \frac{1}{1-x} \right ]=\frac{d}{dx}\left [ \left ( 1-x\right )^{-1} ]=-1( 1-x\right )^{-2}(-1)=( 1-x)^{-2}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/495643/gif.latex)

![f''(x)=\frac{d}{dx}[( 1-x)^{-2}]=-2( 1-x)^{-3}(-1)=2( 1-x)^{-3}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/495645/gif.latex)

![f'''(x)=\frac{d}{dx}[2( 1-x)^{-3}]=-6( 1-x)^{-4}(-1)=6( 1-x)^{-4}](https://vt-vtwa-assets.varsitytutors.com/vt-vtwa/uploads/formula_image/image/495647/gif.latex)

Substituting these values into the taylor polynomial we get


The Taylor polynomial simplifies to

Now that we know the nth term of the Taylor polynomial, we can find the Taylor series.
The Taylor series is defined as
 where the expression within the summation is the nth term of the Taylor polynomial.
where the expression within the summation is the nth term of the Taylor polynomial.
For this problem, the taylor series is


Use the above to calculate the taylor series expansion of  at
at  ,
,

The Taylor series is defined as

To find the Taylor series expansion of 

The nth term of the Taylor polynomial is defined as
For, 

We need to find terms in the taylor polynomial until we can determine the pattern for the nth term.
Substituting these values into the taylor polynomial we get
The Taylor polynomial simplifies to
Now that we know the nth term of the Taylor polynomial, we can find the Taylor series.
The Taylor series is defined as

For this problem, the taylor series is
Use the above to calculate the taylor series expansion of 

Compare your answer with the correct one above
Use the first 3 terms of the Maclaurin series to approximate 
Use the first 3 terms of the Maclaurin series to approximate
The Maclaurin series for sine is 
Plugging in  for x gives:
for x gives:

The Maclaurin series for sine is
Plugging in 
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Use the first 4 terms of the Maclaurin series to approximate 
Use the first 4 terms of the Maclaurin series to approximate
The Maclaurin series for  is
is 
Plugging in 0.78 for x gives:

The Maclaurin series for 
Plugging in 0.78 for x gives:
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Use the first four terms of the Maclaurin series to approximate  to 6 decimal places.
to 6 decimal places.
Use the first four terms of the Maclaurin series to approximate 
The Maclaurin series for  is
is 
Plugging in x = 0.38 gives:

The Maclaurin series for 
Plugging in x = 0.38 gives:
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Compare your answer with the correct one above
Compare your answer with the correct one above

















